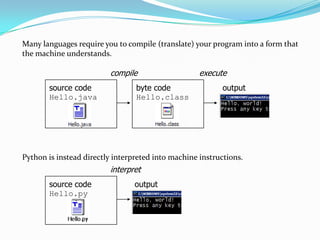
The document provides an overview of Python programming, explaining how it directly interprets source code and covers essential concepts like variables, assignment statements, input/output, loops, and file handling. It illustrates these concepts with examples, highlighting the use of classes and objects in Python. Overall, it serves as a foundational introduction to basic programming techniques in Python.