The document provides information about an introduction to Python programming presented by Kiattisak Anoochitarom. It begins with welcoming messages and details about the presenter. It then discusses various Python topics like data types, operators, control flow statements, functions, built-in functions, and string and list methods. Examples are provided throughout to demonstrate different Python concepts and syntax. The goal is to teach the basics of the Python language.















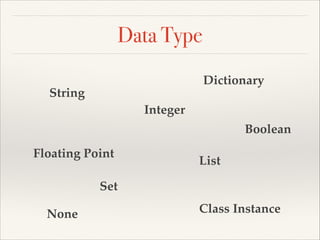
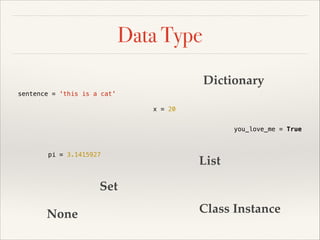
![Data Type
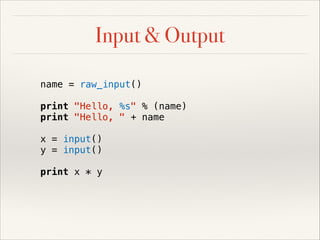
Dictionary
sentence = 'this is a cat'
x = 20
you_love_me = True
pi = 3.1415927
even_numbers = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
Set
nothing = None
Class Instance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-26-320.jpg)
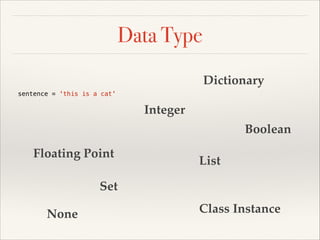
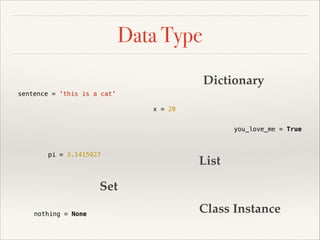
![Data Type
Dictionary
sentence = 'this is a cat'
x = 20
you_love_me = True
pi = 3.1415927
even_numbers = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
odd_numbers = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
nothing = None
Class Instance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-27-320.jpg)
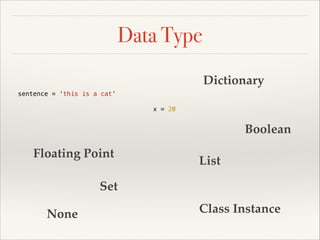
![Data Type
profile = { 'name': 'Bas',
'email': 'macbaszii@gmail.com'}
sentence = 'this is a cat'
x = 20
you_love_me = True
pi = 3.1415927
even_numbers = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
odd_numbers = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
nothing = None
Class Instance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-28-320.jpg)
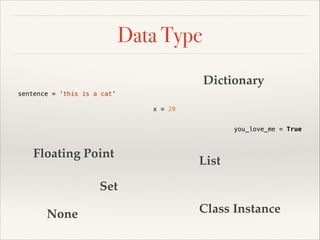
![Data Type
profile = { 'name': 'Bas',
'email': 'macbaszii@gmail.com'}
sentence = 'this is a cat'
x = 20
you_love_me = True
pi = 3.1415927
even_numbers = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
odd_numbers = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
nothing = None
my_car = Car('Lamborghini',
'Aventador LP 700-4', 'White')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-29-320.jpg)
![Data Type
profile = { 'name': 'Bas',
'email': 'macbaszii@gmail.com'}
sentence = 'this is a cat'
x = 20
you_love_me = True
pi = 3.1415927
even_numbers = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
odd_numbers = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
nothing = None
my_car = Car('Lamborghini',
'Aventador LP 700-4', 'White')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-30-320.jpg)





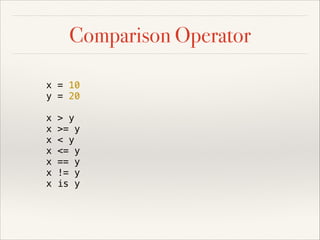
![Comparison Operator
x = 10
y = 20
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
> y
>= y
< y
<= y
== y
!= y
is y
# Chain Comparison
5 < x < y
1 < y < 100
# Contains Operator
prime = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11]
9 in prime # False
sentence = 'this is a cat'
'cat' in sentence # True](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-37-320.jpg)




![Range and Lazy Generator
range(10)
# [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
range(3, 10)
# [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
range(1, 20, 3)
# [1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19]
xrange(10)
xrange(3, 10)
xrange(1, 20, 3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-42-320.jpg)


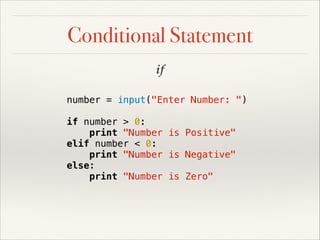





![Iteration Statement
for
for i in xrange(1, 11):
print i**2
socials = ['Facebook', 'Twitter']
for social in socials:
print 'I played %s' % social](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-51-320.jpg)
![Iteration Statement
for
for i in xrange(1, 11):
print i**2
socials = ['Facebook', 'Twitter']
for social in socials:
print 'I played %s' % social
message = 'Hello, CPSU'
for letter in message:
print letter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-52-320.jpg)
![Iteration Statement
for
for i in xrange(1, 11):
print i**2
socials = ['Facebook', 'Twitter']
for social in socials:
print 'I played %s' % social
message = 'Hello, CPSU'
for letter in message:
print letter
# Endless Loop #
while True:
# Do something](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-53-320.jpg)



