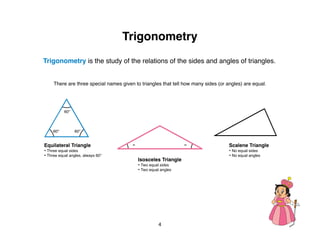
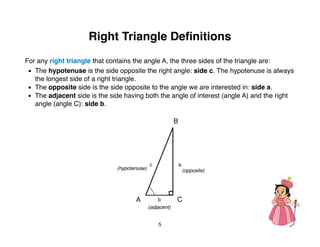
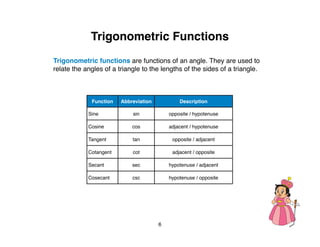
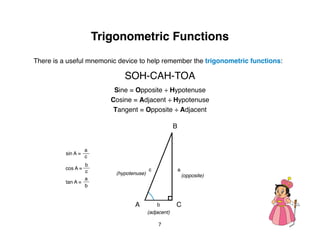
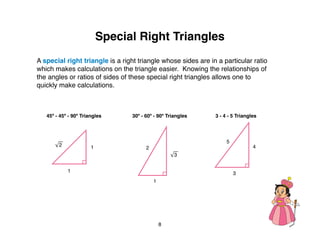
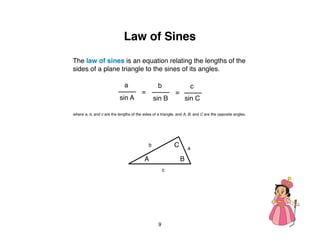
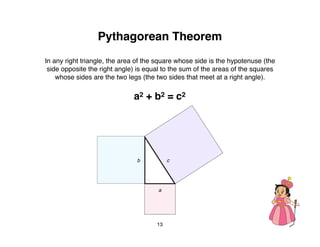
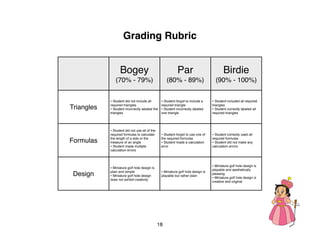
The document outlines a teacher's guide for a Level 3 Math educational program focused on trigonometry and mathematical proofs, covering key topics such as trigonometric functions, special right triangles, and the Pythagorean theorem. It includes a suggested time for teaching, practice activities, and a final project, alongside grading rubrics for assessing student work. The goal is to enhance students' understanding of triangles and their relationships, reinforced through activities and proofs.