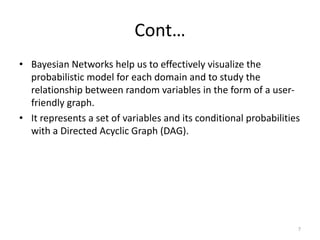
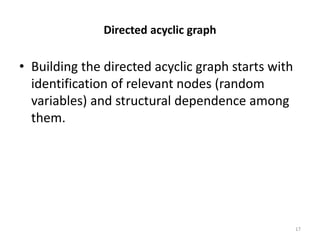
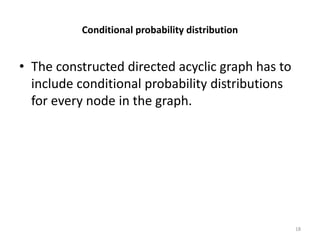
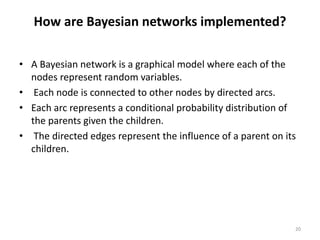
- Bayesian networks are probabilistic graphical models that represent conditional dependencies between random variables through a directed acyclic graph. Each node corresponds to a random variable, and edges represent conditional probabilities.
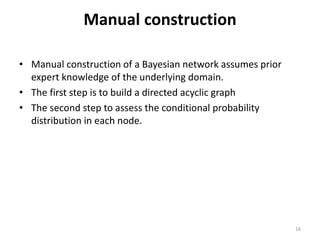
- There are two main ways to build a Bayesian network - manually defining the graph structure and conditional probabilities, or automatically learning the structure from data. Bayesian networks can handle incomplete data and help uncover causal relationships.
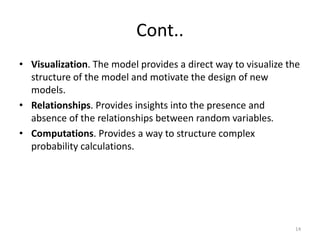
- Bayesian networks have advantages like explaining relationships visually, handling missing data, and combining data with expert knowledge. However, they are difficult to design and don't work as well with high dimensional data. An example shows using disease symptoms to predict disease probabilities.










![Example
24
]
For example, with a given symptom we can predict the
probability of a disease occurring with several other factors
contributing to the disease.
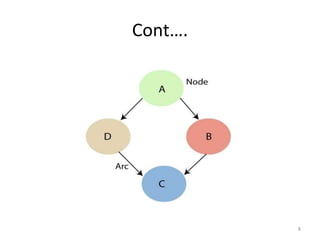
In the below diagram A, B, C and are 3 random variables
represented by nodes given in the network of the graph. To
node B is its parent node and C and A is its child node](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-220828083812-f6e7fd9f/85/Presentation1-pptx-24-320.jpg)

