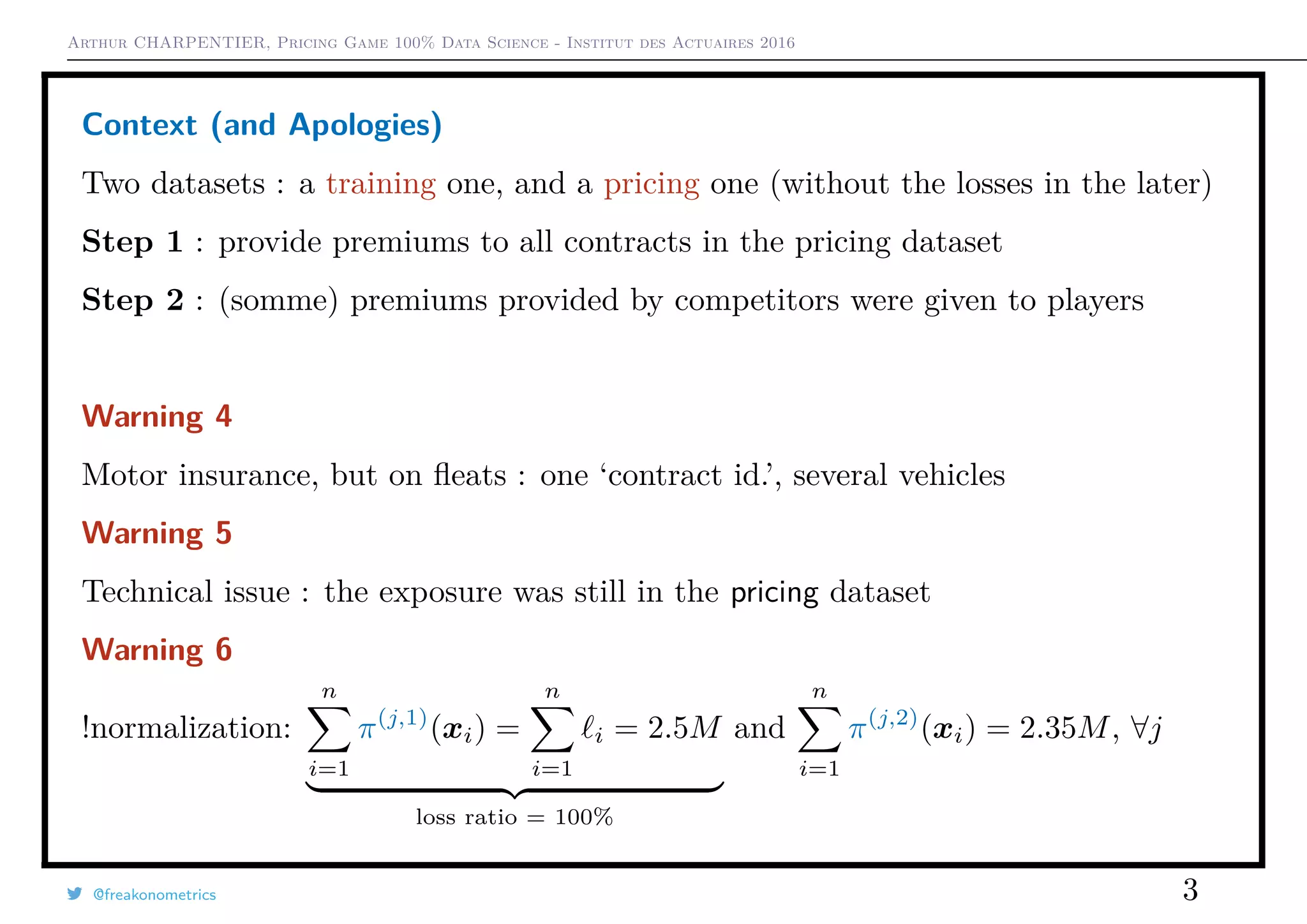
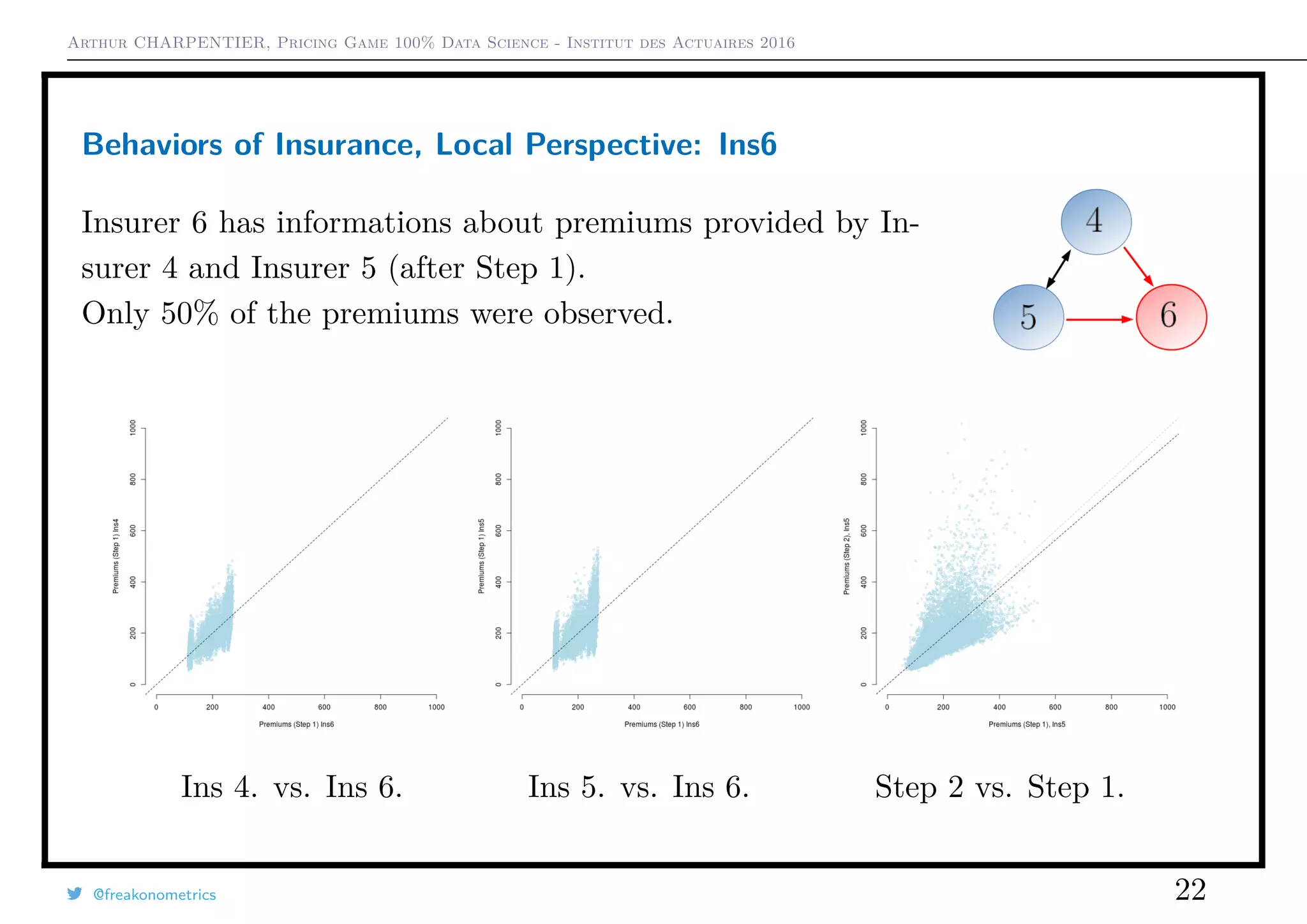
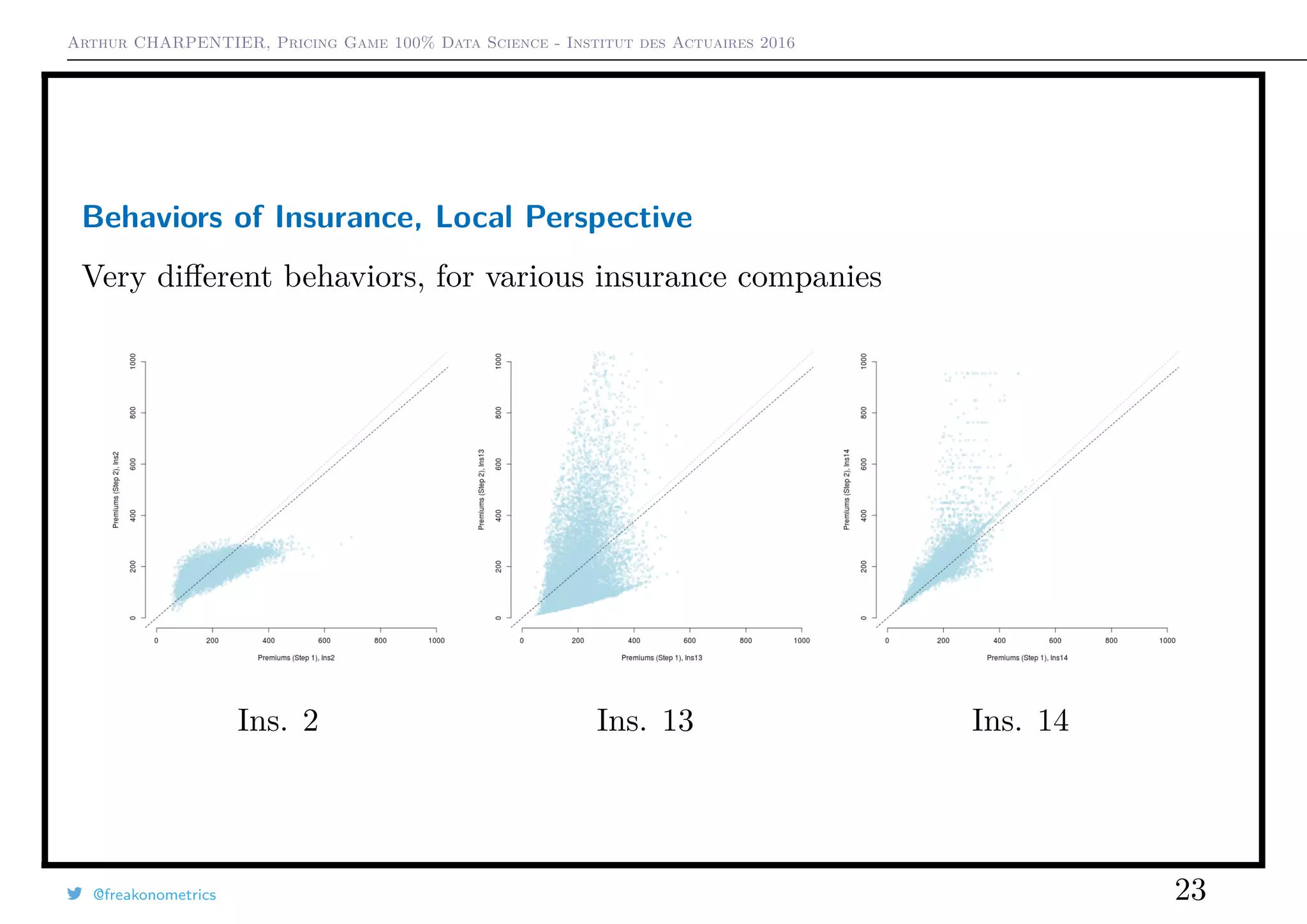
