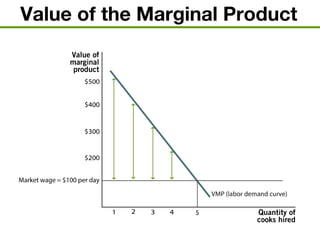
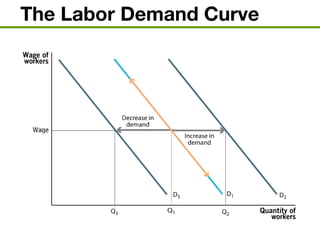
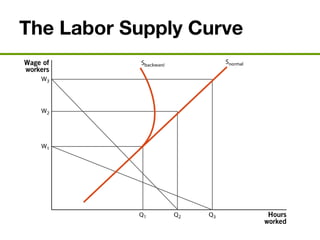
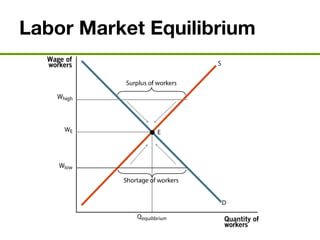
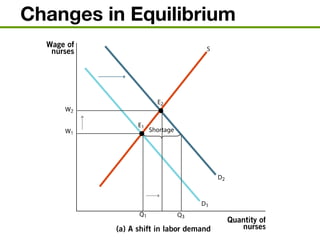
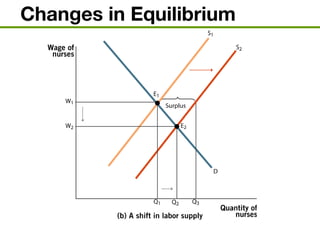
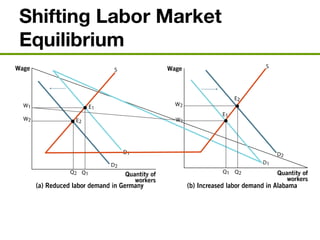
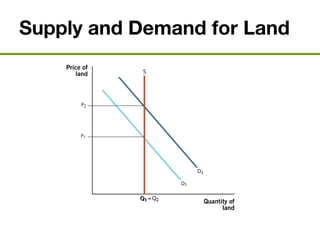
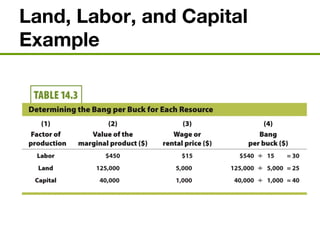
The document discusses the demand and supply of resources, specifically labor, land, and capital. It explains that the demand for labor is derived from the demand for the output that labor produces. Firms demand labor up to the point where the value of the marginal product of an additional worker equals the wage. The supply of labor depends on the wage rate and the labor-leisure tradeoff. The labor market reaches equilibrium when the quantity demanded of labor equals the quantity supplied at the prevailing wage. Outsourcing can lower costs for firms but may reduce wages or employment for some domestic workers in the short run. A monopsony gives the single buyer of labor the ability to leverage market power to lower wages.