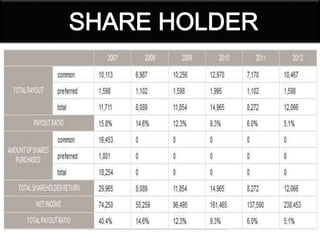
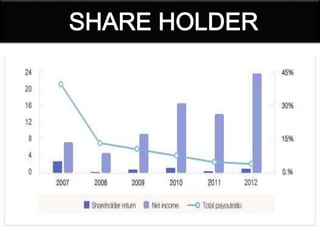
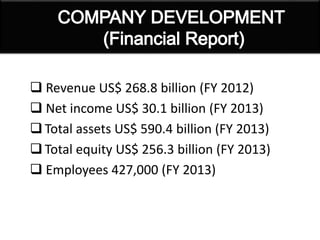
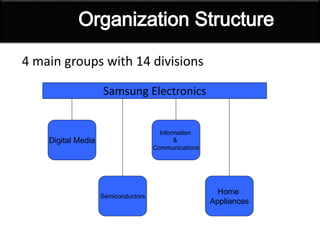
This document provides a history of Samsung's logo designs and business operations from 1938 to the present. It traces the evolution of Samsung's logos over time from its founding in 1938 as a trading company up until its current logo adopted in 1993. It also outlines the key events and expansions in Samsung's business over the decades, such as entering the electronics industry in the late 1960s, rising as an international corporation in the 1990s, and becoming the world's largest mobile phone maker by 2012. The document presents details on Samsung's various business segments and financial information as of 2013.