This document summarizes the results of an actuarial pricing game simulation with multiple insurance companies. It finds that:
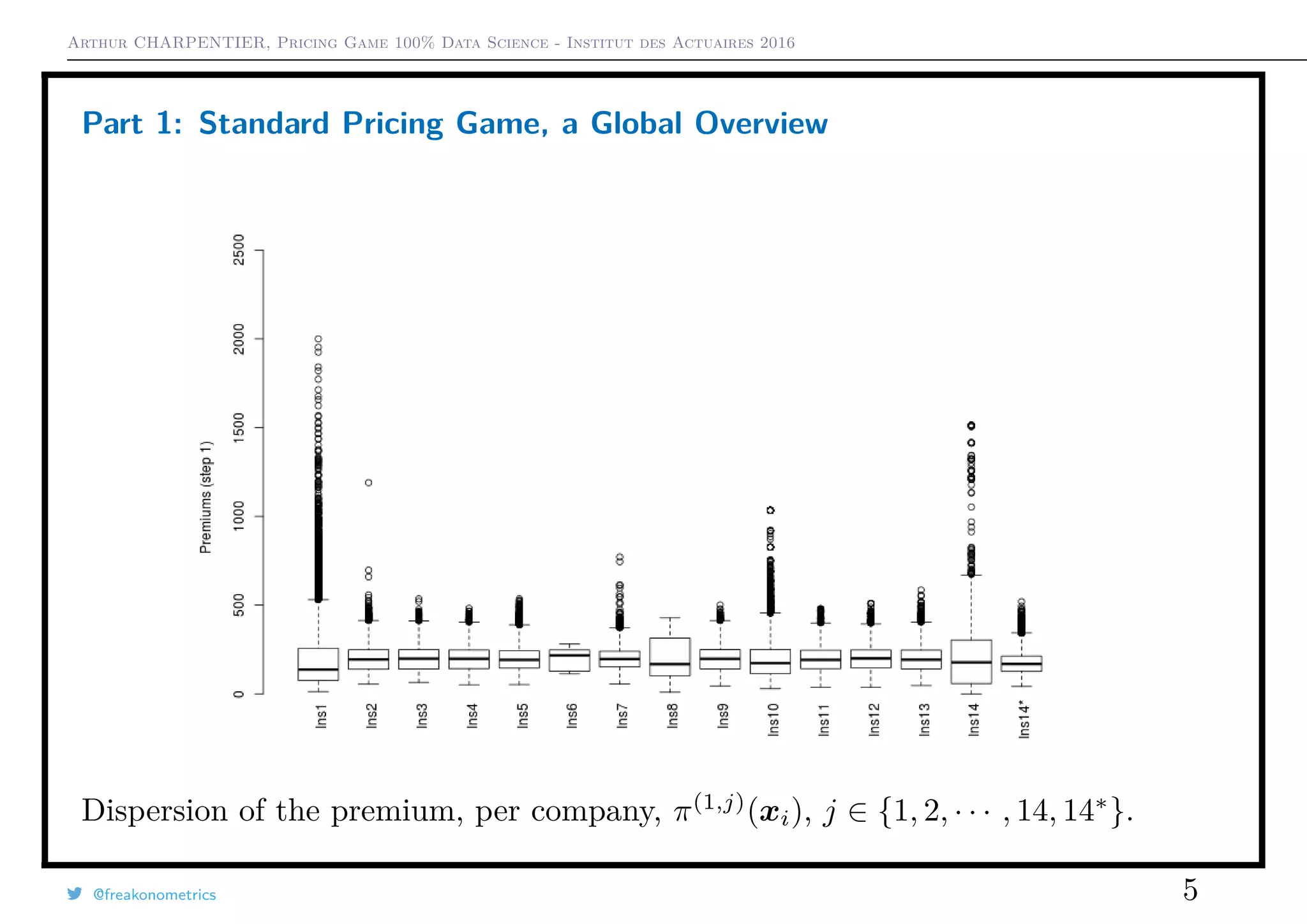
