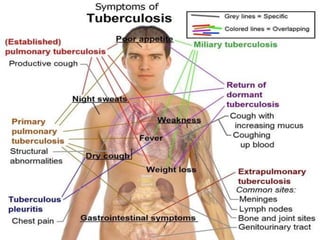
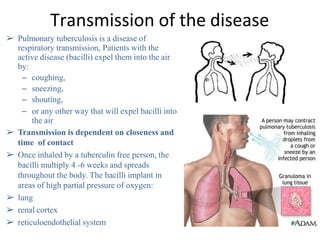
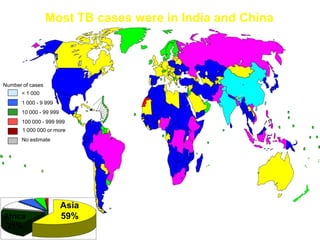
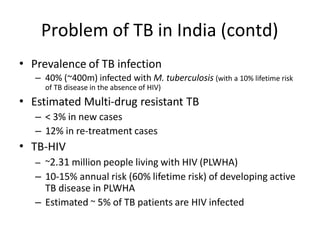
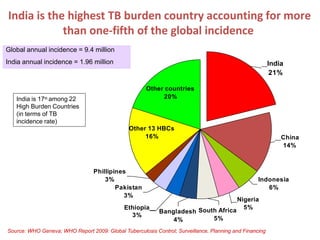
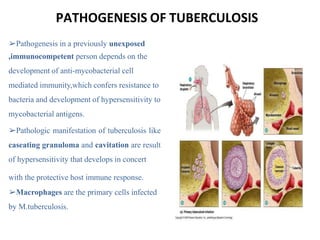
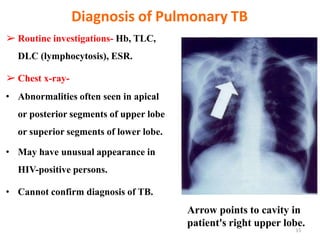
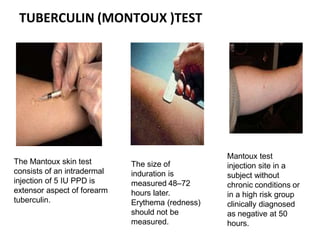
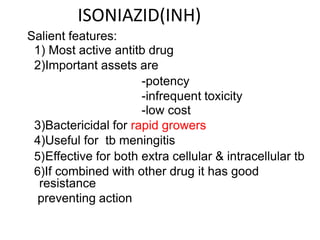
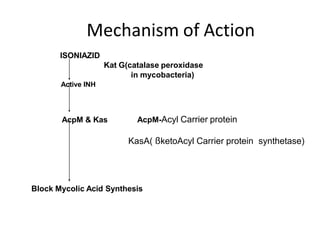
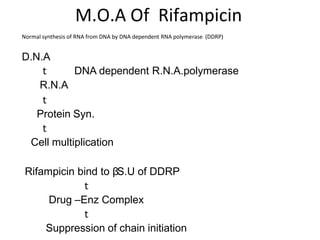
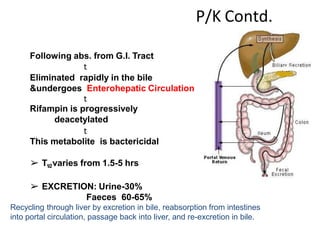
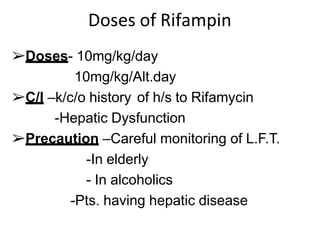
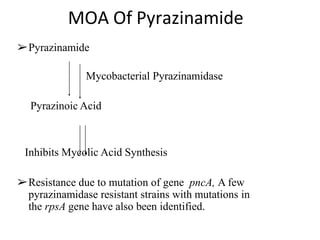
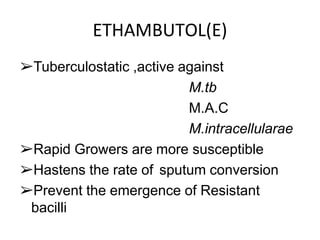
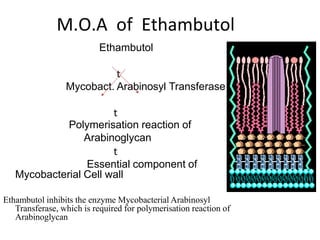
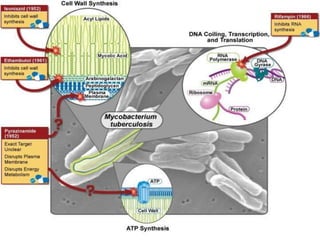
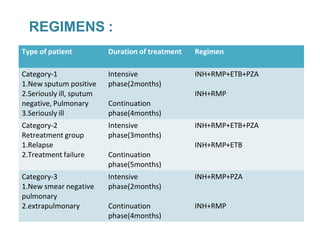
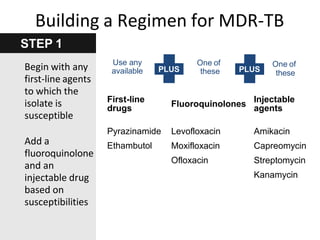
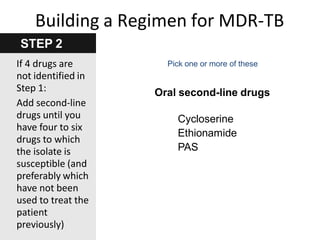
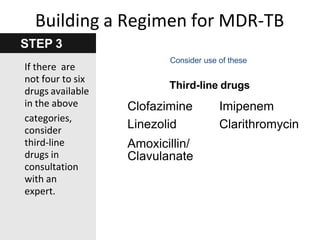
