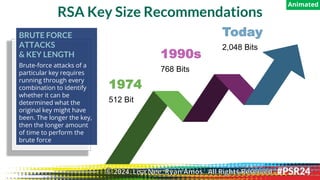
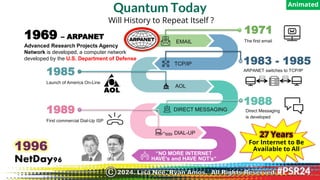
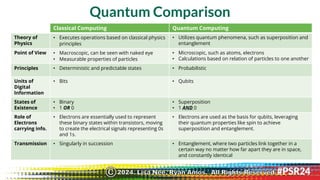
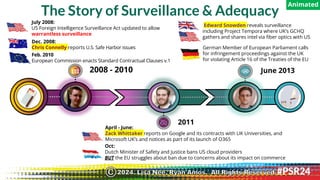
The document discusses the backgrounds of presenters Ryan Amos and Lisa Nee, detailing their expertise in quantum computing, privacy engineering, and data protection. It highlights key issues related to privacy and security in quantum computing, as well as significant historical milestones in data sharing and legislation. Additionally, it outlines a program schedule covering topics of encryption, quantum technology, and evolving data privacy frameworks.








![Comparing the Data Sharing
EU-US
Safe Harbor
EU-US
Privacy Shield
EU-US / Trans-Atlantic
Data Privacy Framework
US STATE LAWS
REGISTRATION Dept. of Commerce Dept. of Commerce Dept. of Commerce None (yet)
CERTIFICATION At Certification Annually Annually None (yet)
MONITORING None; only privately Yes Yes None; only privately
ENFORCEMENT
Federal Trade
Commission
Federal Trade
Commission
Federal Trade
Commission
State Agency or
State Attorney General
THIRD PARTIES Yes Yes Yes Depends on State
THIRD PARTY
SUBPROCESSORS
No Yes Yes Depends on State
DATA PROTECTION
ADDENDUM
No Yes Yes Depends on State
LIABLE FOR THIRD
PARTIES
No
Yes, unless proven no
responsibility
Yes, unless proven no
responsibility
Depends on State
REDRESS FOR EU DATA
SUBJECT
No Omnibus Person EU Data Protection Review Court Depends on State
LIMITS SURVEILLANCE No No Somewhat limits No
PROHIBITS [UNKNOWN]
FEDERAL DATA SEIZURE
No No (only after the fact) No (only after the fact) No
Animated
2024. Lisa Nee, Ryan Amos. All Rights Reserved.
©](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumcomputingasecuritythreataprivacysolutionandaprivacyrightnewestupdate-241008101950-05ff7755/85/Quantum-Computing_A-Security-Threat-a-Privacy-Solution-and-a-Privacy-Right_Newest_Update-pdf-11-320.jpg)