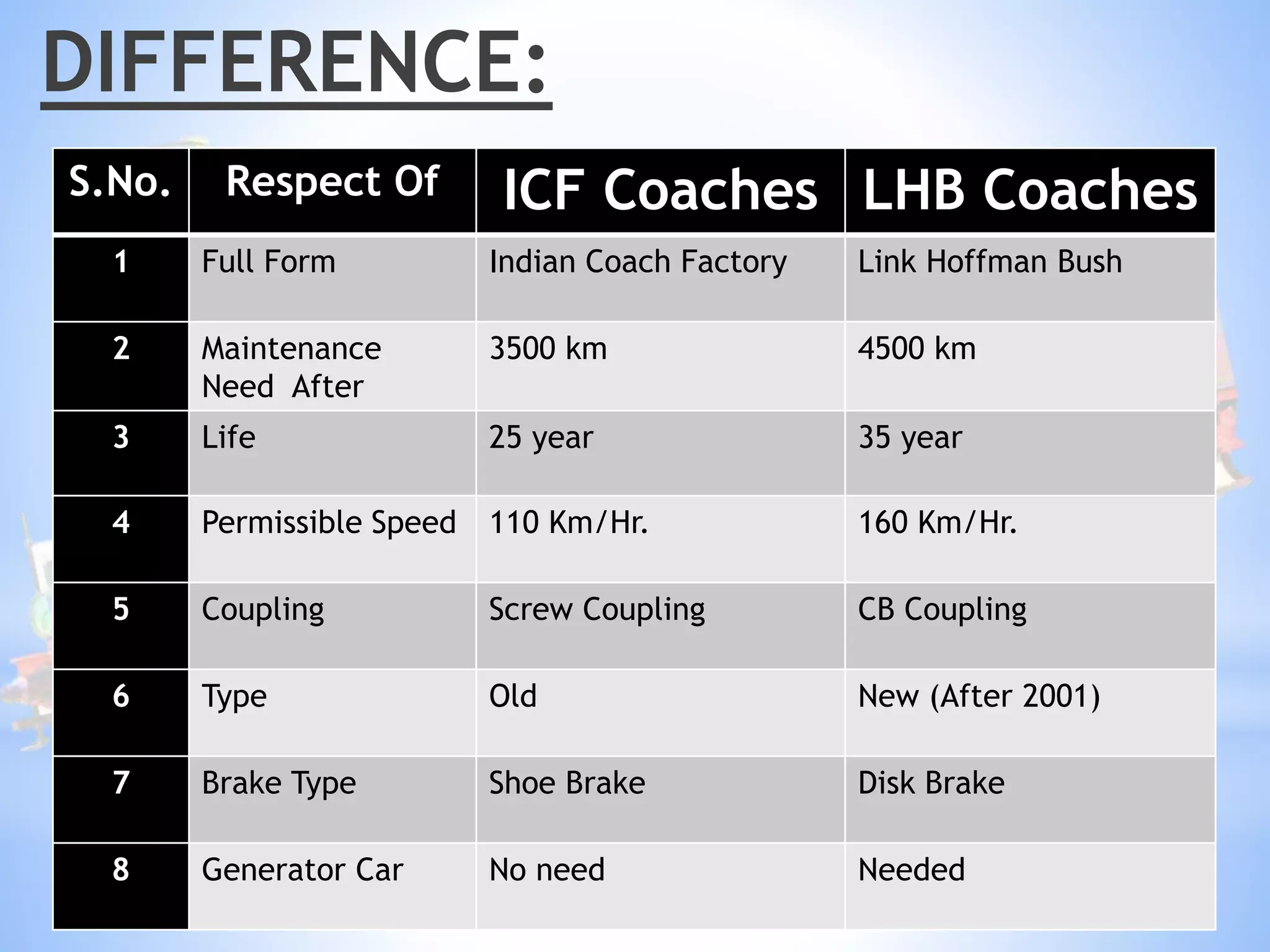
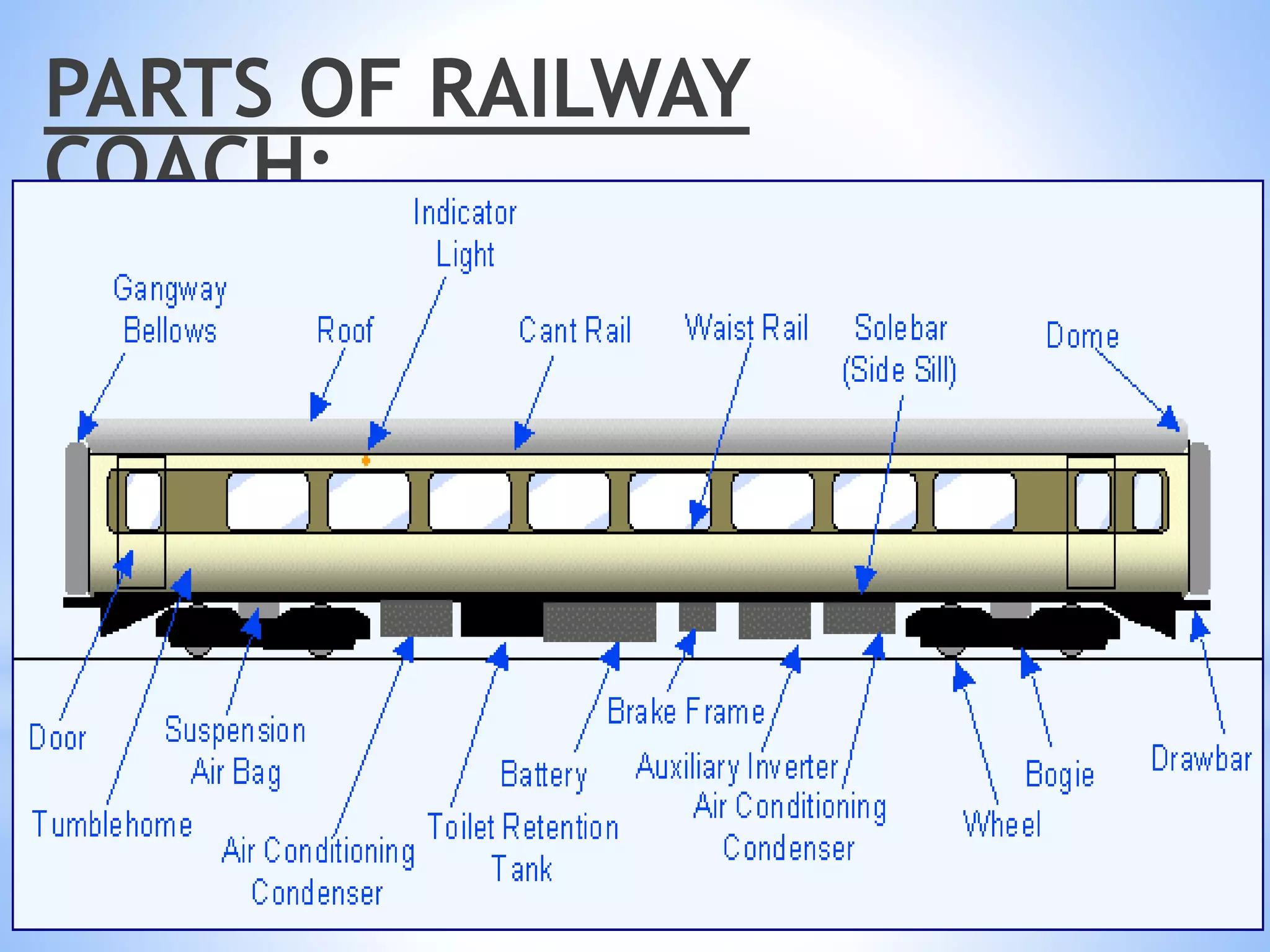
Ritik Baghmar presented on their industrial training at the North Western Railway in Jaipur. They discussed the history of Indian railways and how it became a single nationalized network by 1946. They described the different types of railway coaches used in India, including ICF and LHB coaches. They explained the key parts of a railway coach such as the bogie, wheel, suspension system, braking system, and CDTS. Finally, they covered maintenance procedures for railway coaches, including washing, sick line repairs, and primary and secondary maintenance checks.