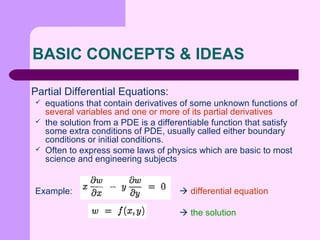
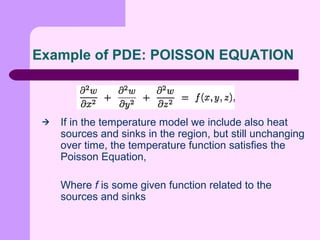
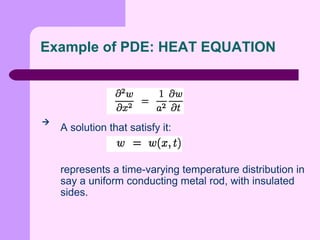
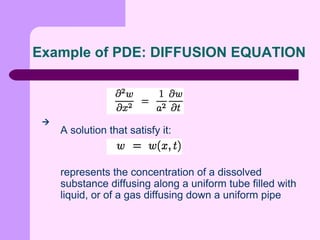
This document provides an introduction to partial differential equations (PDEs). It defines PDEs as equations that contain derivatives of unknown functions of several variables and one or more partial derivatives. The solutions to PDEs are differentiable functions that satisfy boundary or initial conditions. PDEs are often used to express laws of physics. Examples of common PDEs discussed include the Laplace equation, Poisson equation, wave equation, heat equation, and diffusion equation.