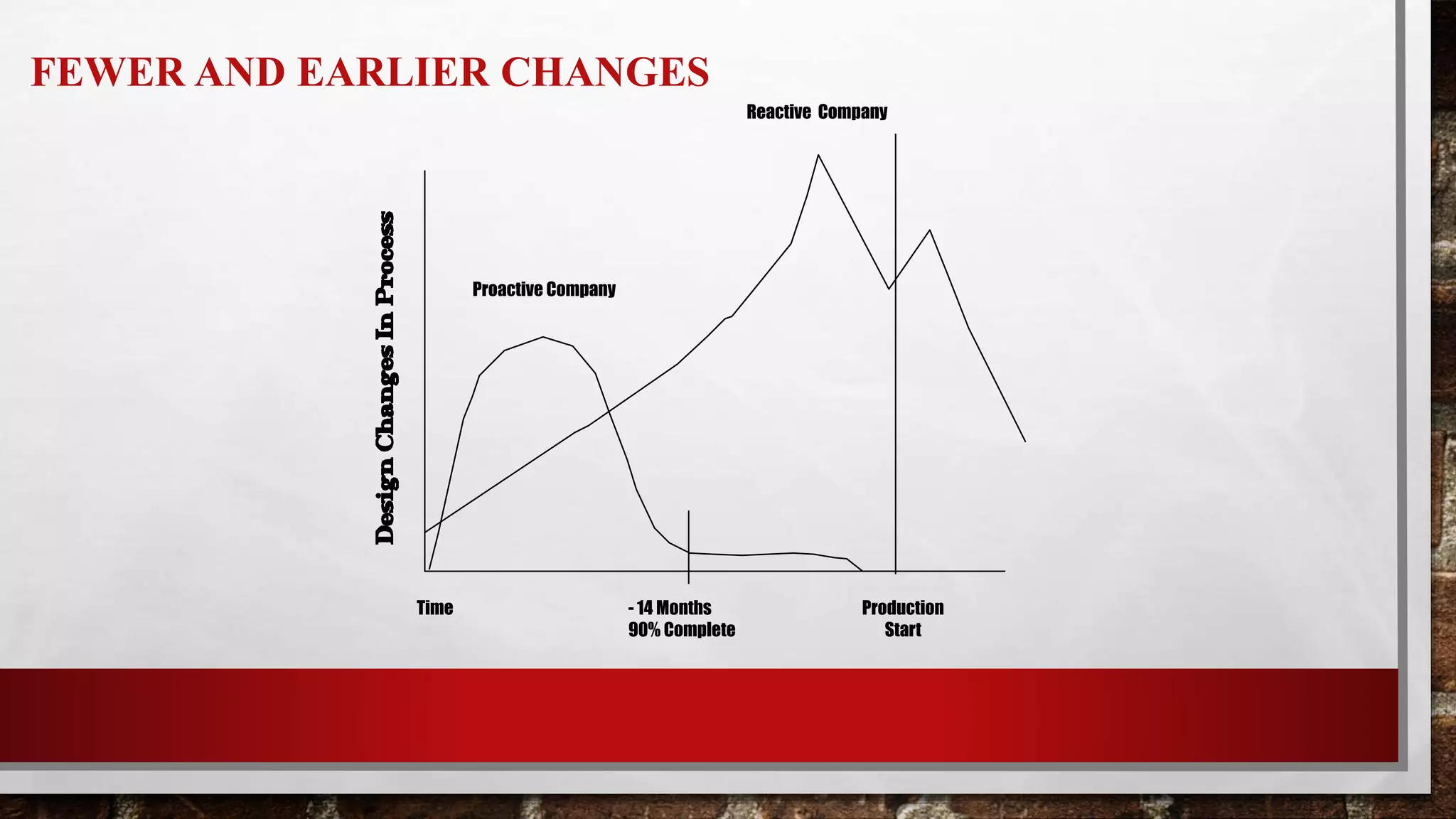
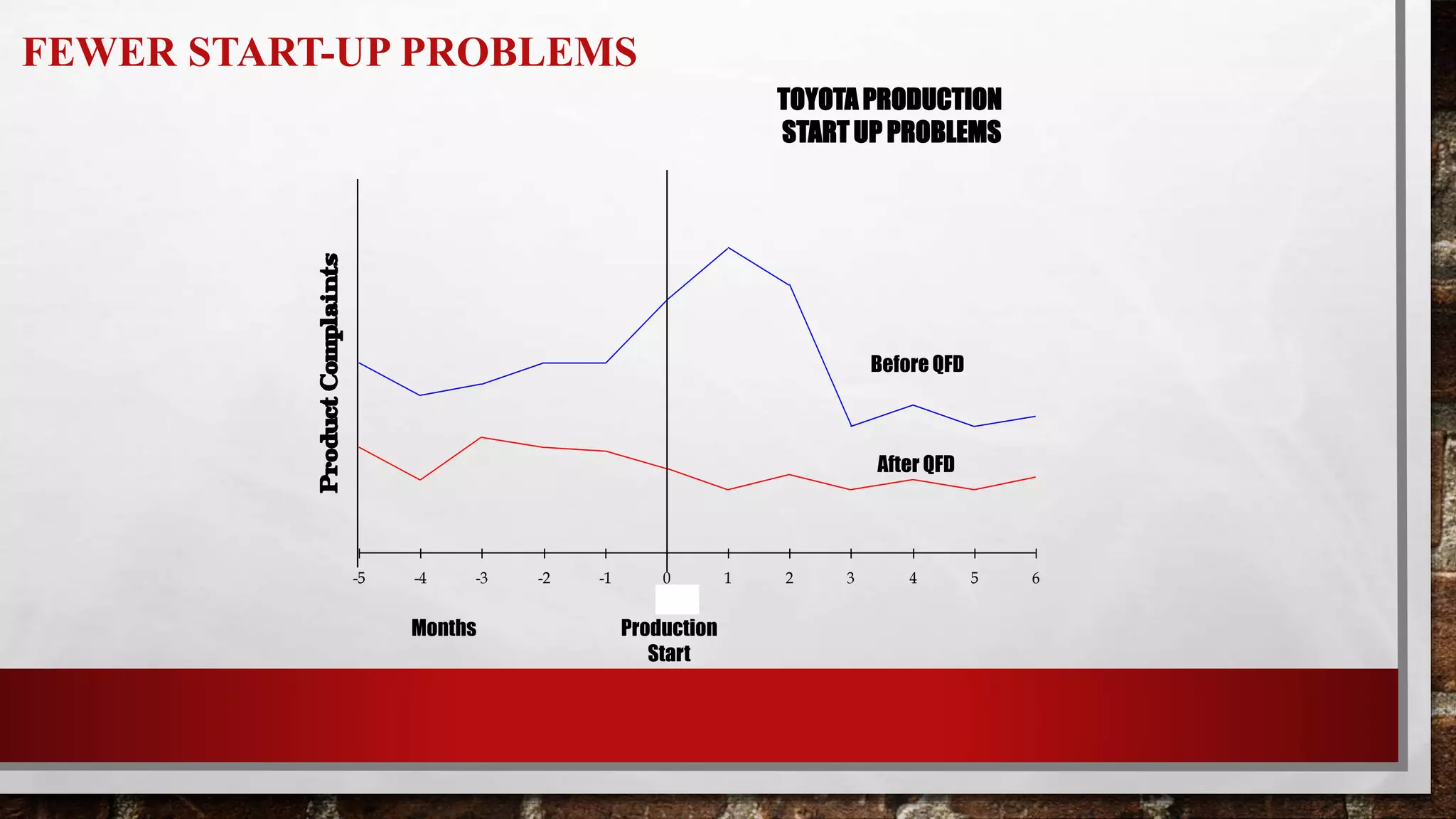
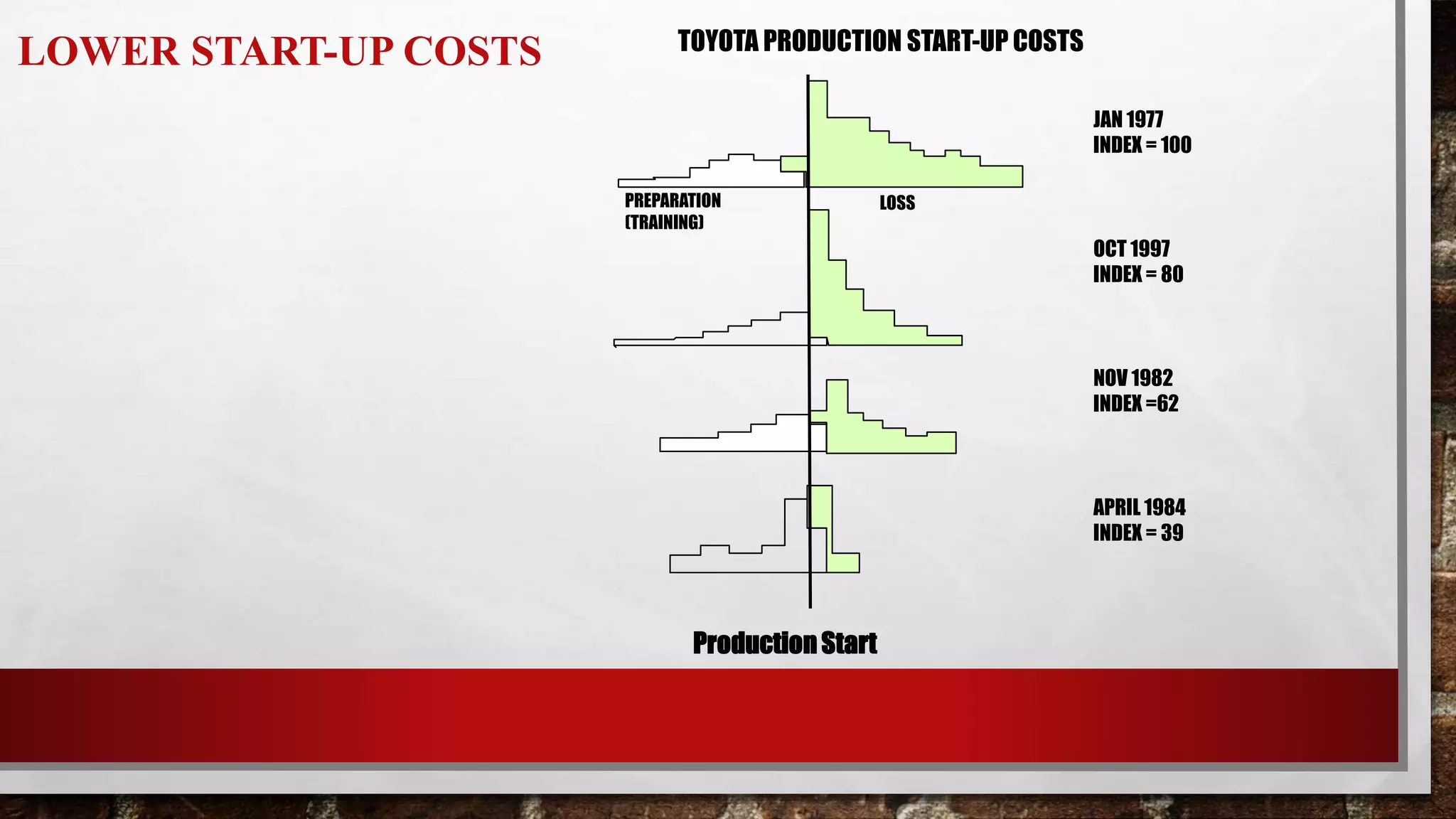
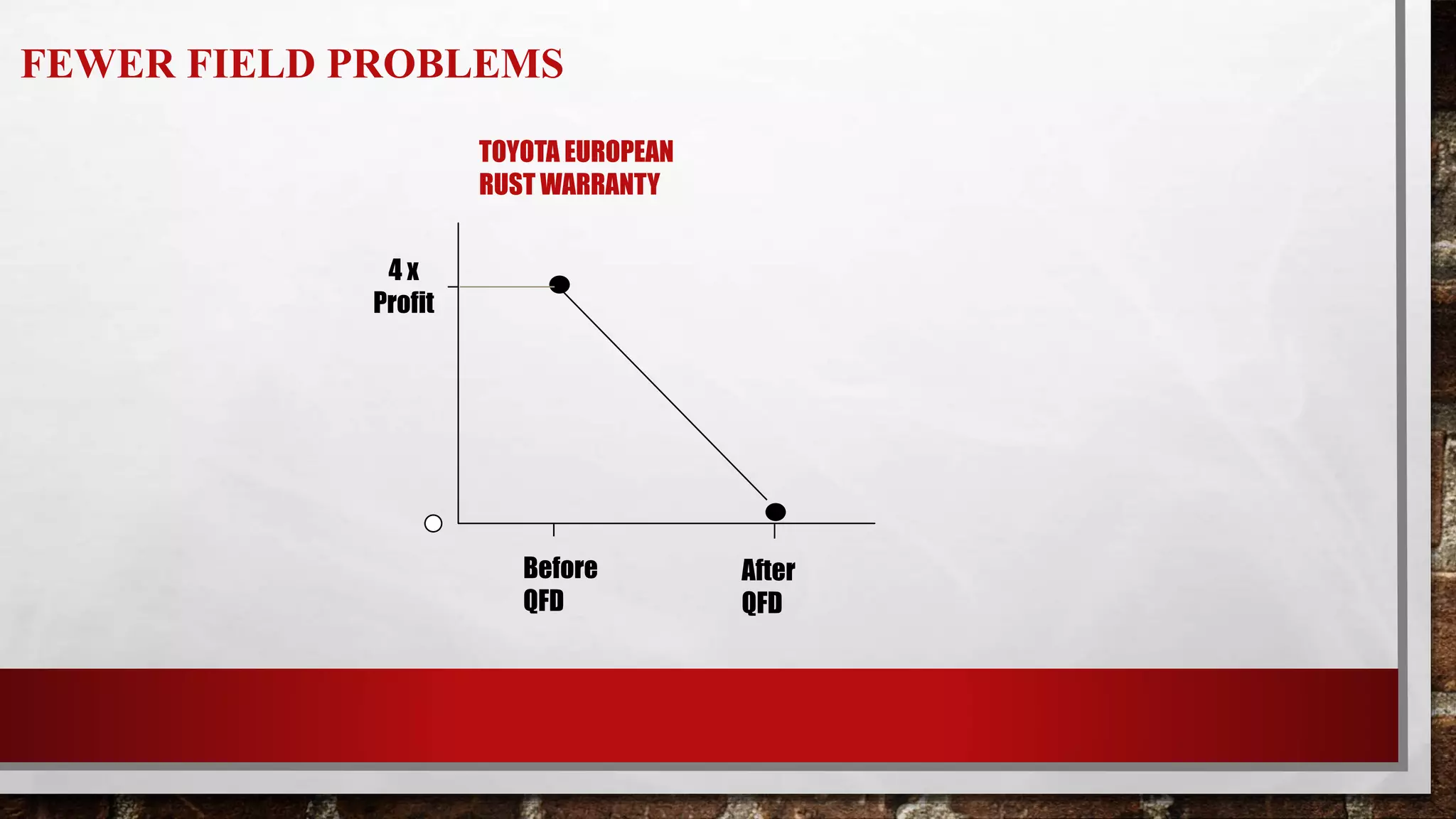
This document discusses Quality Function Deployment (QFD), which is a system for translating customer requirements into technical requirements at each stage of product development. It defines QFD and outlines its timeline and key aspects such as understanding customer requirements, organizing them, and using the House of Quality tool to relate customer needs to technical specifications. The benefits of QFD include fewer changes late in development, less time spent in development, fewer startup problems, and higher customer satisfaction.