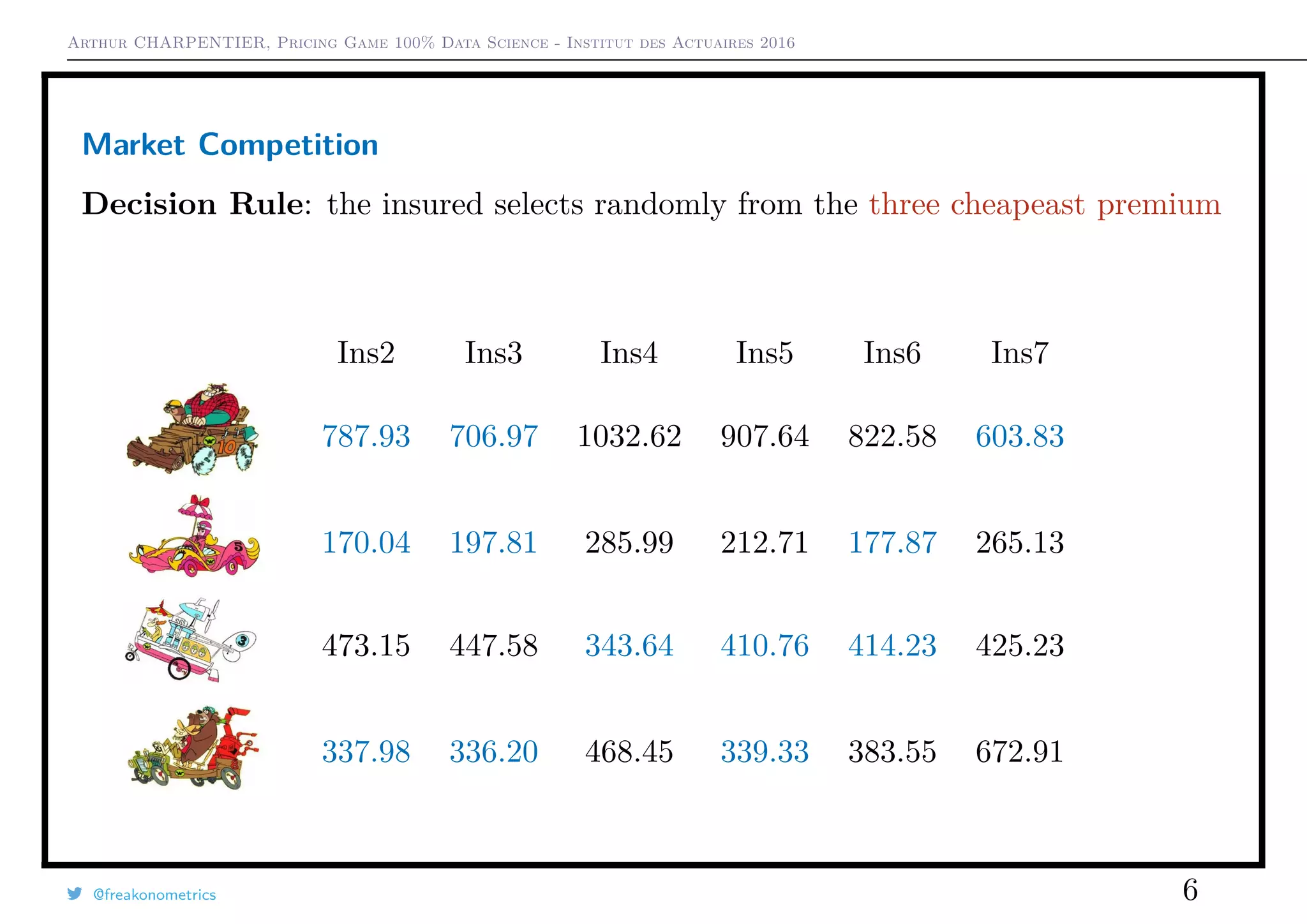
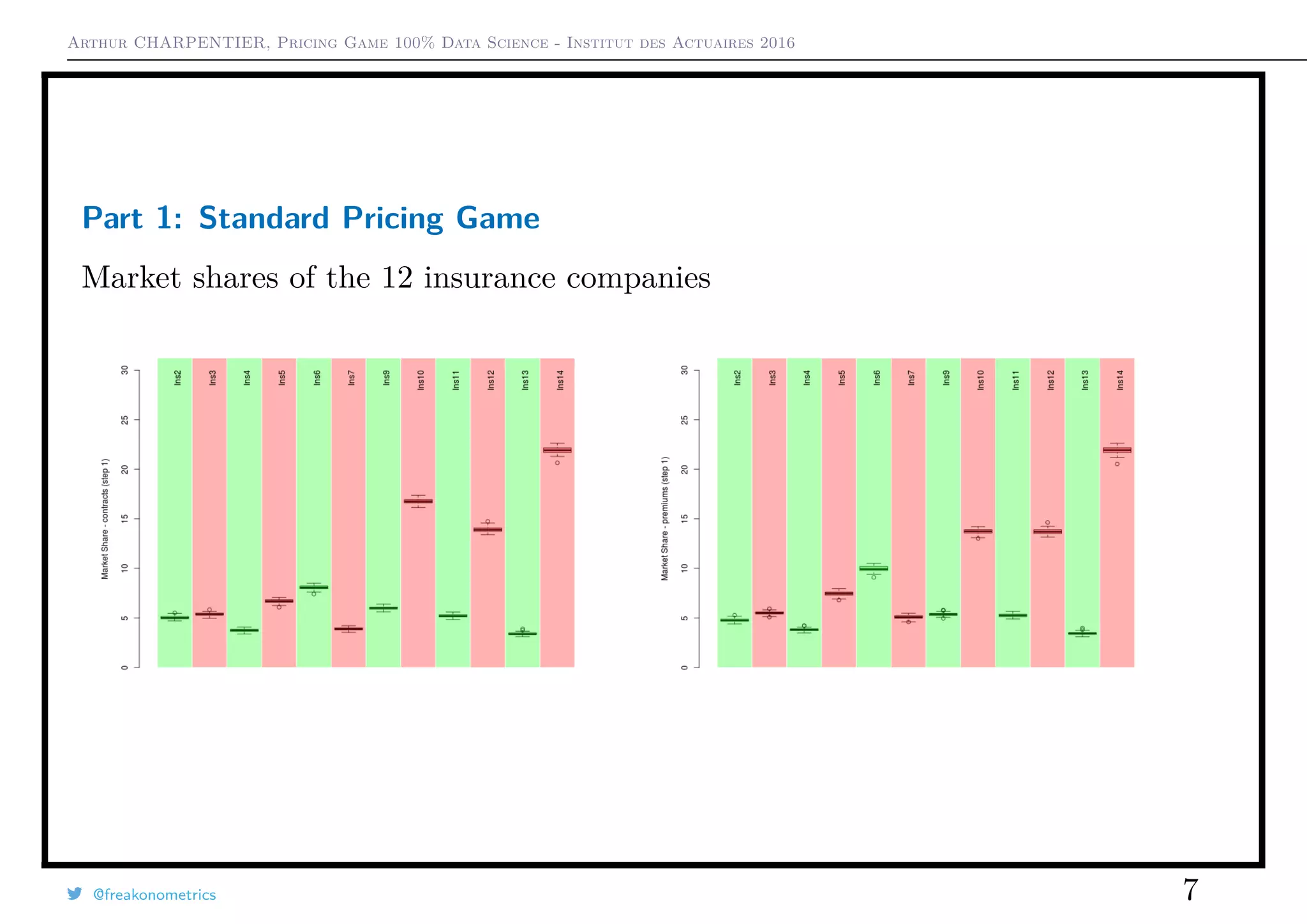
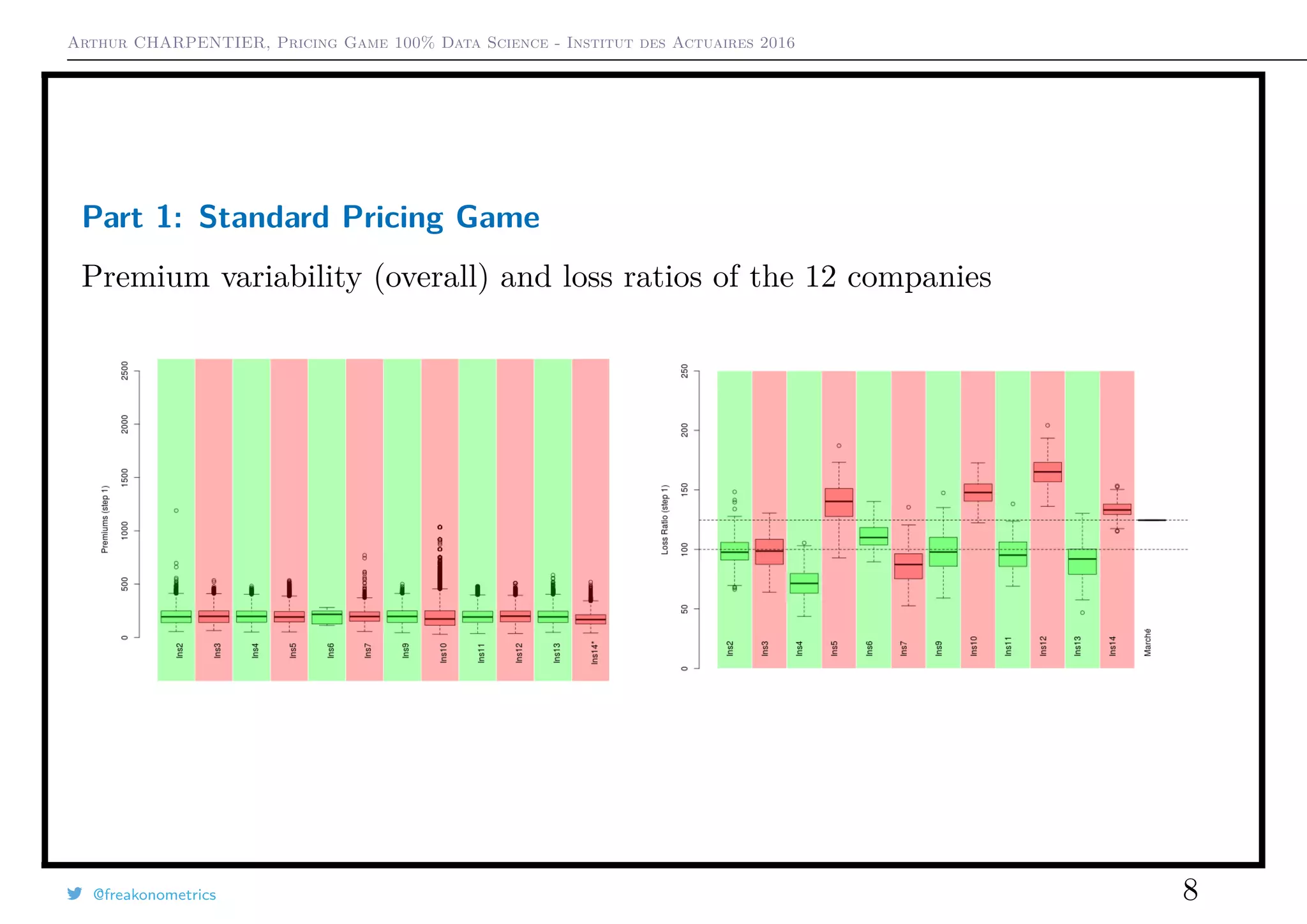
