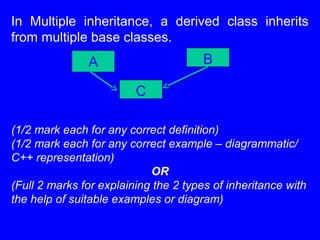
1. Data encapsulation refers to wrapping up data and functions together in a class. Data hiding keeps data private to prevent accidental changes and only accessible by member functions.
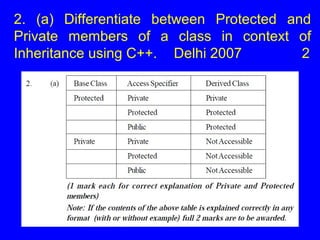
2. Private members are only accessible by member functions of the class, while public members are accessible by member functions of the class and derived classes, as well as by objects of the class.
3. An example class illustrates that a private member cannot be accessed directly by a derived class, while a public member function of the base class can be called by the derived class.











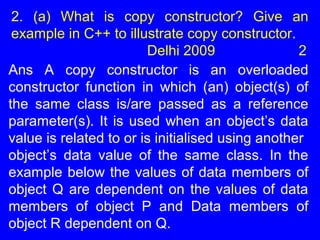


![void main ()
{
Play P; //Call for constructor
P.Disp (); P.Change(90,80) ;
Play Q(P); //Copy constructor call
Q.Disp();
Play R=Q; //Copy constructor ca11 [same as P1ay
R(Q);]
R. Disp();
}
(1 Mark for correct explanation of Copy Constructor)
(1 Mark for a valid example of Copy Constructor)
Note: Member function other than the constructors
are optional](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qno2a-160325122728/85/Qno-2-a-17-320.jpg)








![2. (a) What do you understand by Data
Encapsulation and Data Hiding ?’ Also, give
an example in C++ to illustrate both.
Outside Delhi 2010 2
class Computer
{
char CPU[lO] ;int RNM; //Data Hiding
public: //Data Encapeulation
void STOCK();
void SHOW();
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qno2a-160325122728/85/Qno-2-a-26-320.jpg)










![2. (a) What do you understand by Data
Encapsulation and Data Hiding ?’ Also, give
an example in C++ to illustrate both.
Outside Delhi 2010 SAMPLE PAPER 2009 SET I 2
class Computer
{
char CPU[lO] ;int RNM; //Data Hiding
public: //Data Encapeulation
void STOCK();
void SHOW();
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qno2a-160325122728/85/Qno-2-a-37-320.jpg)






![class Computer
{
char CPU[lO] ;int RNM; //Data Hiding
public: //Data Encapeulation
void STOCK();
void SHOW();
};
2. (a) What do you understand by Data Encapsulation and
Data Hiding ?’ Also, give an example in C++ to illustrate
both. 2
Outside Delhi 2010, SAMPLE PAPER 2009 SET I,
SAMPLE PAPER 2010 SET I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qno2a-160325122728/85/Qno-2-a-44-320.jpg)

