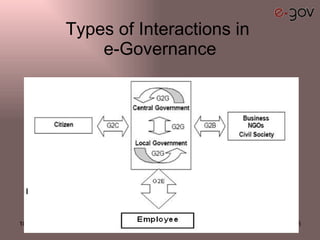
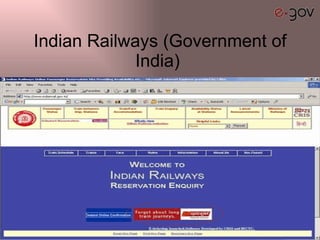
The document discusses e-governance and its components, types of interactions, benefits and challenges in India. It outlines some key Indian e-governance initiatives including customs and excise, Indian railways, CARD registration project and LOKMITRA. The relevance of e-governance to India includes transparency, public participation, public services and accountability. However, e-governance projects often face challenges such as lack of integration, key personnel and differences in languages. Most studies find that over 50% of e-government projects fail or see only partial success due to limitations in design and implementation challenges.