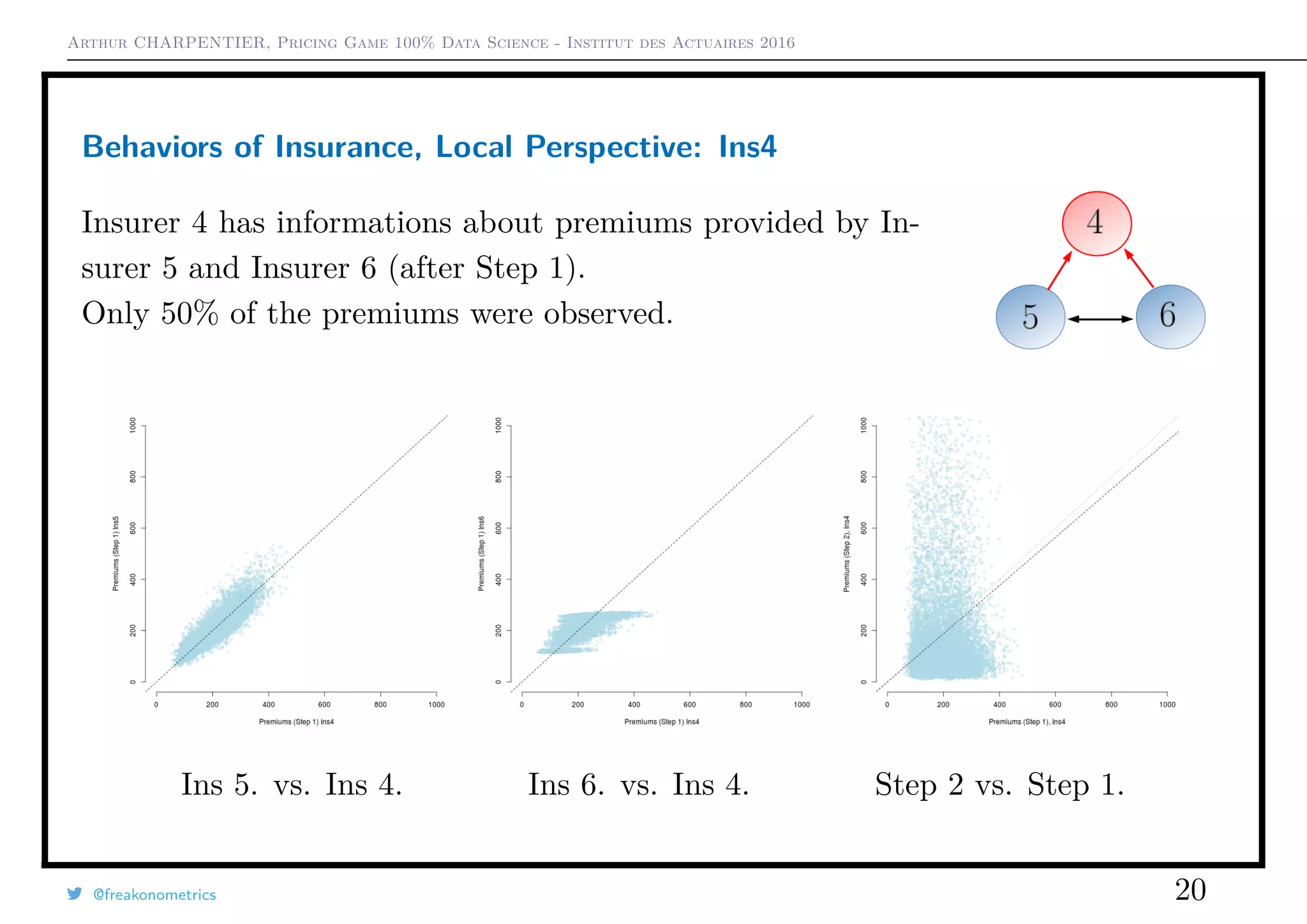
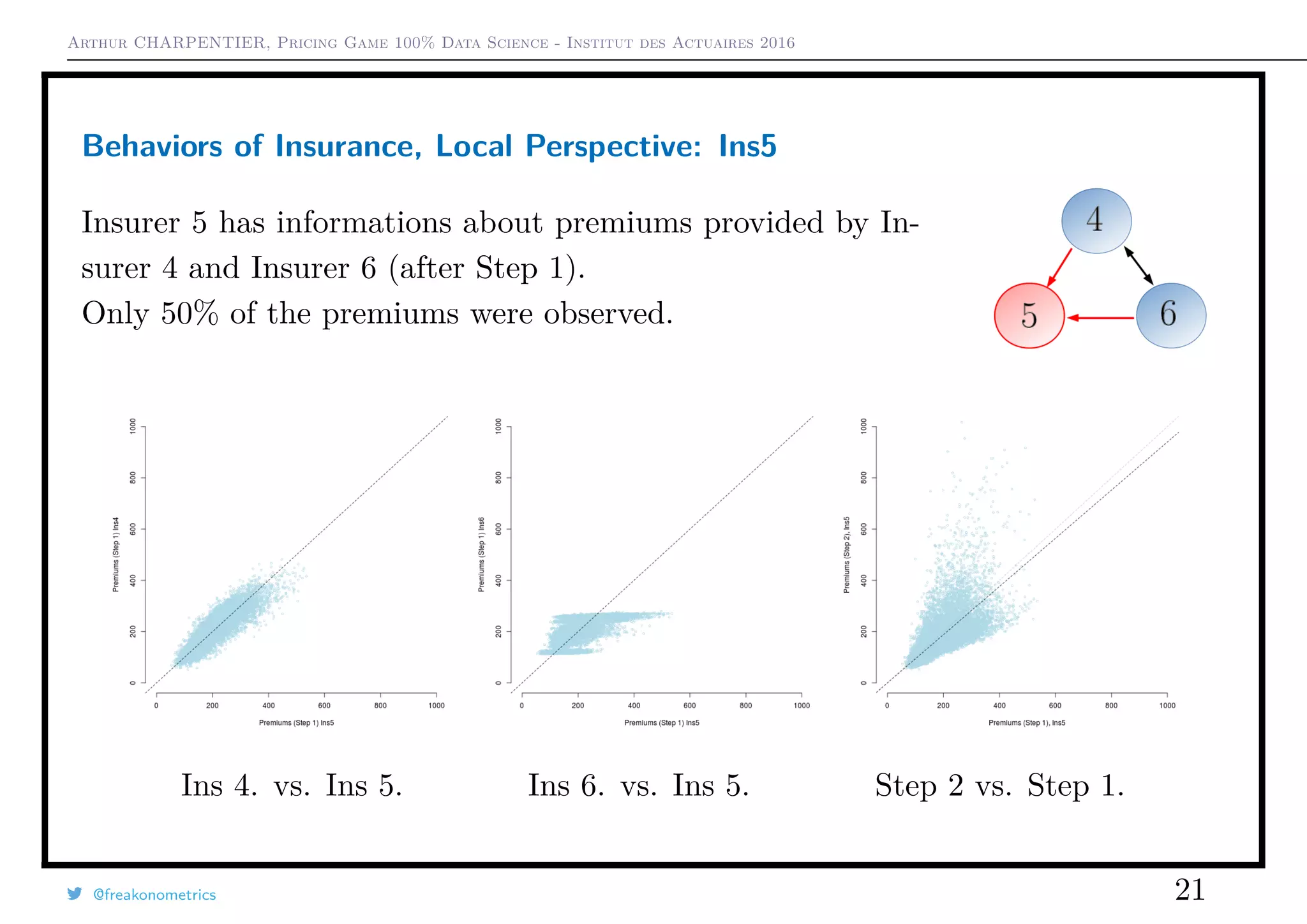
1) In the initial game with all companies, premium levels varied widely between