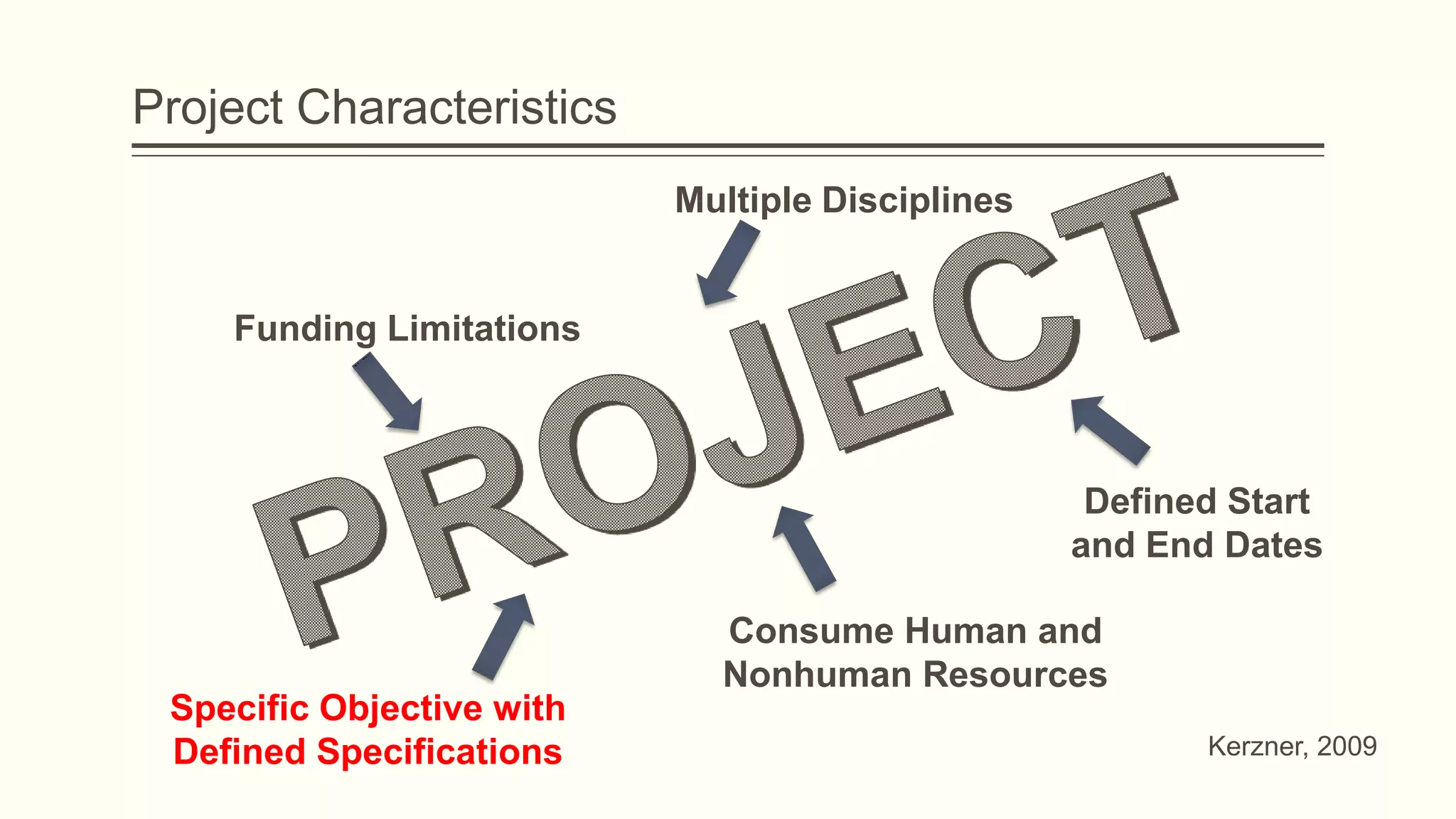
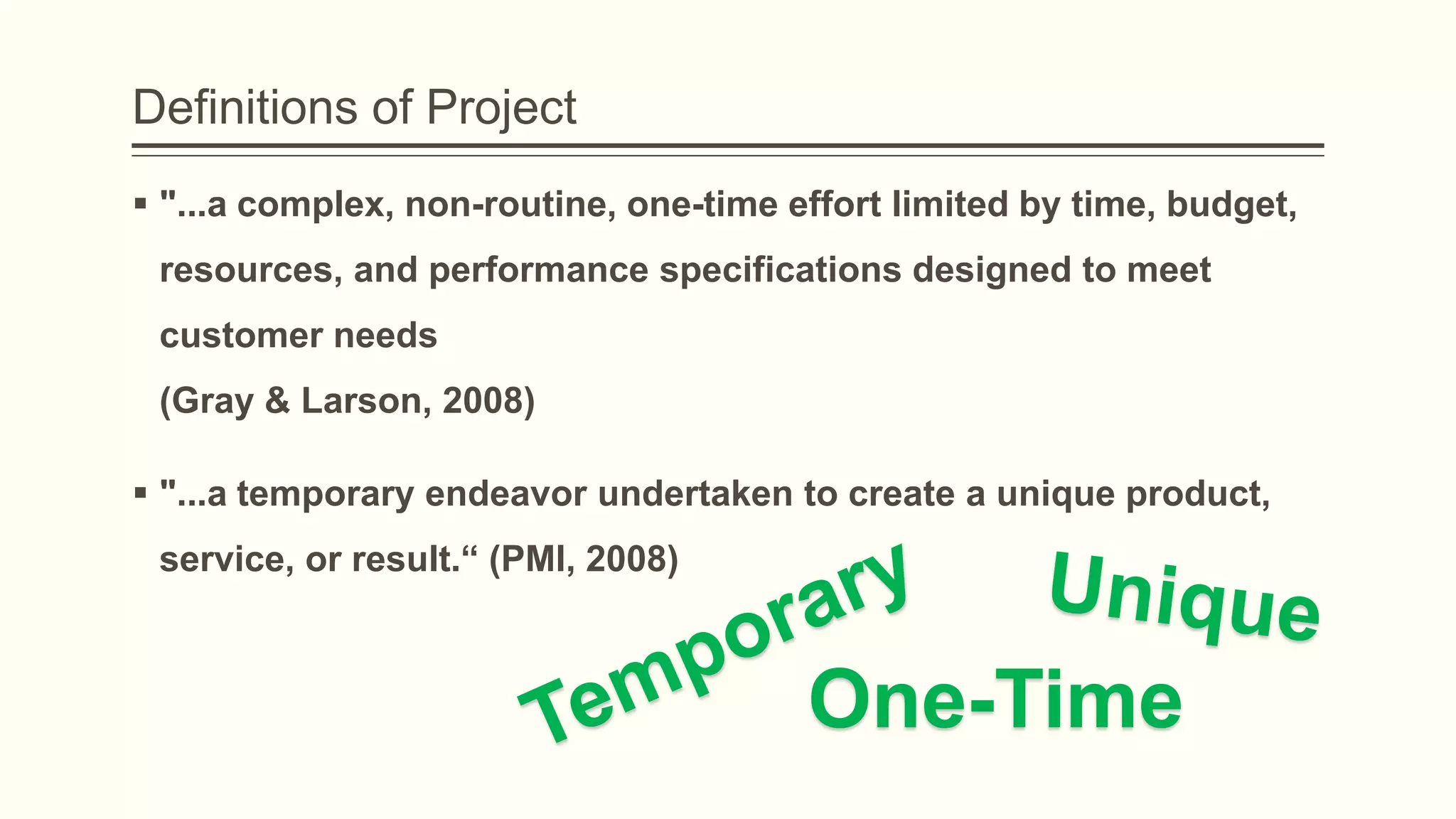
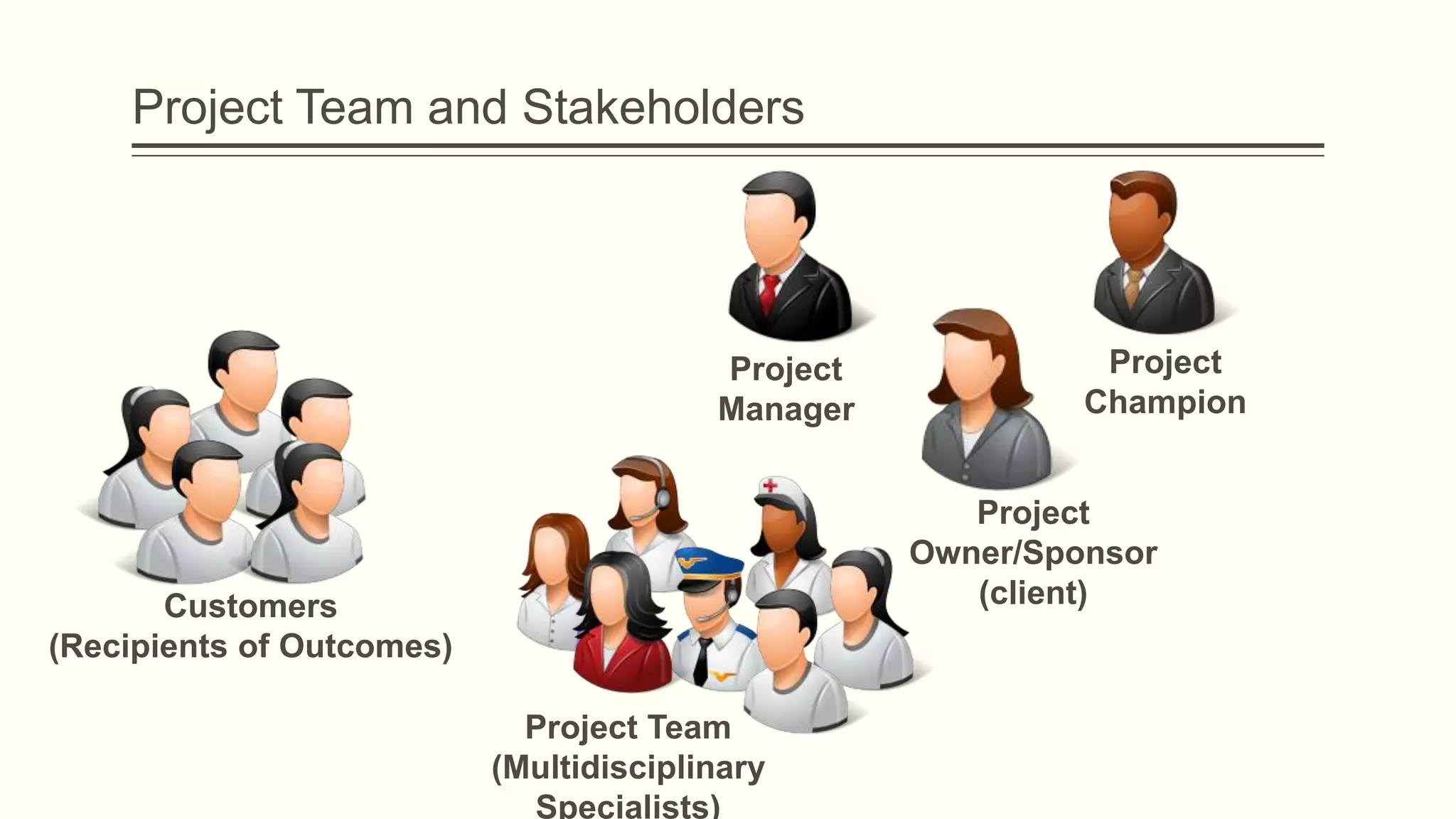