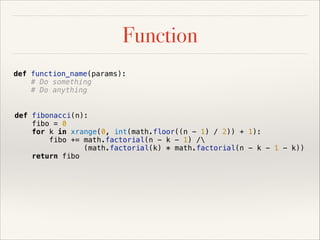
![Function
def function_name(params):
# Do something
# Do anything
def fibonacci(n):
fibo = 0
for k in xrange(0, int(math.floor((n - 1) / 2)) + 1):
fibo += math.factorial(n - k - 1) /
(math.factorial(k) * math.factorial(n - k - 1 - k))
return fibo
def colorMultiply(r, g=0, b=0):
return [ r * 3.14159,
g * 1.414,
b * 3.27 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-58-320.jpg)



![Indexing and Slice
message = 'Hello, world'
message[0] # H
message[len(message) - 1] # d
message[-1] # d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-62-320.jpg)
![Indexing and Slice
message = 'Hello, world'
message[0] # H
message[len(message) - 1] # d
message[-1] # d
fibo = [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
fibo[:5] # [1, 1, 2, 3, 5]
fibo[2:] # [2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
fibo[3:6] # [3, 5, 8, 13]
fibo[::2] # [1, 2, 5, 13, 34]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-63-320.jpg)
![Indexing and Slice
message = 'Hello, world'
message[0] # H
message[len(message) - 1] # d
message[-1] # d
fibo = [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
fibo[:5] # [1, 1, 2, 3, 5]
fibo[2:] # [2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
fibo[3:6] # [3, 5, 8, 13]
fibo[::2] # [1, 2, 5, 13, 34]
fibo[::-1] # ???
message[::-1] # ???](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-64-320.jpg)


![List Comprehensive
The Other way to create and manipulation Python’s List
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-67-320.jpg)
![List Comprehensive
The Other way to create and manipulation Python’s List
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
squares = []
for x in range(10):
squares.append(x**2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-68-320.jpg)
![List Comprehensive
The Other way to create and manipulation Python’s List
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-69-320.jpg)
![List Comprehensive
The Other way to create and manipulation Python’s List
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]
set1 = [1, 2, 3]
set2 = [3, 1, 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-70-320.jpg)
![List Comprehensive
The Other way to create and manipulation Python’s List
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]
set1 = [1, 2, 3]
set2 = [3, 1, 4]
combs = []
for x in set1:
for y in set2:
if x != y:
comb.append((x, y))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-71-320.jpg)
![List Comprehensive
The Other way to create and manipulation Python’s List
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]
set1 = [1, 2, 3]
set2 = [3, 1, 4]
combs = [(x, y) for x in set1 for y in set2 if x != y]
[(1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 1), (2, 4), (3, 1), (3, 4)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-72-320.jpg)
![List Comprehensive
The Other way to create and manipulation Python’s List
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]
set1 = [1, 2, 3]
set2 = [3, 1, 4]
combs = [(x, y) for x in set1 for y in set2 if x != y]
[(1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 1), (2, 4), (3, 1), (3, 4)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-73-320.jpg)
![List Comprehensive
The Other way to create and manipulation Python’s List
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]
set1 = [1, 2, 3]
set2 = [3, 1, 4]
combs = [(x, y) for x in set1 for y in set2 if x != y]
[(1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 1), (2, 4), (3, 1), (3, 4)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-74-320.jpg)
![List Comprehensive
The Other way to create and manipulation Python’s List
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]
set1 = [1, 2, 3]
set2 = [3, 1, 4]
combs = [(x, y) for x in set1 for y in set2 if x != y]
[(1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 1), (2, 4), (3, 1), (3, 4)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-75-320.jpg)



![Working with File
open('filename', mode)
# r: open file for read
# w: open file for write
# a: open file for append
f = open('data.txt', r)
f.read() # read file to string
f.readline() # read file for one line
f.readlines() # read file to lines
f.write('this is a cat') # write string to file
f.writelines([list of line]) # write lines to file](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-79-320.jpg)



![Object Oriented Programming
class Book:
def __init__(self, name, size):
self.name = name
self.size = size
class BookStack:
def __init__(self):
self.books = []
self.top = 0
def push(self, book):
self.books.append(book)
self.top += 1
def pop(self):
self.top -= 1
return self.books.pop()
!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-83-320.jpg)



![Unit Test
import unittest
! TestBookStack(unittest.TestCase):
class
# when book is created, it can return name, size
def test_book_created(self):
hunger_book = Book('The Hunger Games', 4)
self.assertEqual(hunger_book.name, 'The Hunger Games')
self.assertEqual(hunger_book.size, 4)
# when Book Stack is created / top is 0
def test_book_stack_created(self):
book_stack = BookStack()
self.assertEqual(book_stack.top, 0)
self.assertEqual(book_stack.books, [])
# when push book / top increase by one
def test_book_stack_push(self):
hunger_book = Book('The Hunger Games', 4)
book_stack = BookStack()
book_stack.push(hunger_book)
self.assertEqual(book_stack.top, 1)
self.assertEqual(book_stack.books[0].name, 'The Hunger Games')
book_stack.push(hunger_book)
self.assertEqual(book_stack.top, 2)
# when pop book / top decrease by one
def test_book_stack_pop(self):
hunger_book = Book('The Hunger Games', 4)
harry_book = Book('Harry Potter', 3)
book_stack = BookStack()
book_stack.push(hunger_book)
book_stack.push(harry_book)
present_size = book_stack.top
poped_book = book_stack.pop()
self.assertEqual(book_stack.top, present_size - 1)
self.assertEqual(poped_book.name, 'Harry Potter')
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonslide-131110094851-phpapp02/85/Python-slide-87-320.jpg)

