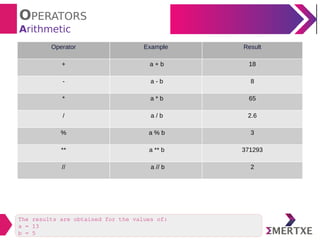
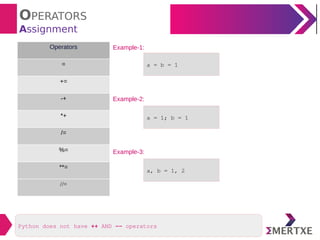
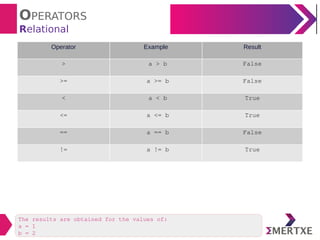
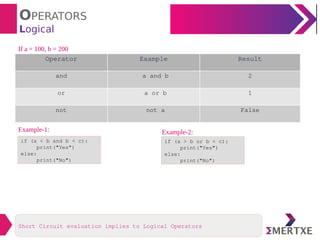
The document provides an overview of various types of operators in Python, including arithmetic, assignment, unary, relational, logical, boolean, bitwise, membership, and identity operators, along with examples and results for each type. It also discusses operator precedence and associativity, highlighting specific functionalities such as short circuit evaluation and mathematical functions from the math module. Additionally, the document includes examples demonstrating the operators in action to clarify their usage.





![OPERATORS
Membership
Operator Description
in Returns True, if an item is found in the specified sequence
not in Returns True, if an item is not found in the specified sequence
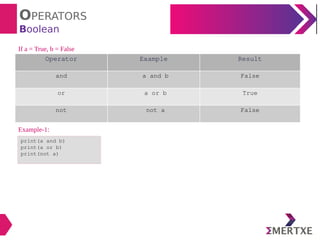
Example-1:
names = ["Ram", "Hari", "Thomas"]
for i in names:
print(i)
Example-2:
postal = {"Delhi": 110001, "Chennai": 600001, "Bangalore": 560001}
for city in postal:
print(city, postal[city])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operators-190509065524/85/Python-Operators-11-320.jpg)

![OPERATORS
Identity
To compare two objects, use ‘==’ operator
Example-1:
a = [1, 2, 3, 4]
b = [1, 2, 3, 4]
if (a == b):
print("Objects are same")
else:
print("Objects are not same")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operators-190509065524/85/Python-Operators-13-320.jpg)
![OPERATORS
Precedence & Associativity
Operator Name
(expressions...), [expressions...], {key:
value...}, {expressions...}
Binding or tuple display, list display, dictionary
display, set display
x[index], x[index:index], x(arguments...),
x.attribute
Subscription, slicing, call, attribute reference
** Exponentiation
+, -, ~ Positive, negative, bitwise NOT
*, @, /, //, % Multiplication, matrix multiplication, division,
floor division, remainder
+, - Addition, Subraction
<<, >> Bitwise Left, Right shift
& Bitwise AND
^ Bitwise XOR
| Bitwise OR
in, not in, is, is not, <, <=, >, >=, !=, == Comparisons, including membership tests and identity
tests
not Boolean not
and Boolean and
or Boolean or
if-else Conditional Expression
lambda Lambda Expression
All operators follow, Left – Right associativity, except ** which
follows Right - Left](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operators-190509065524/85/Python-Operators-14-320.jpg)

