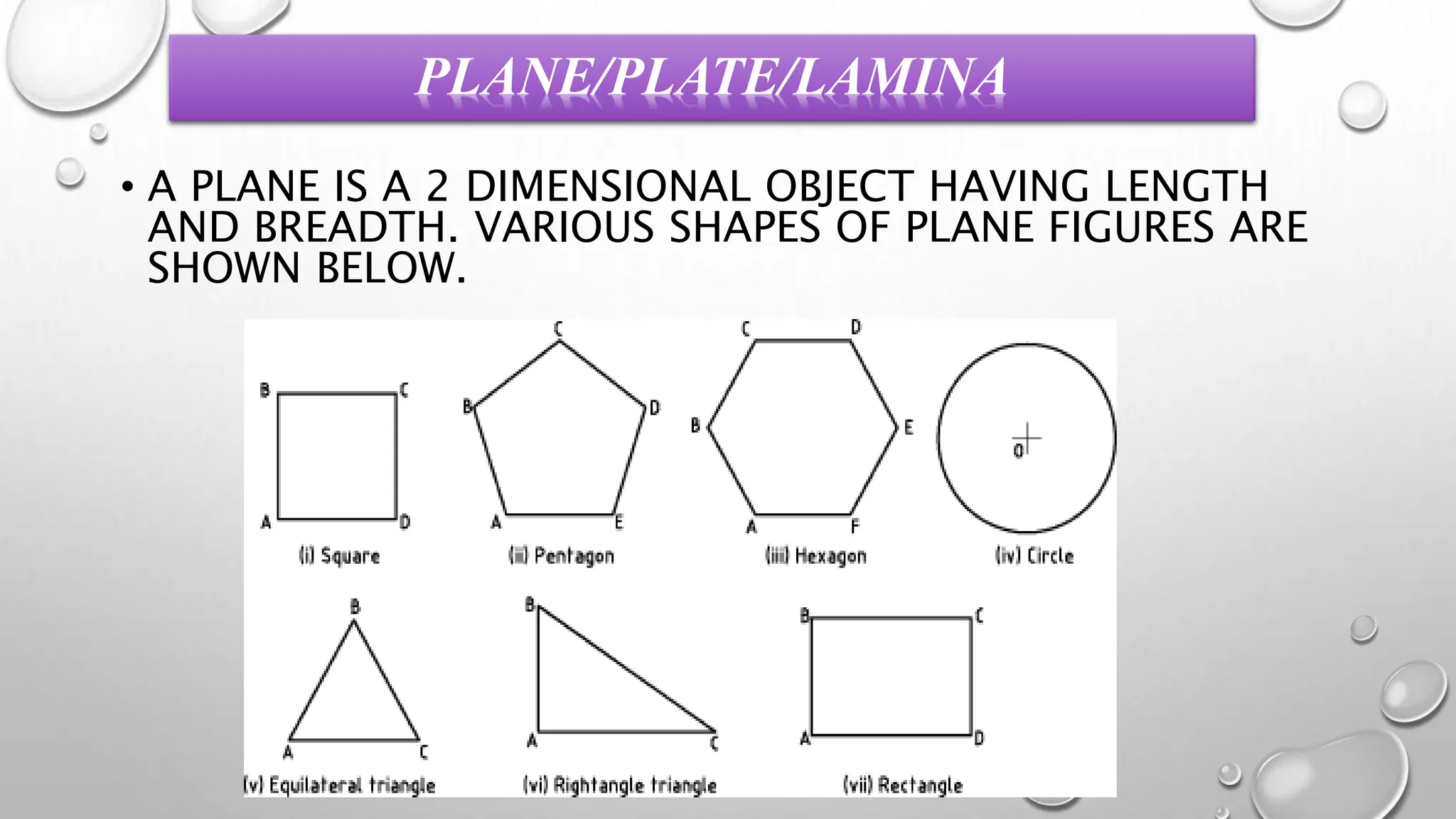
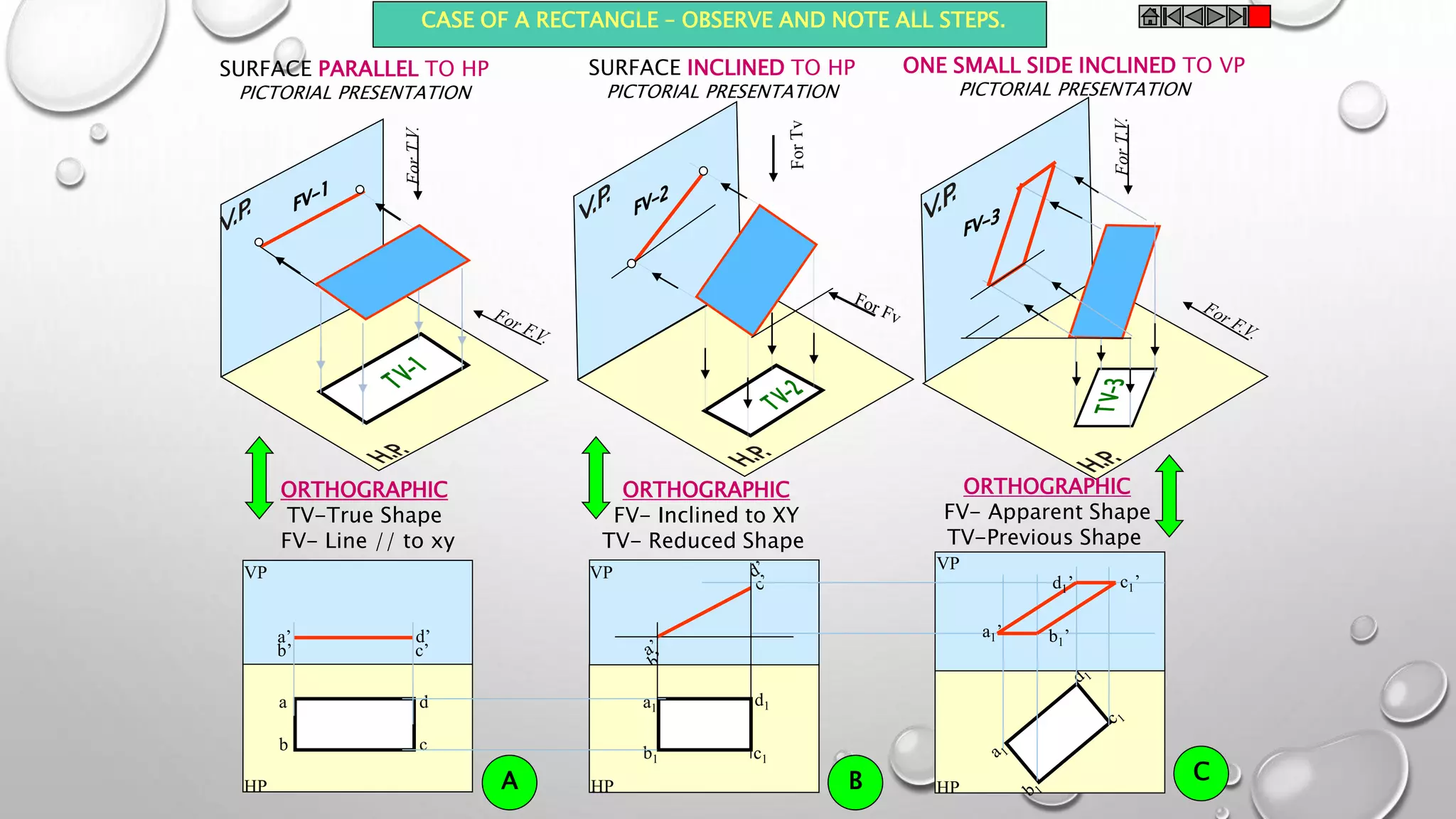
