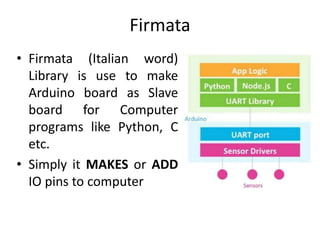
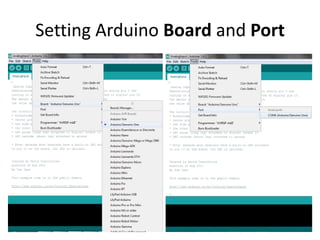
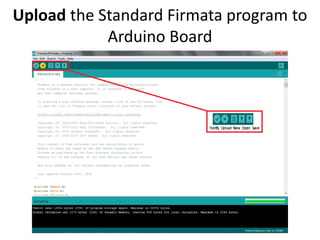
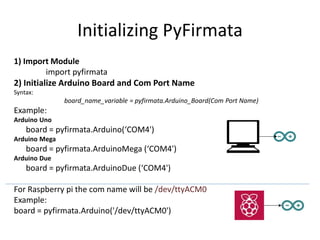
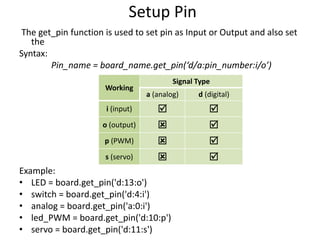
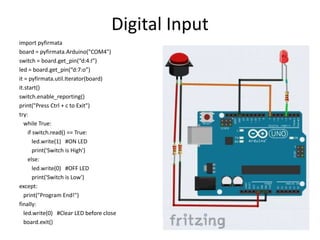
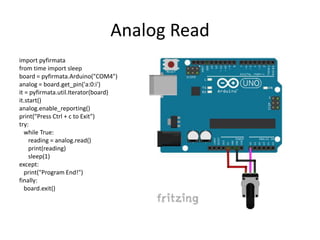
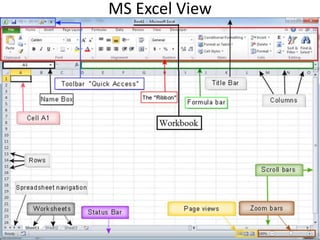
The document discusses interfacing an Arduino board with Python using the PyFirmata library, including initializing communication between an Arduino and Python, configuring pins for input/output, and examples of digital output, analog output, reading analog/digital sensors, and interfacing with MS Excel by writing data to sheets and adding charts.









![Writing data in MS Excel through Python
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
ws1 = wb.create_sheet()
ws.title = "Workshop Sheet"
ws['A1'] = "Integer"
ws['B1'] = "Float"
ws['C1'] = "String"
ws['A2'] = 1000
ws['B2'] = 50.50
ws['C2'] = "Hamdard"
wb.save(r"C:.........workshop.xlsx")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopsession6-180918172945/85/Python-workshop-session-6-24-320.jpg)

![Add Image and Merge Cell
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.drawing.image import Image
try:
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
ws.merge_cells('A1:B1') #Merge Cell
ws['A1'] = "Pakistan Zindabad"
Pak_Flag = Image(r"C:.........Pakistan.PNG")
ws.add_image(Pak_Flag, 'A2')
wb.save(r"C:.........workshop.xlsx")
except PermissionError:
print("Please close the MS Excel Workbook")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopsession6-180918172945/85/Python-workshop-session-6-26-320.jpg)
![Add Sheet to Workbook
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import Workbook
try:
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active #First Sheet
ws.title = "First"
ws['A25'] = "First Sheet"
ws2 = wb.create_sheet() #New Sheet
ws2['A25'] = "Second Sheet"
ws2.title = "Second"
ws3 = wb.create_sheet() #New Sheet
ws3['A25'] = "Third Sheet"
ws3.title = "Third"
wb.save(r"C:.........workshop.xlsx")
except PermissionError:
print("Please close the MS Excel Workbook")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopsession6-180918172945/85/Python-workshop-session-6-27-320.jpg)
![Accessing Multiple cell
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import Workbook
try:
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
ws['A1'] = "Number"
ws['B1'] = "Square"
for i in range(10):
ws.cell(row = i+2 , column = 1 , value = i)
ws.cell(row = i+2 , column = 2 , value = i*i)
wb.save(r"C:.........workshop.xlsx")
except PermissionError:
print("Please close the MS Excel Workbook")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopsession6-180918172945/85/Python-workshop-session-6-28-320.jpg)

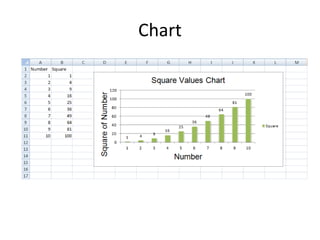
![Adding Chart to Worksheet
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.chart import
BarChart,Reference,Series
try:
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
ws['A1'] = "Number"
ws['B1'] = "Square"
for i in range(1,11):
ws.cell(row = i+1 , column = 1 , value = i)
ws.cell(row = i+1 , column = 2 , value = i*i)
#Working for Chart
chart = BarChart()
chart.title = "Square Values Chart"
chart.style = 13
chart.x_axis.title = 'Number'
chart.y_axis.title = 'Square of Number'
x_axis = Reference(ws, min_col=1, min_row=2,
max_row=i+1)
y_axis = Reference(ws, min_col=2, min_row=1,
max_col=2, max_row=i+1)
chart.add_data(y_axis, titles_from_data=True)
chart.set_categories(x_axis)
ws.add_chart(chart, "D2")
#Save Workbook
wb.save(r"C:UsersHomeDesktopworkshop.xlsx")
except PermissionError:
print("Please close the MS Excel Workbook")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonworkshopsession6-180918172945/85/Python-workshop-session-6-30-320.jpg)