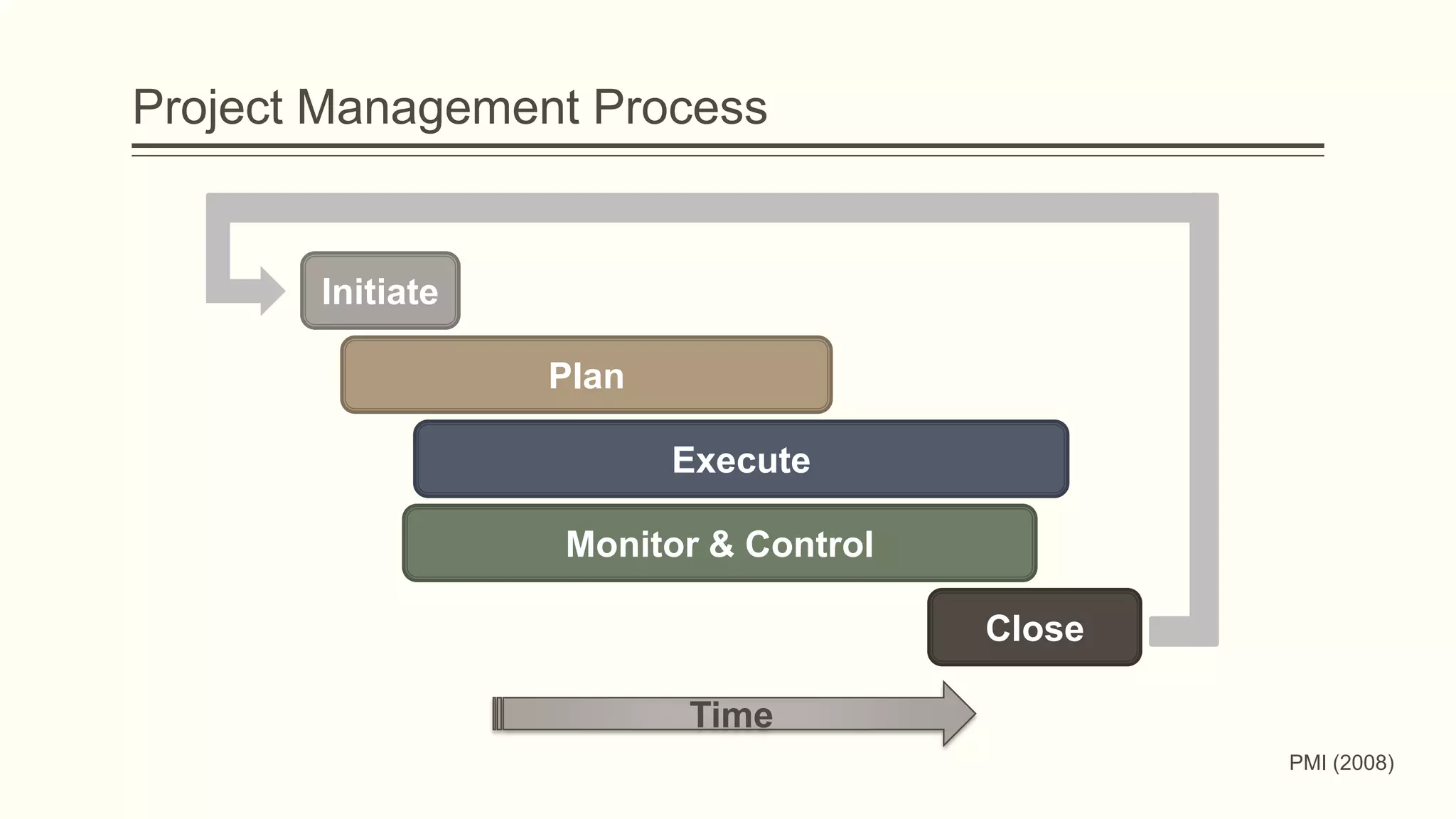
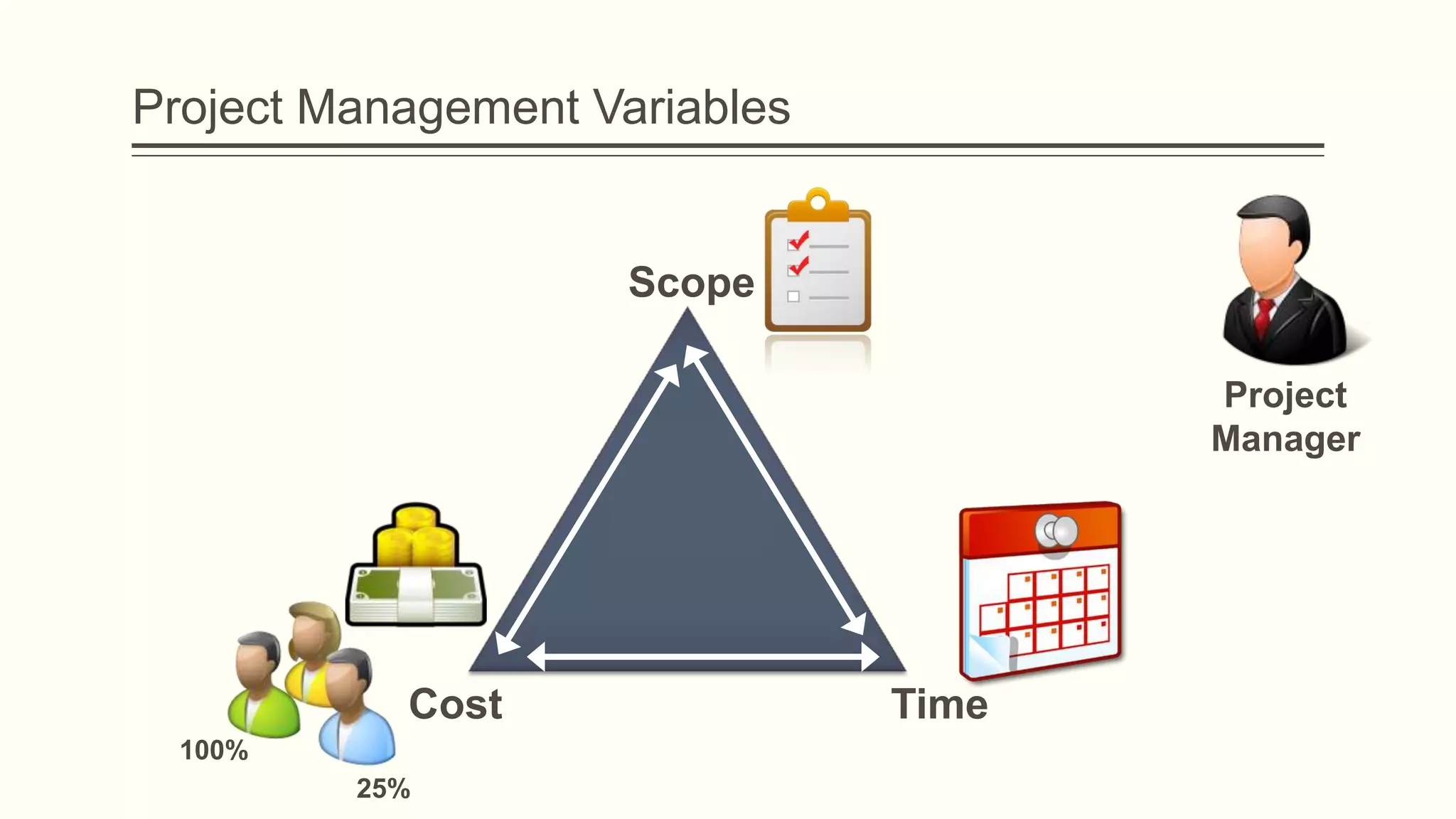
