This document discusses hypothesis testing, which is a method used in scientific research to either accept or reject hypotheses. It outlines the key steps:
1) Formulating a research question and hypothesis, which is either the null hypothesis or alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the statement being tested.
2) Collecting and analyzing data and using a statistical test to calculate the p-value, which represents the probability of obtaining results as extreme as the actual outcome by chance alone.
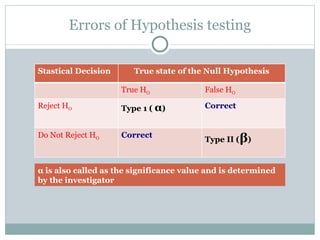
3) Comparing the p-value to the significance level (usually 0.05) to either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, with type 1 and type 2 errors representing incorrect decisions.












![Significance - Definition The significance level of a test is the probability that the test statistic will reject the null hypothesis when the [hypothesis] is true .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-2-101013001340-phpapp02/85/Presentation-2-15-320.jpg)