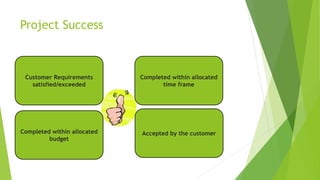
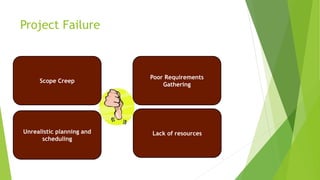
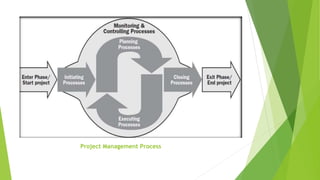
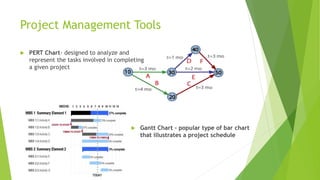
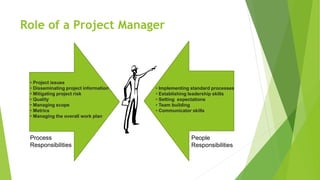
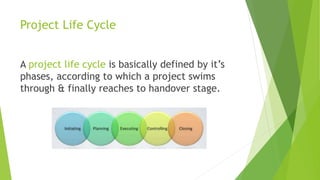
The document discusses the key aspects of project management including the project life cycle and its phases. It describes the five phases of a project life cycle as initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closeout. For each phase, it provides the key outputs and activities. For example, in the planning phase the outputs include creating a work breakdown structure, developing schedules, and determining roles and responsibilities. The document also covers other areas such as what is a project, factors for project success and failure, the role of a project manager, and common project management tools.