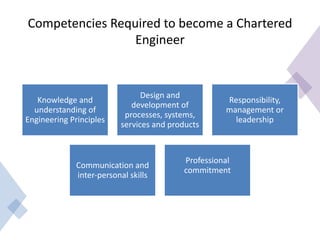
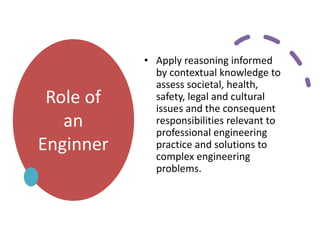
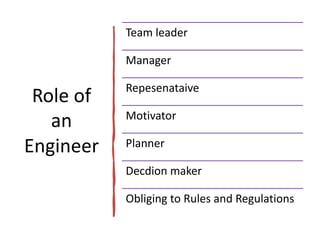
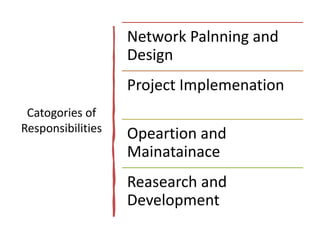
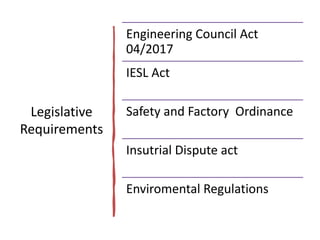
The document outlines the role and responsibilities of chartered engineers, comparing them to scientists and emphasizing the importance of engineering in society. It discusses the necessary competencies, ethical obligations, and social responsibilities of engineers, including public safety and sustainable practices. Additionally, it highlights the professional conduct expected from engineers and their various job functions within the engineering field.