companies and market shares shifted significantly.
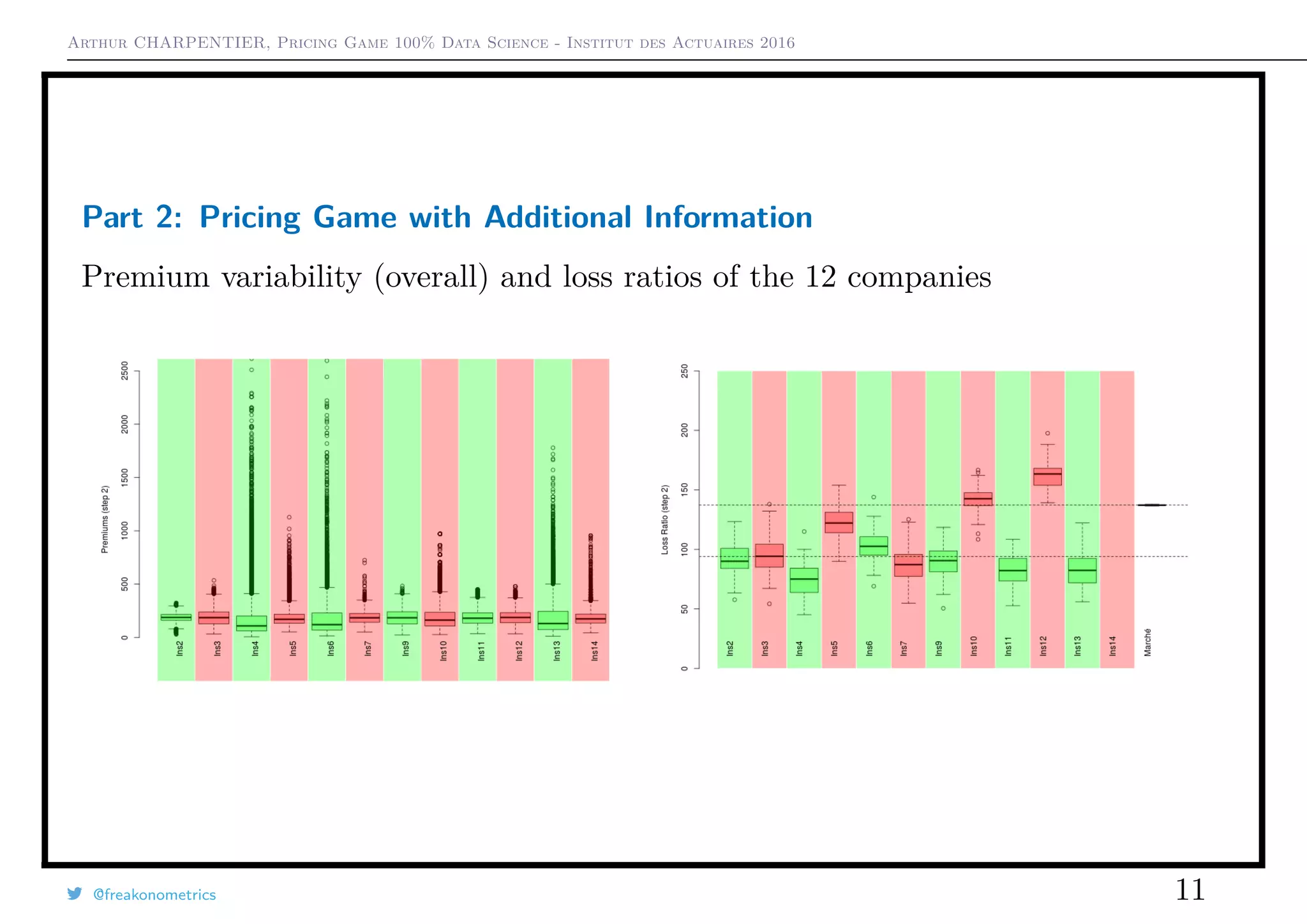
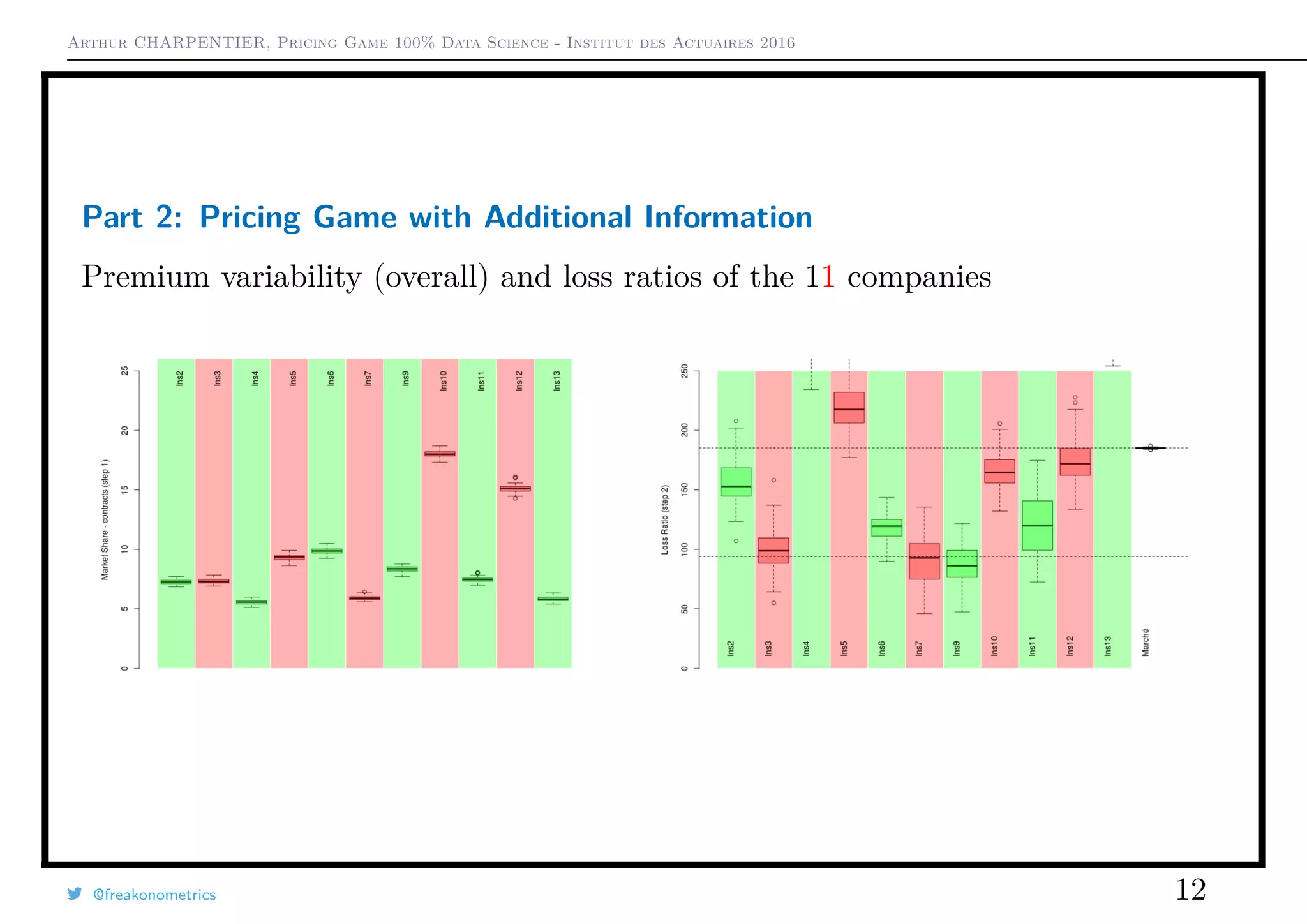