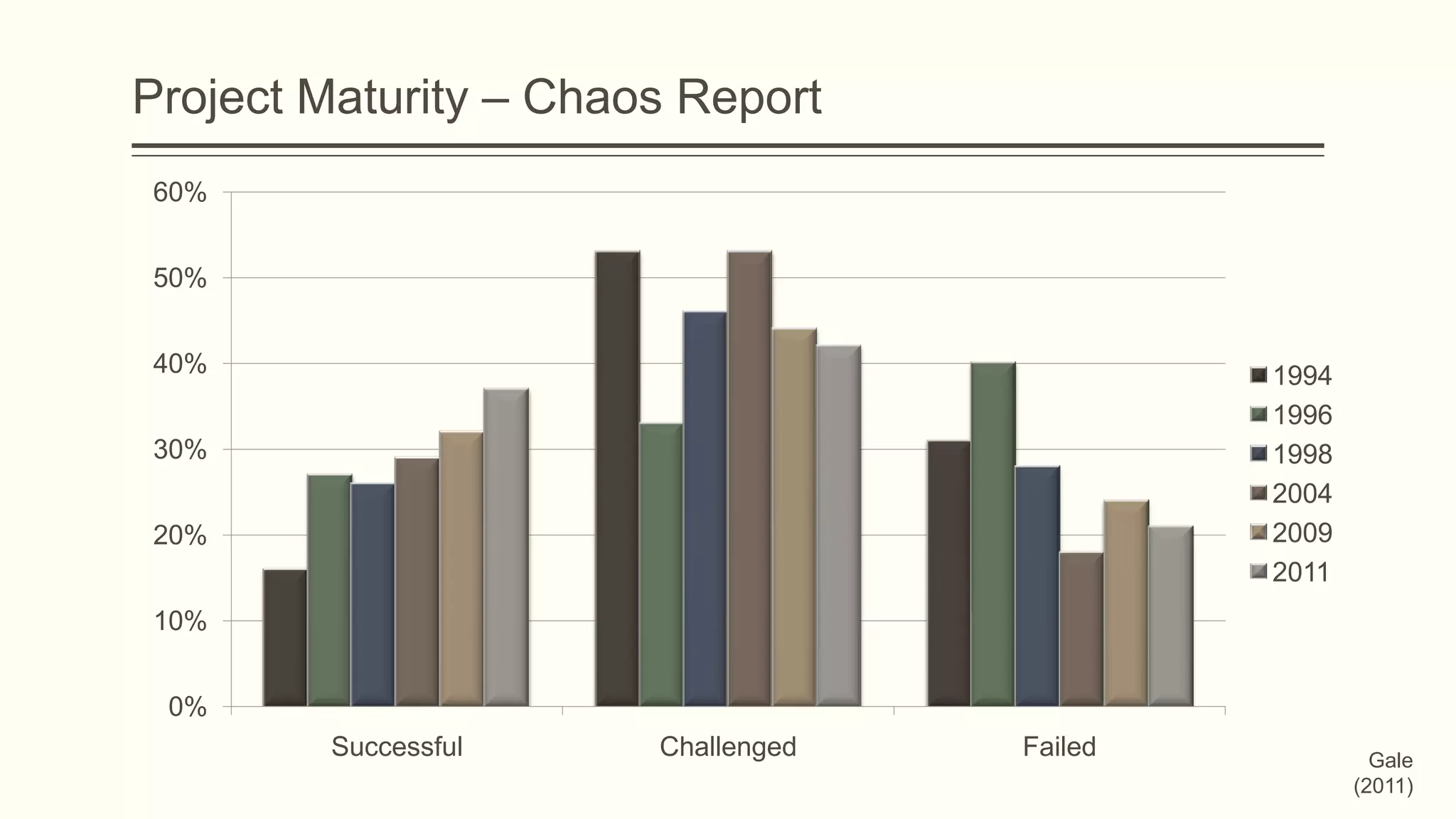
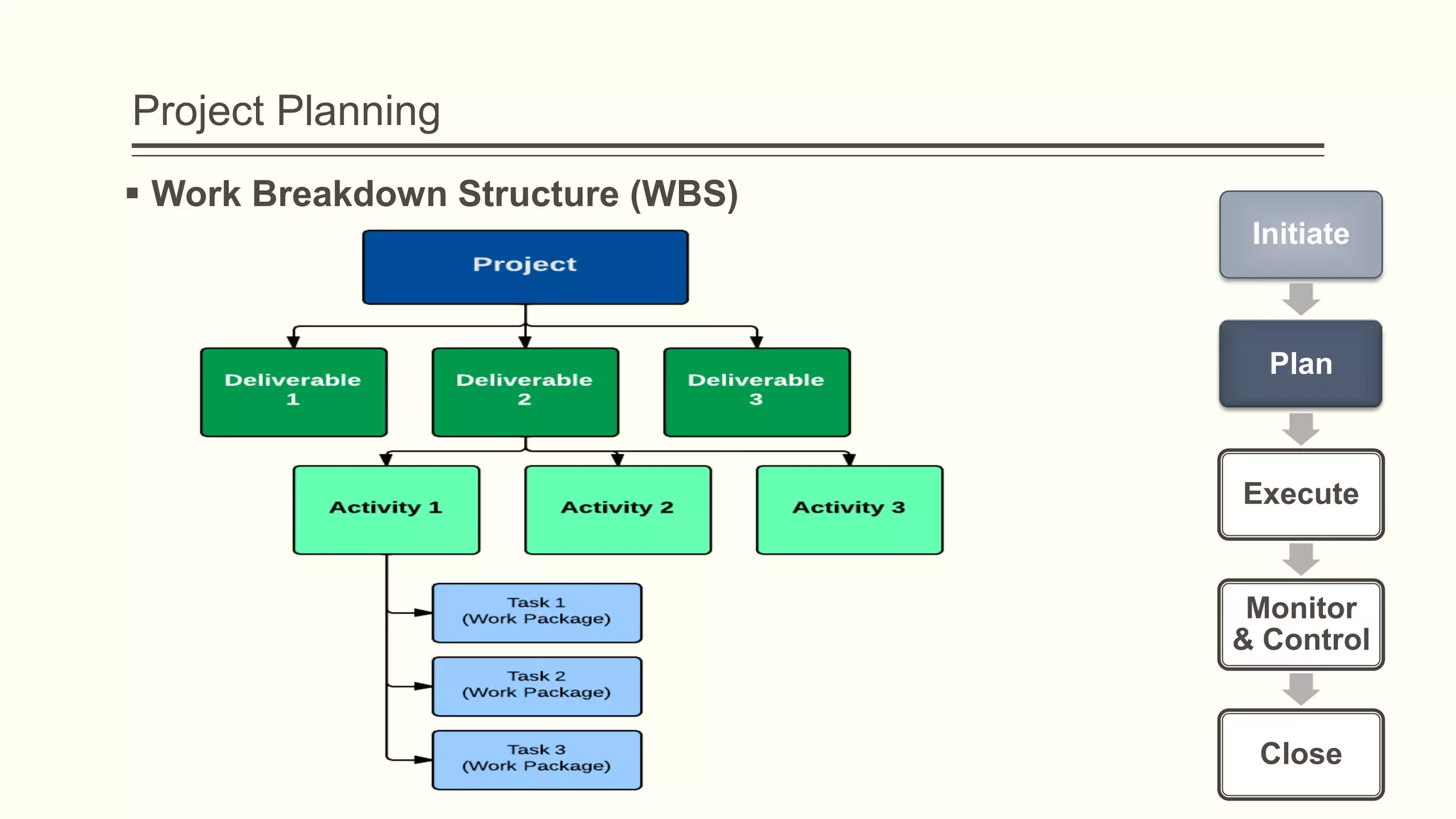
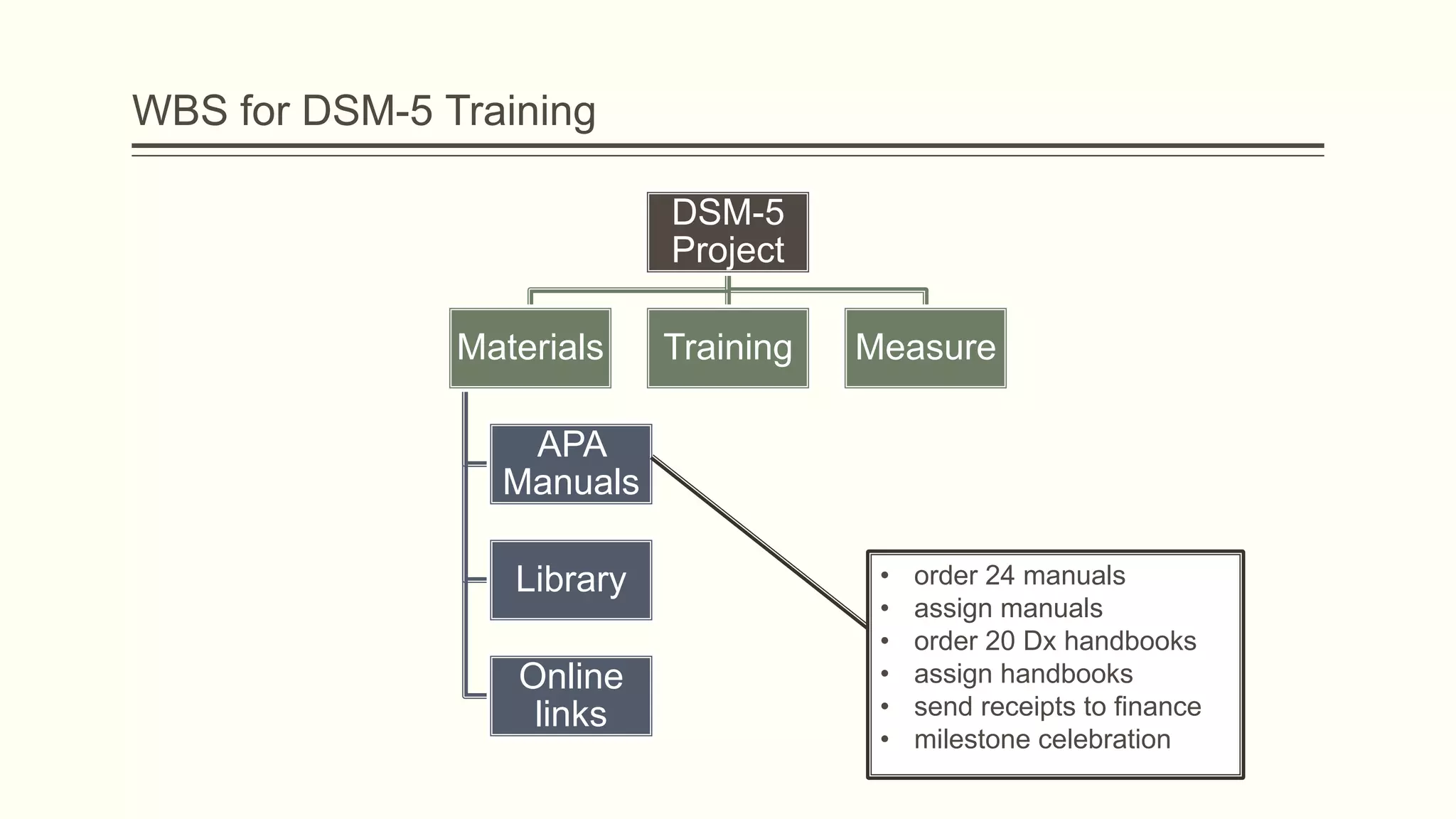
