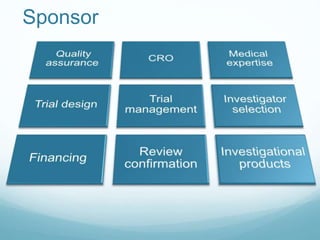
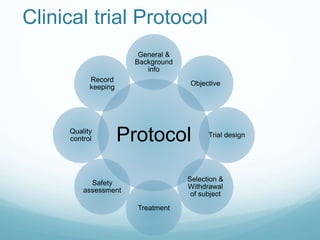
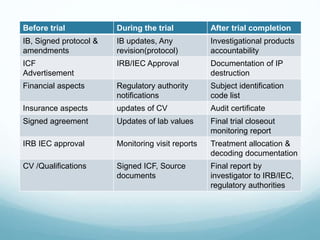
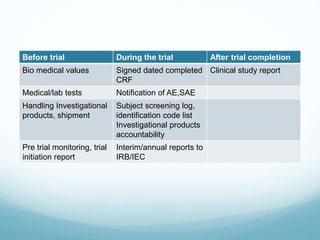
The document provides an overview of ICH (International Conference on Harmonization) and GCP (Good Clinical Practices) guidelines, emphasizing their role in ensuring the ethical and scientific quality of clinical trials. It outlines the responsibilities of various parties involved, including investigators, sponsors, and review boards (IRB/IEC), and highlights the importance of informed consent and quality assurance. Key documents required for compliance and monitoring throughout the clinical trial process are also discussed.