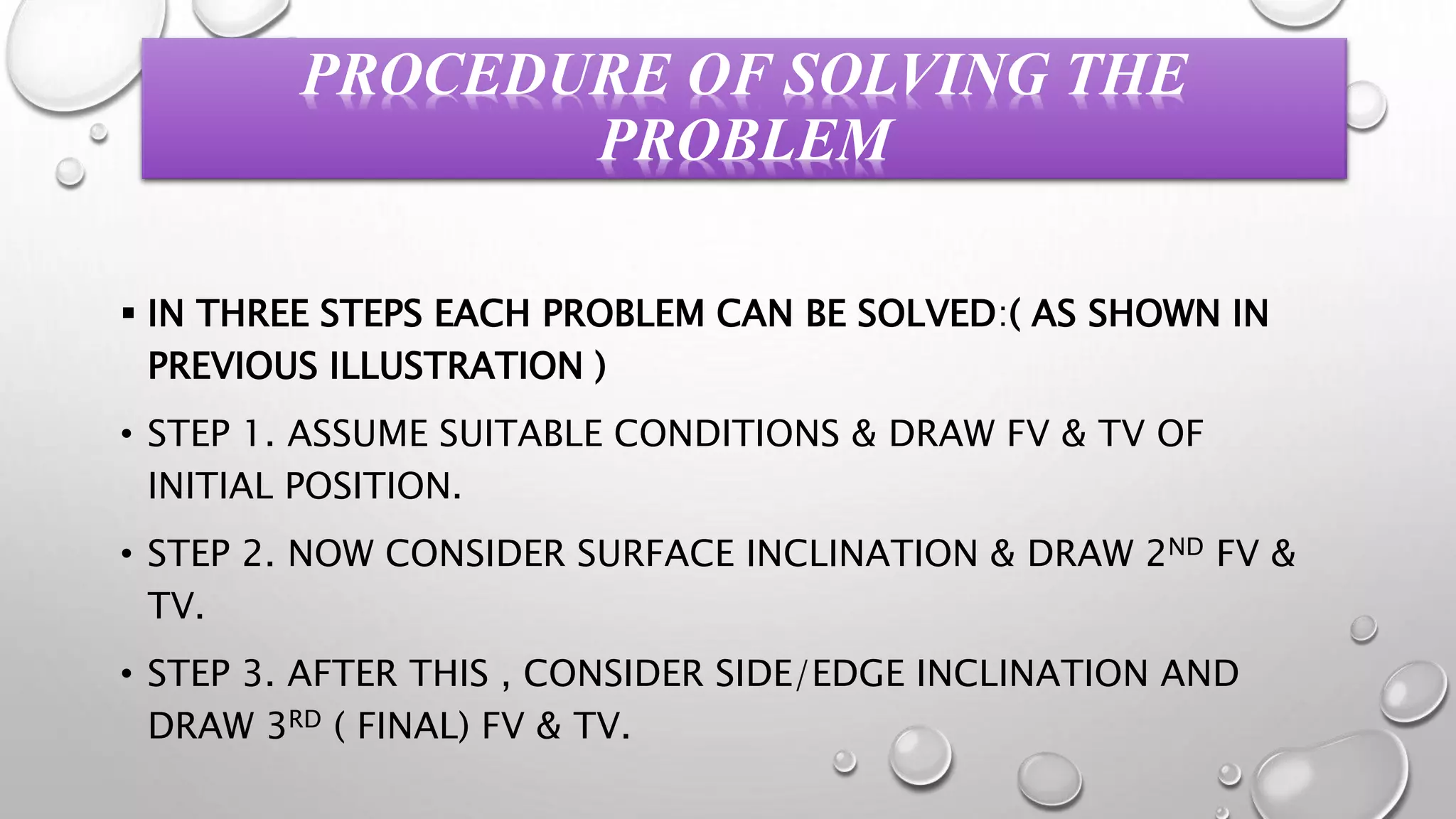
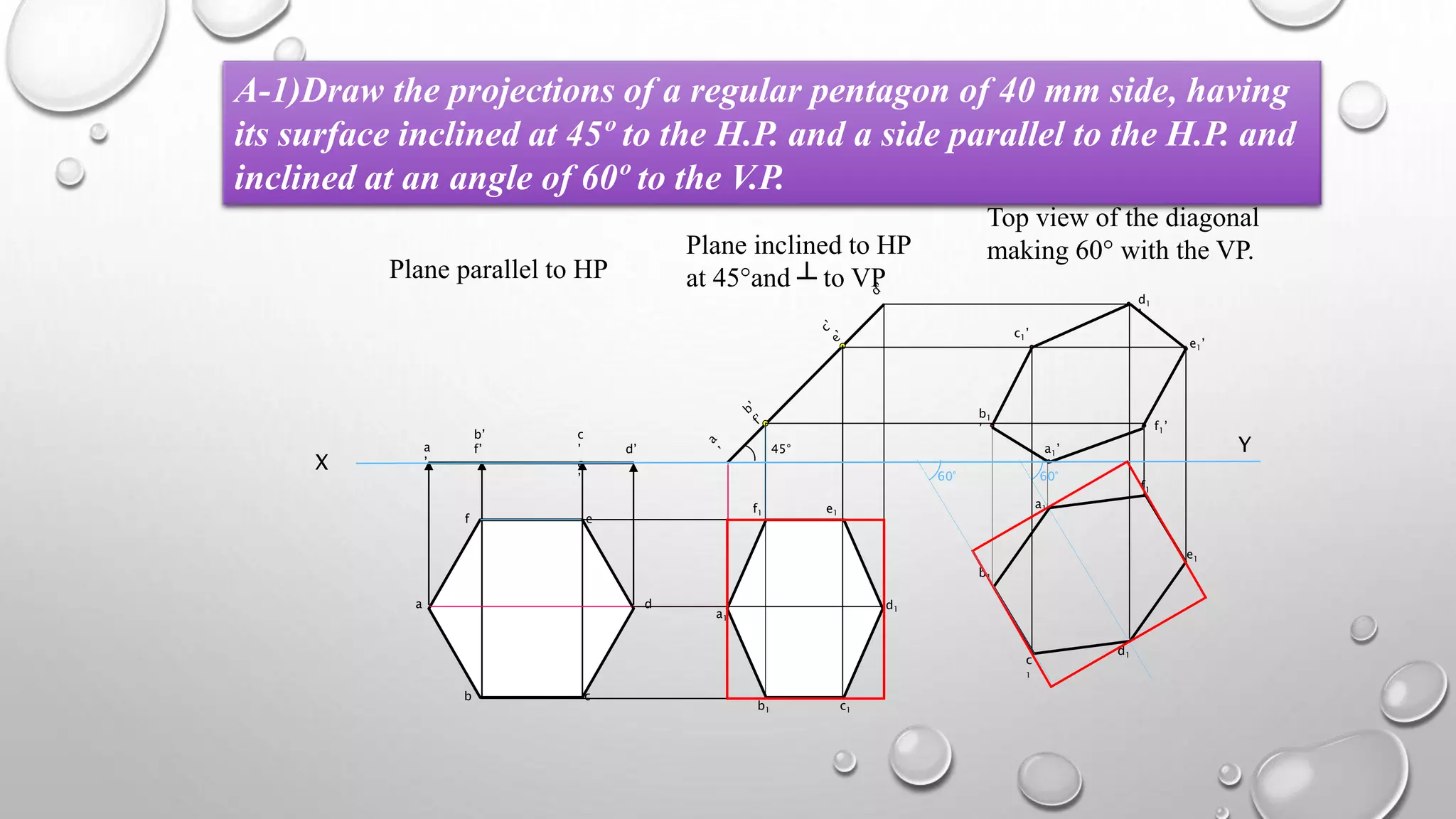
The document provides information on the projection of plane figures:
1) It explains the basics of plane projection problems, including what is typically given (projections of the plane) and asked for (its position relative to reference planes).