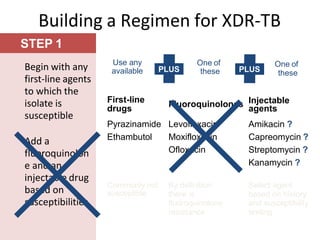
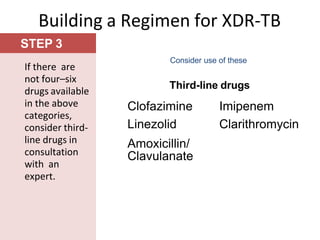
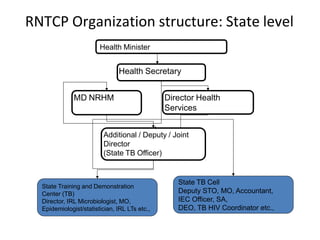
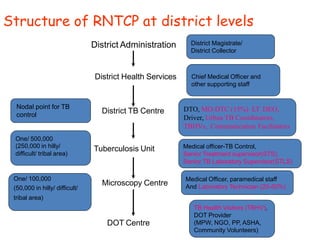
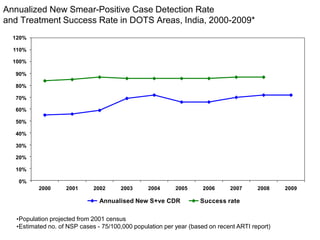
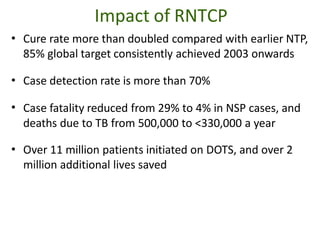
Pulmonary tuberculosis is caused by infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is a small, aerobic bacillus. Symptoms include a prolonged cough lasting over 3 weeks, coughing up sputum or blood, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Diagnosis involves chest x-ray, sputum smear and culture, and the Mantoux tuberculin skin test. Treatment requires a combination of antibiotics like isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol over a period of 6-9 months to prevent drug resistance from developing. Tuberculosis remains a major global health problem and India has a high burden of cases.