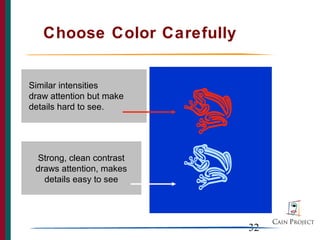
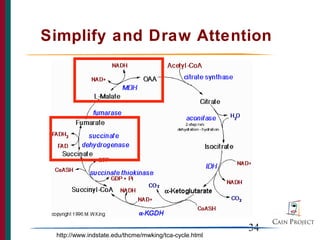
The document provides instructions for using PowerPoint to design effective presentations, including how to plan content by considering the audience, organize slides in a logical manner, display text and visuals clearly, and use animation purposefully. It includes examples and prompts for the reader to perform actions within PowerPoint, such as changing fonts, adding bullets, and creating basic animations.