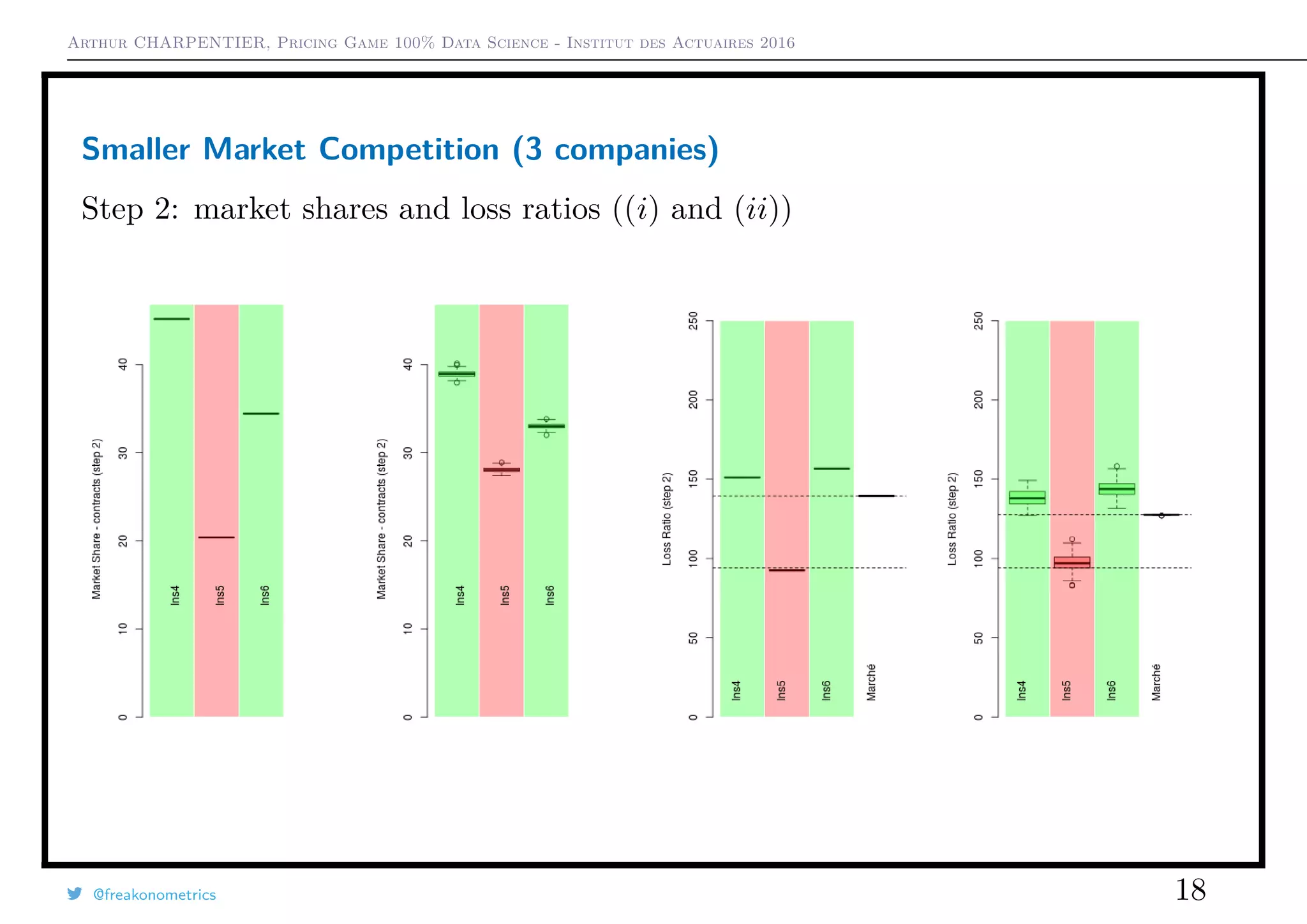
2) When additional data was provided in a second round, premium variability decreased but loss ratios were similar.
