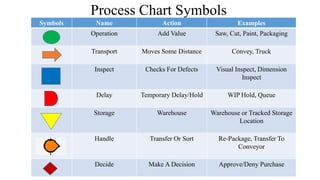
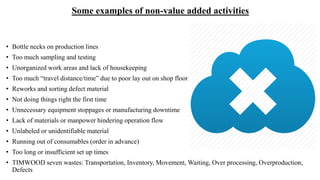
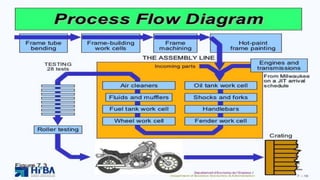
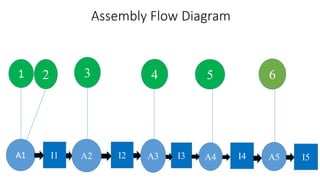
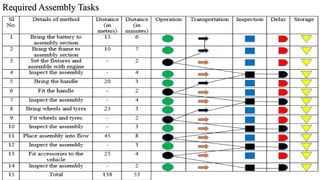
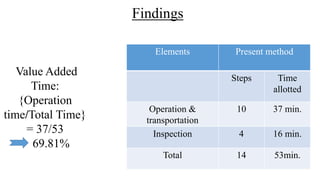
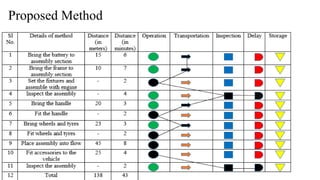
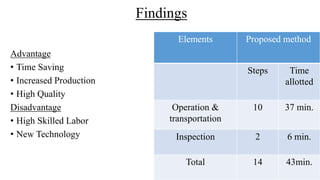
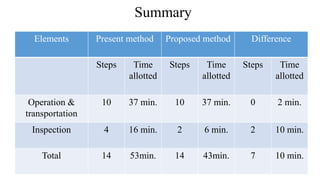
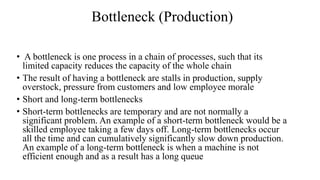
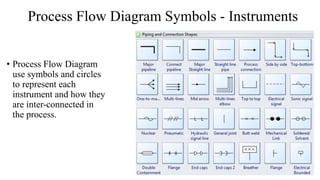
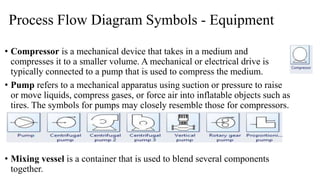
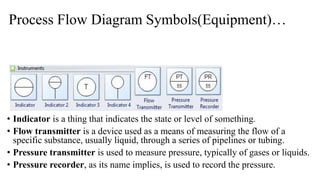
The document discusses the concept of process charts, detailing their purpose as tools for visualizing workflow, identifying areas for improvement, and mapping process components. It outlines various symbols representing actions such as operations, transportation, inspection, delays, and storage, as well as differentiating between value-added and non-value-added activities. Additionally, it covers bottlenecks in production, manufacturing throughput time, and introduces process flow diagram symbols for different equipment and instruments involved in industrial processes.