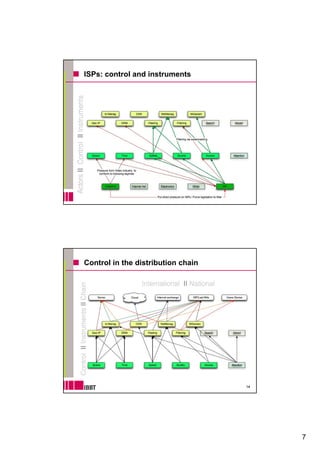
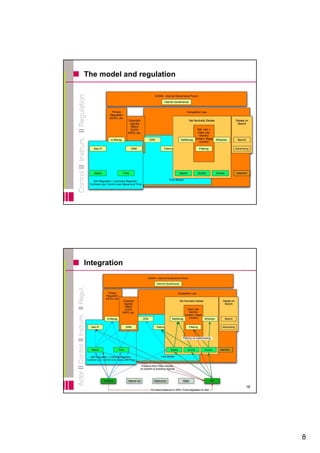
The document discusses developing an analytical framework for understanding how content is distributed on the internet. It examines how technologies, industry practices, and regulation can be used to control various dimensions of content distribution such as time, space, speed, quality, access, and attention. A multi-layer model is proposed to analyze actors, technologies of control, and forms of regulation across the distribution chain from servers to end users. Key issues discussed include geo-blocking, network management, and graduated response copyright enforcement policies.