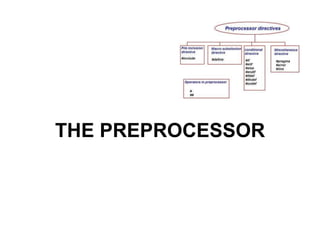
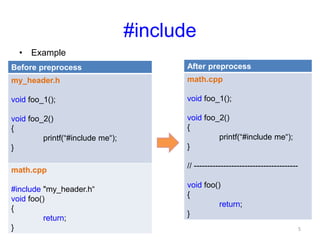
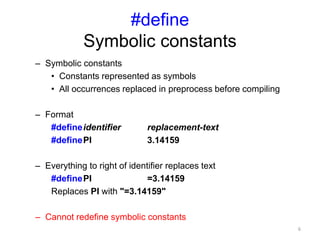
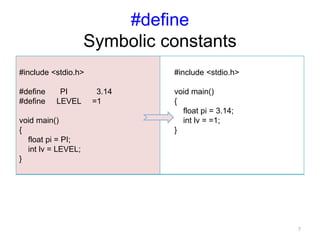
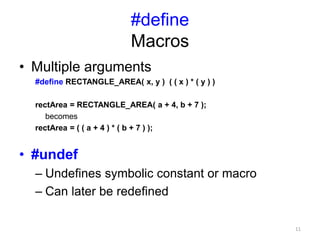
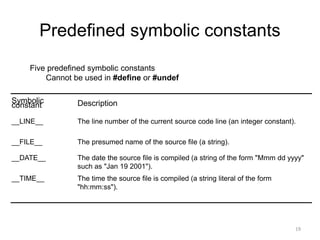
The preprocessor performs text replacement and preprocessing directives before a C/C++ program is compiled. Key functions of the preprocessor include #include to insert external files, #define for symbolic constants and macros, and conditional compilation (#if #ifdef #ifndef etc.) to control compilation. Other directives include #error to print error messages, #pragma for compiler-specific options, and assert to check for invalid values.