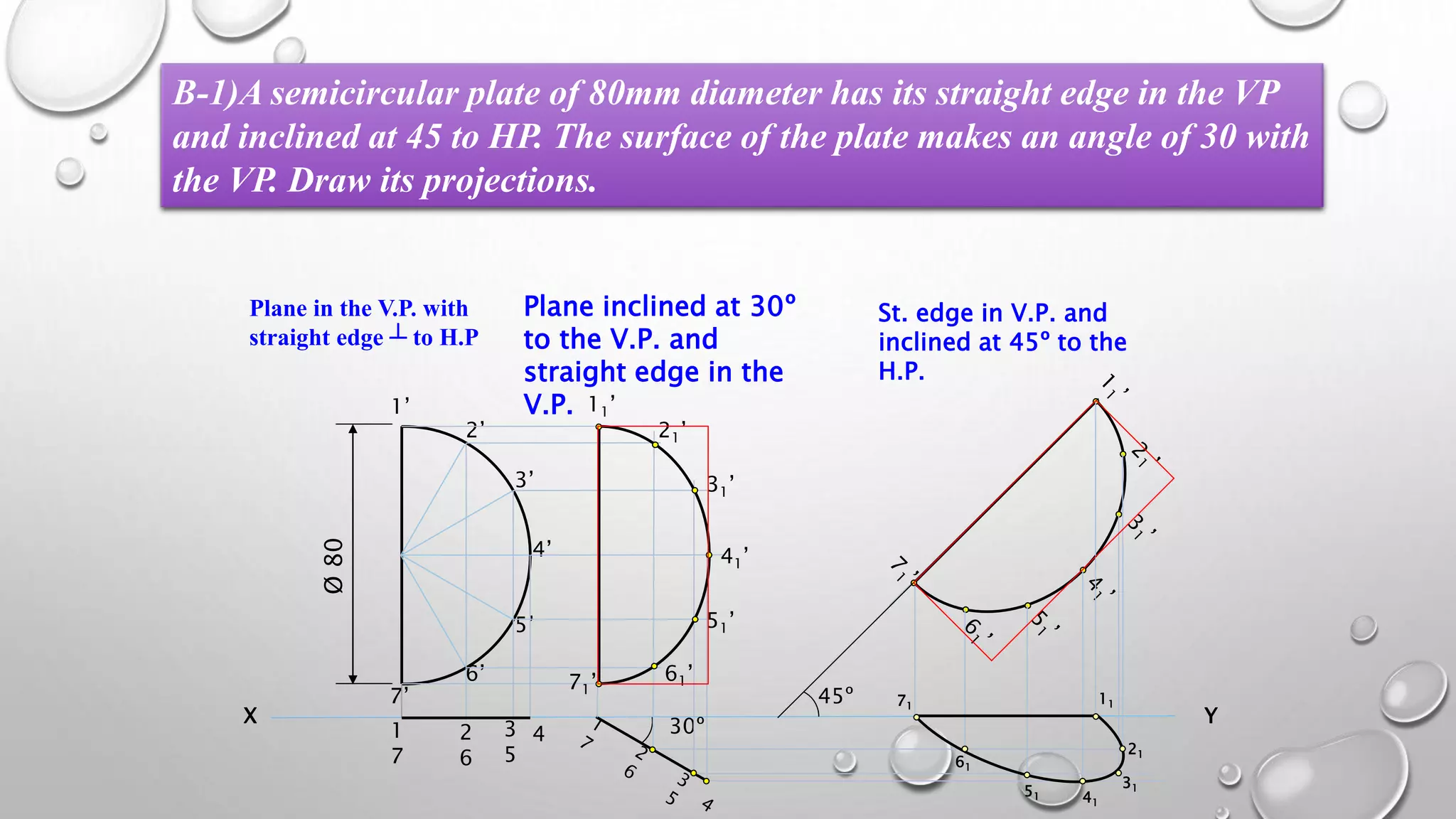
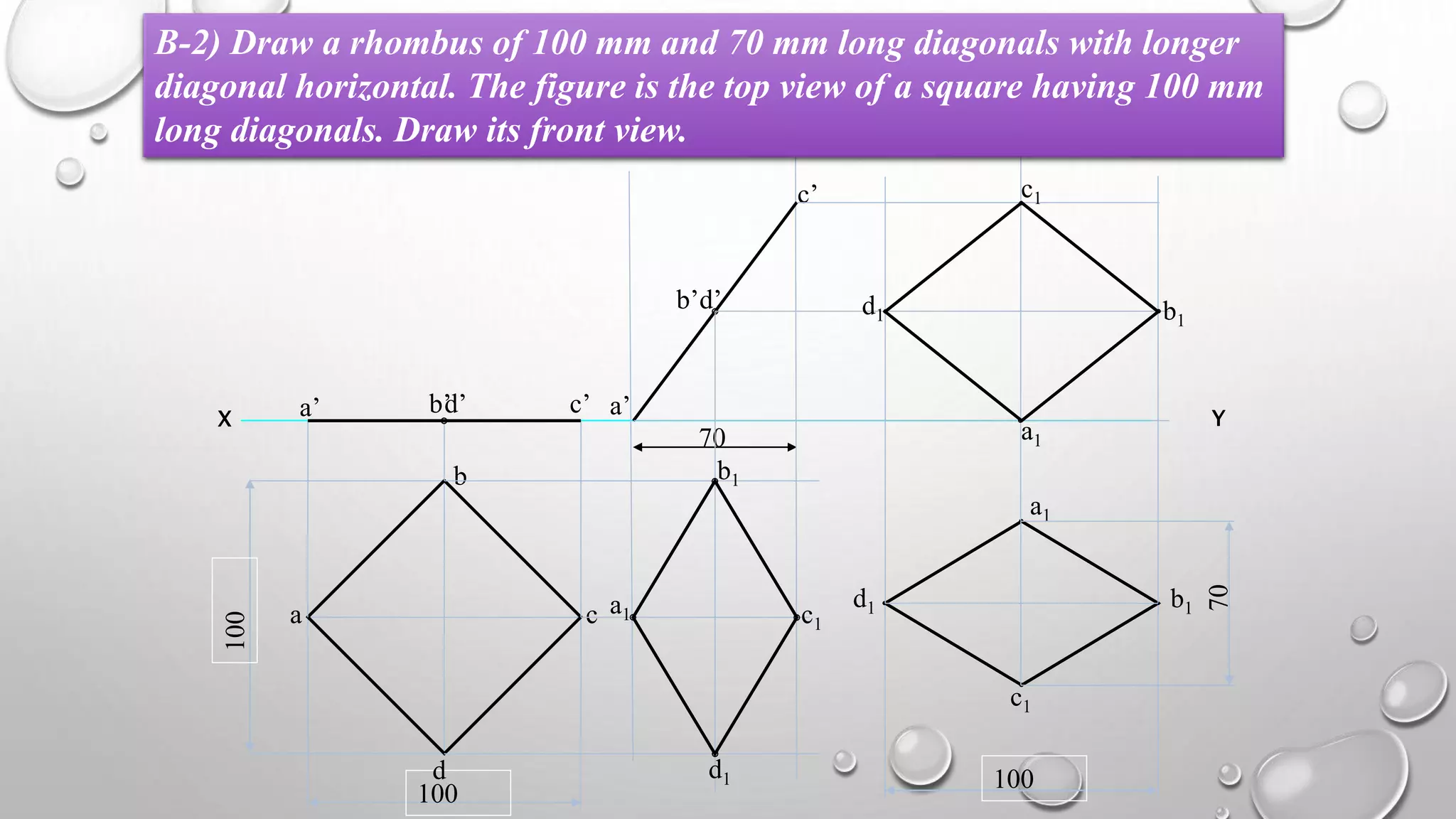
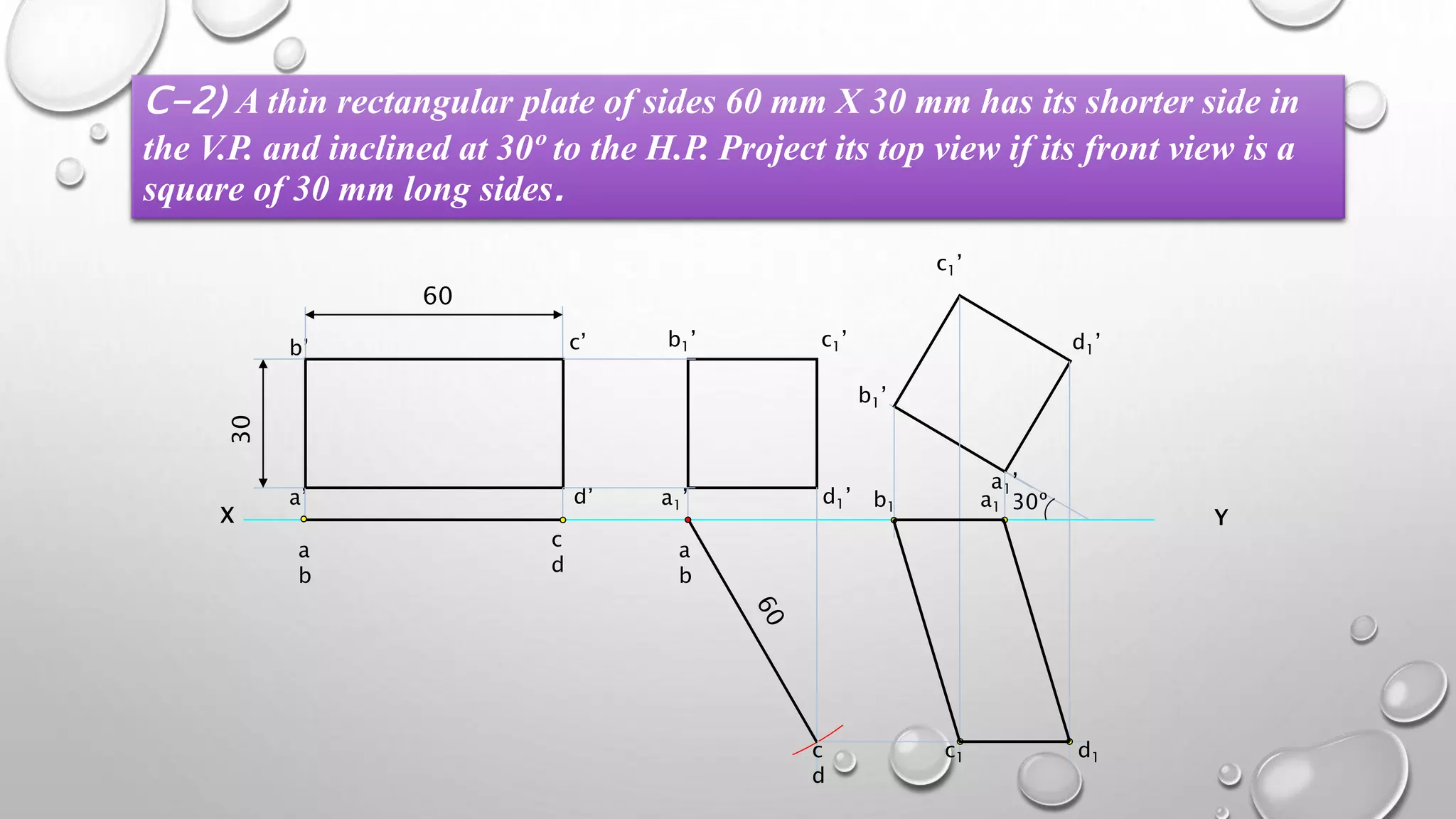
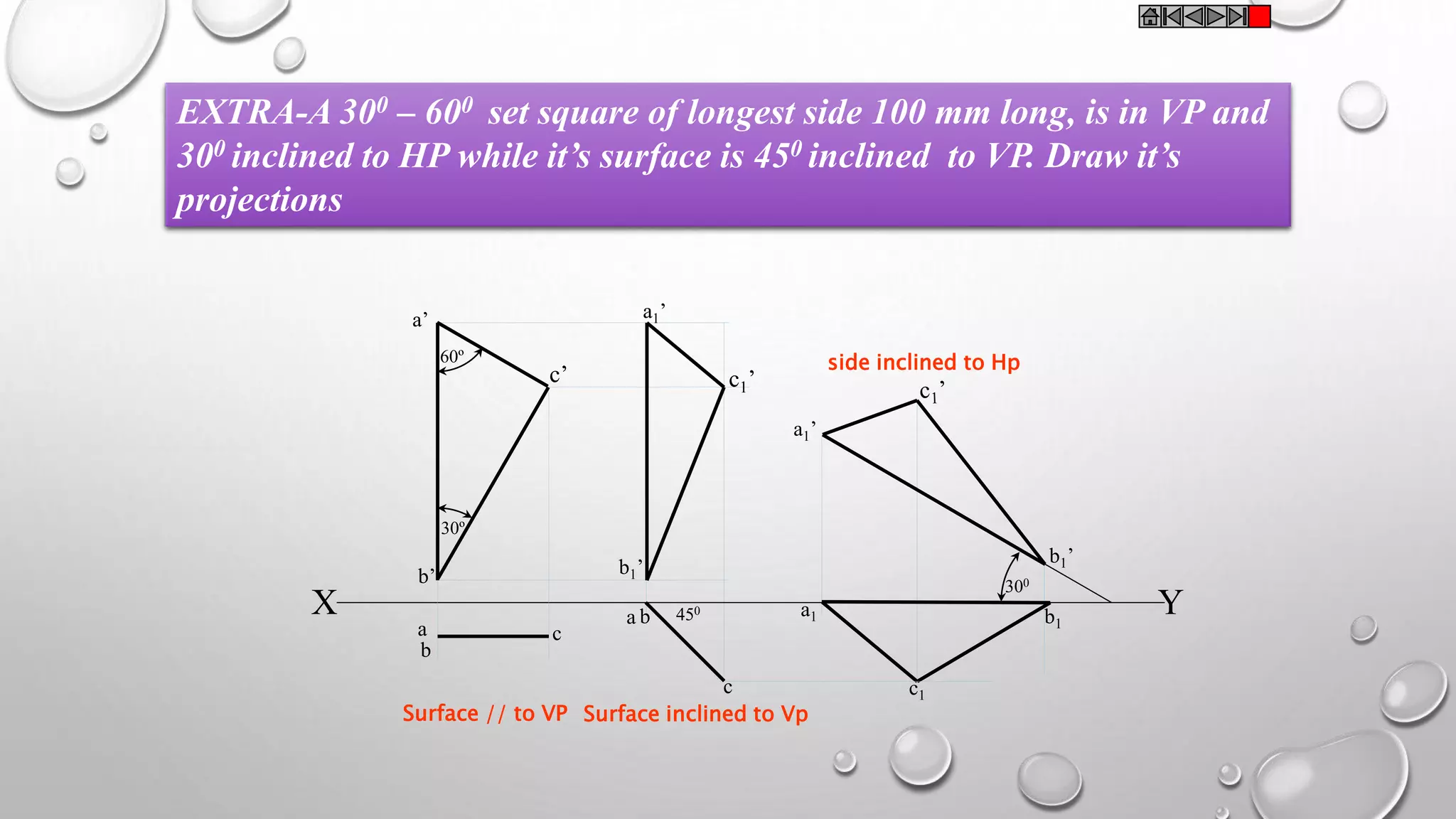
2) Plane figures can have their surface parallel or inclined to the horizontal or vertical planes, and edges parallel or inclined to the other reference plane. The document demonstrates solving problems through 3 steps of initial positioning, surface inclination, and edge inclination.
3) Several example problems are worked through step-by-step to show determining the front, top, and side views of planes in different orientations, such as a pentagon inclined to the horizontal plane and a side to the vertical plane