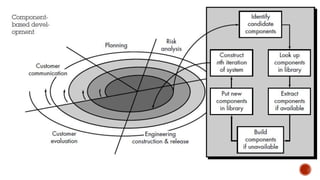
The document discusses several software development process models:
- The Waterfall model is a linear sequential model where each phase must be completed before the next begins. It works best for small, well-defined projects.
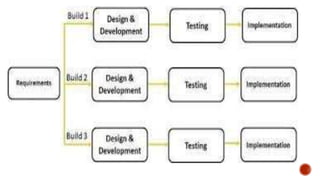
- The Incremental model divides requirements into builds that each pass through phases of requirements, design, implementation, and testing in an iterative manner.
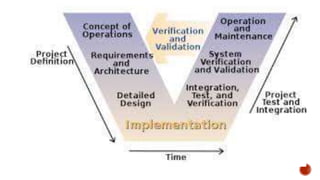
- Specialized models discussed include the Unified Process model, which incorporates iterative and incremental elements, and the Personal Software Process and Team Software Process which emphasize individual and team metrics, planning, and process improvement.