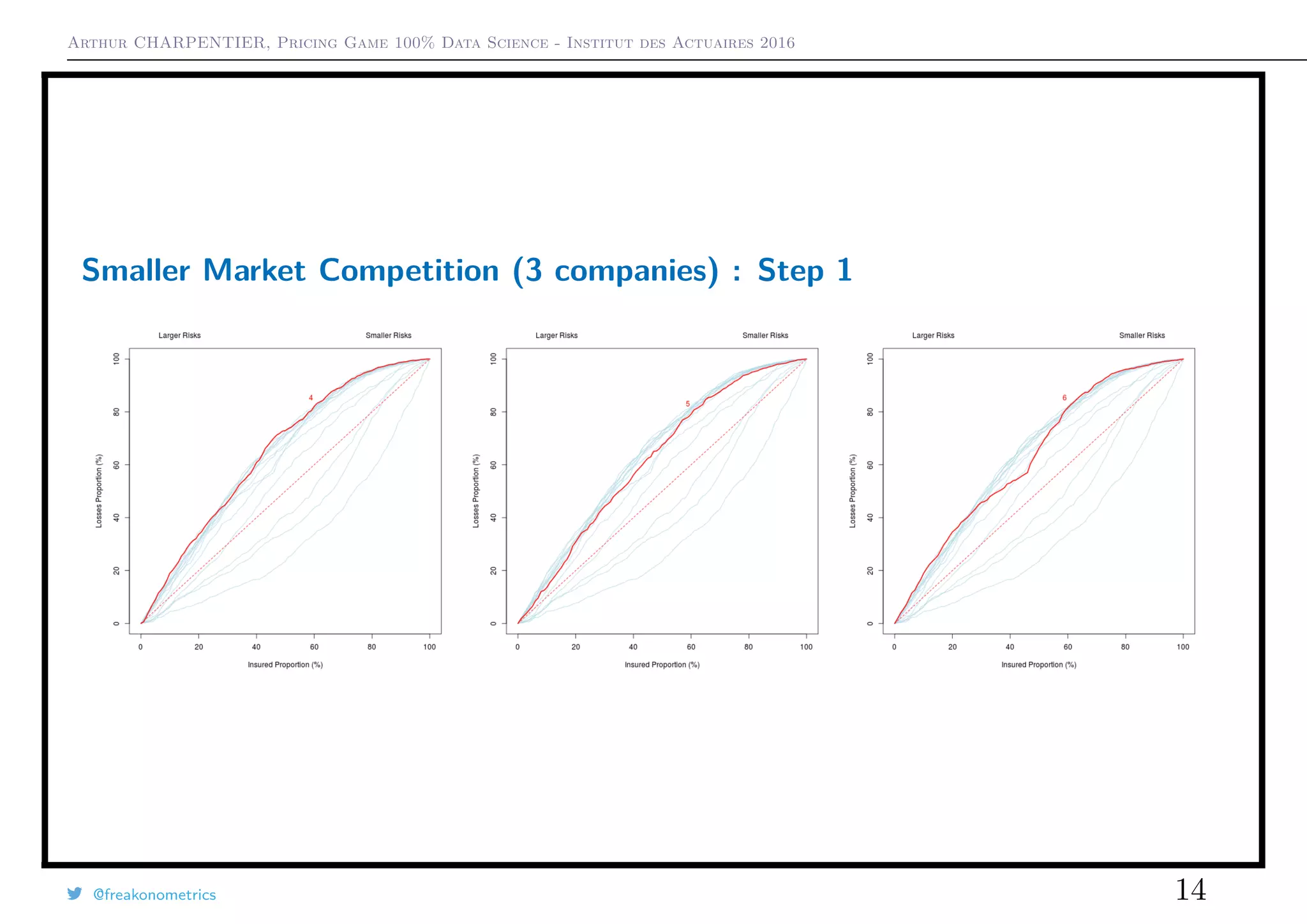
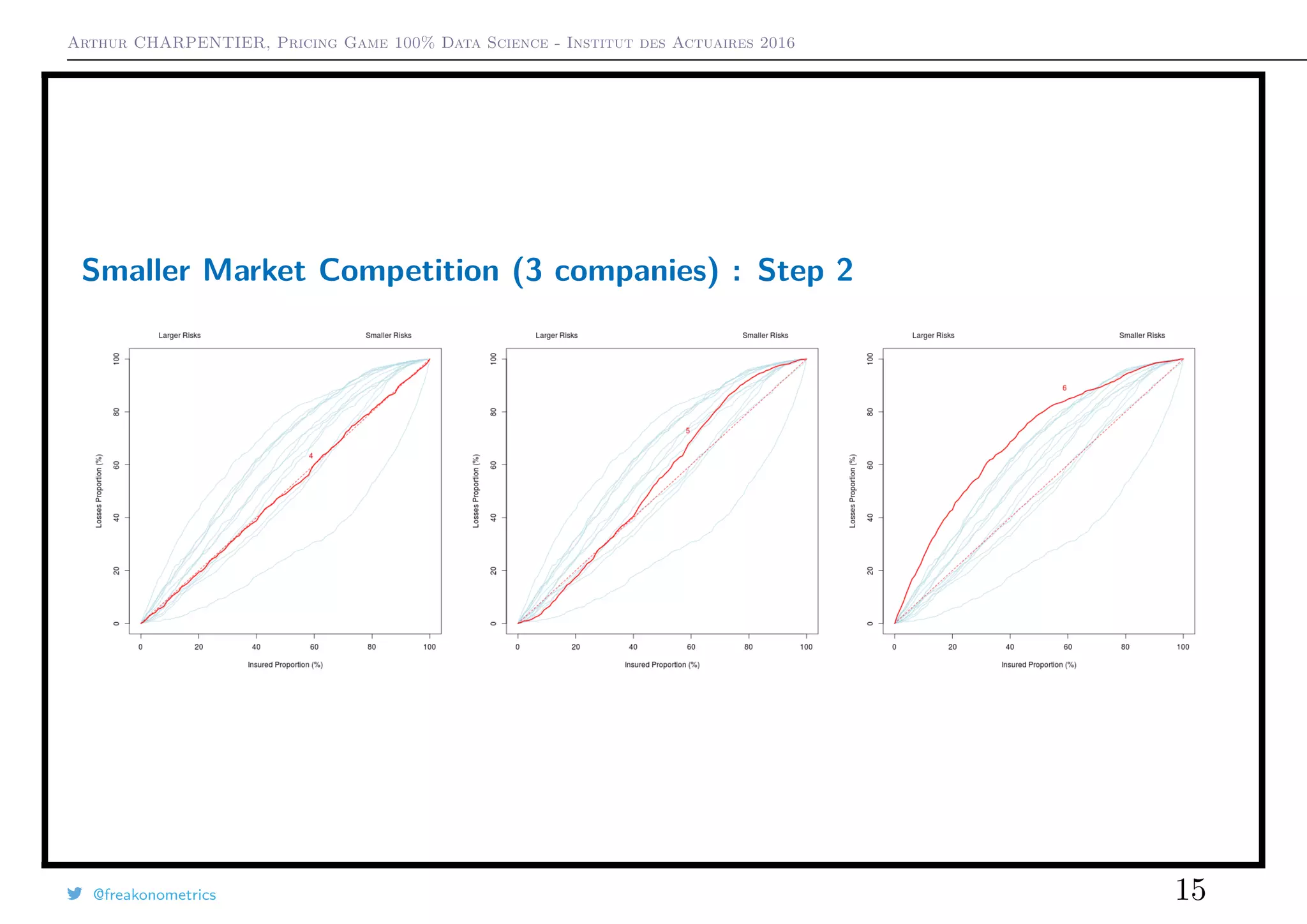
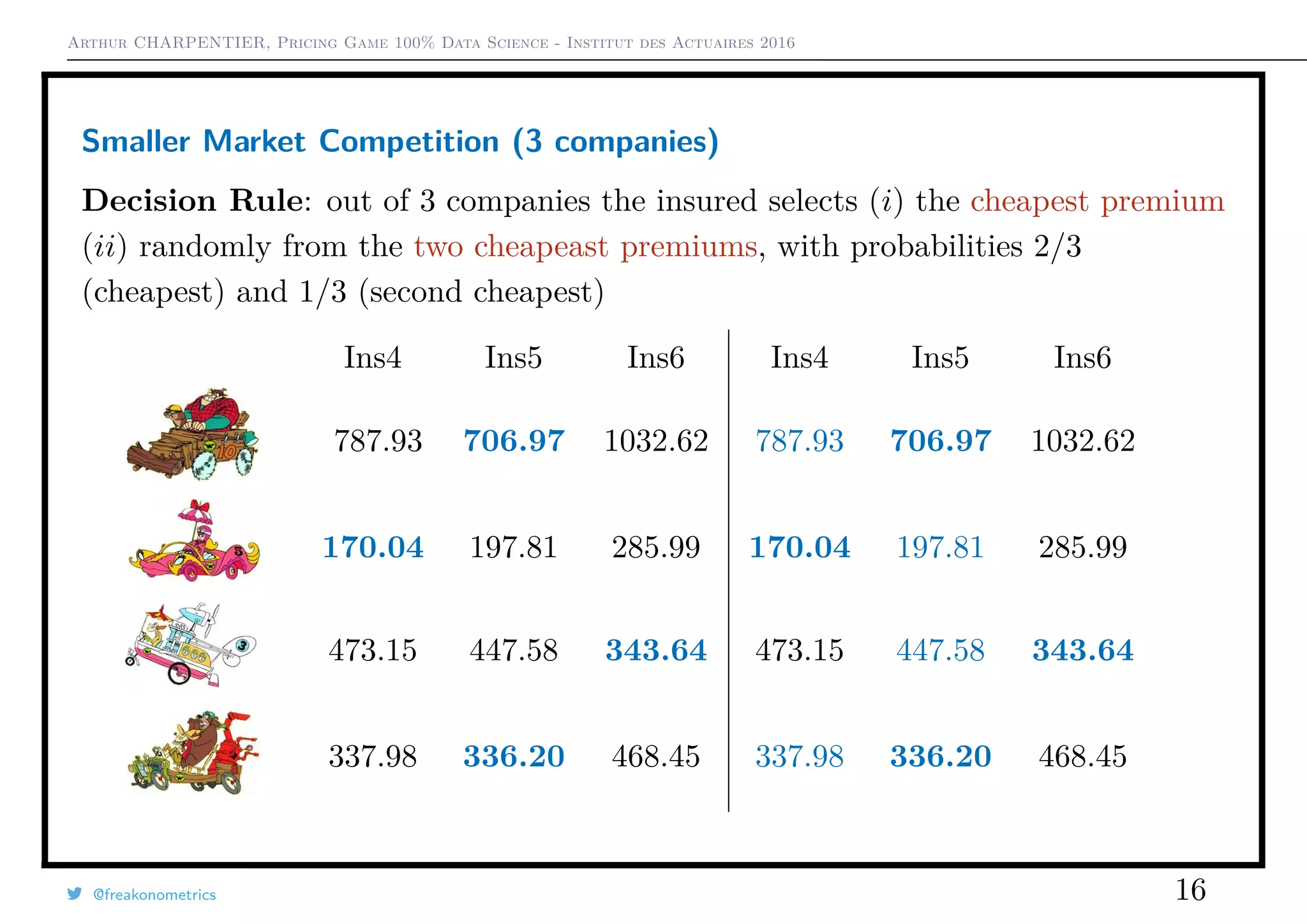
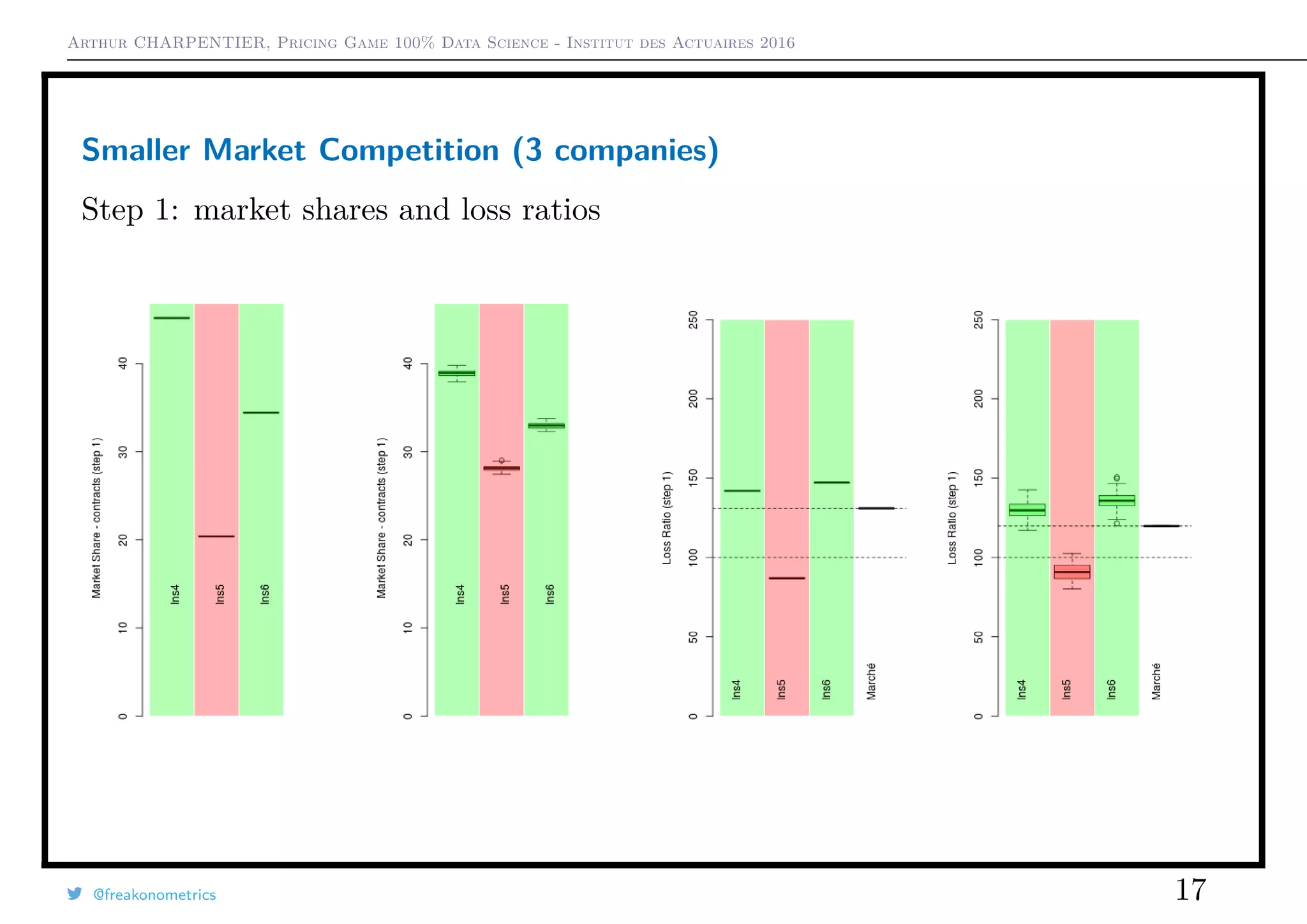
3) A smaller game with just three companies showed that the choice of pricing strategy (always cheapest vs. random between cheapest two) impacted market shares and loss ratios.