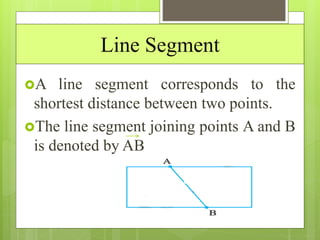
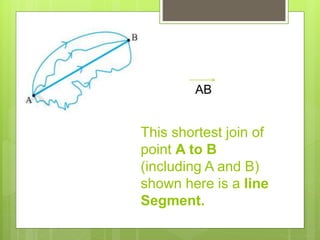
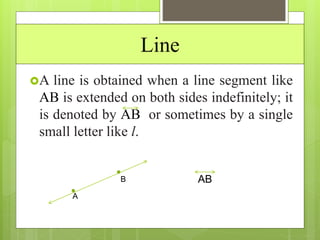
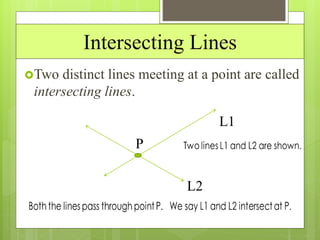
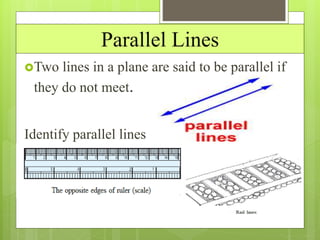
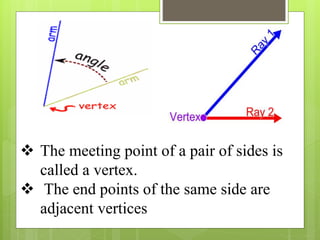
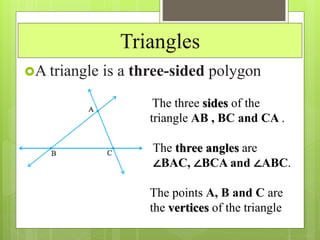
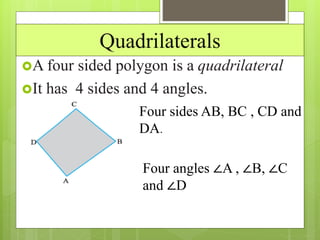
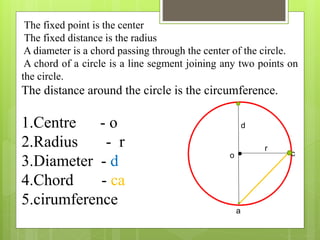
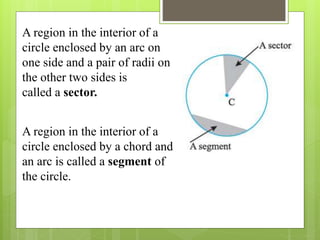
This document provides an overview of basic geometric concepts taught in a 6th grade mathematics class. It defines key terms like point, line, line segment, ray, angle, polygons, triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles. The lesson is taught by two teachers, Pooja Bindal and Shalu Verma, aims to help students understand properties of quadrilaterals and distinguish between different types of quadrilaterals and polygons. Examples and diagrams are provided to explain points, lines, angles, triangles, circles and their components. The intended learning outcome is for students to understand these basic geometric concepts and apply their knowledge.