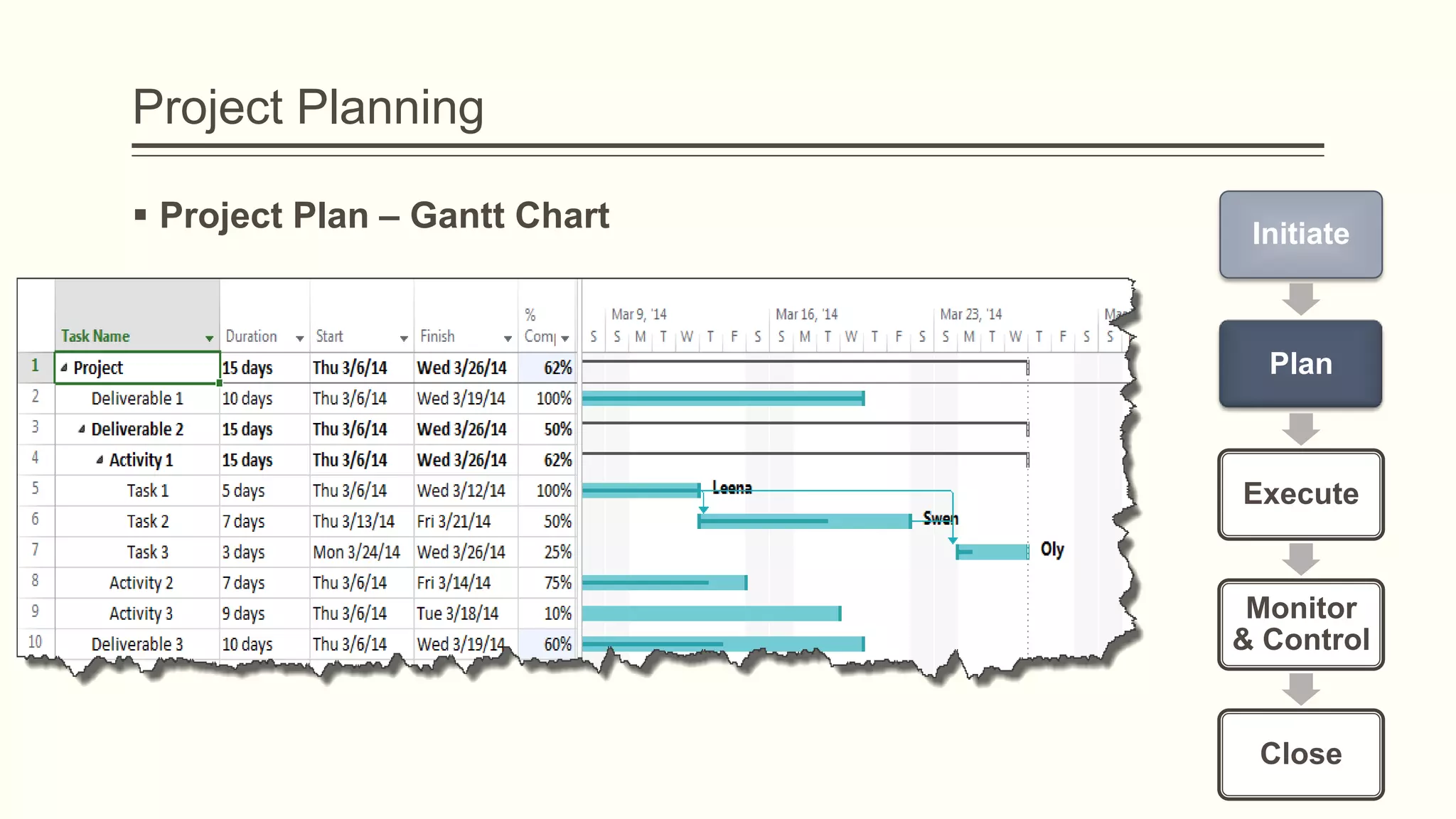
The document outlines the principles and practices of project management specifically tailored for health and human services. It addresses the importance of defining project objectives, the management processes involved, common causes of project failure, and best practices for successful project execution. Additionally, it includes a case study on developing a training program for mental health providers using DSM-5 diagnostic codes, detailing project planning, execution, monitoring, and closing phases.