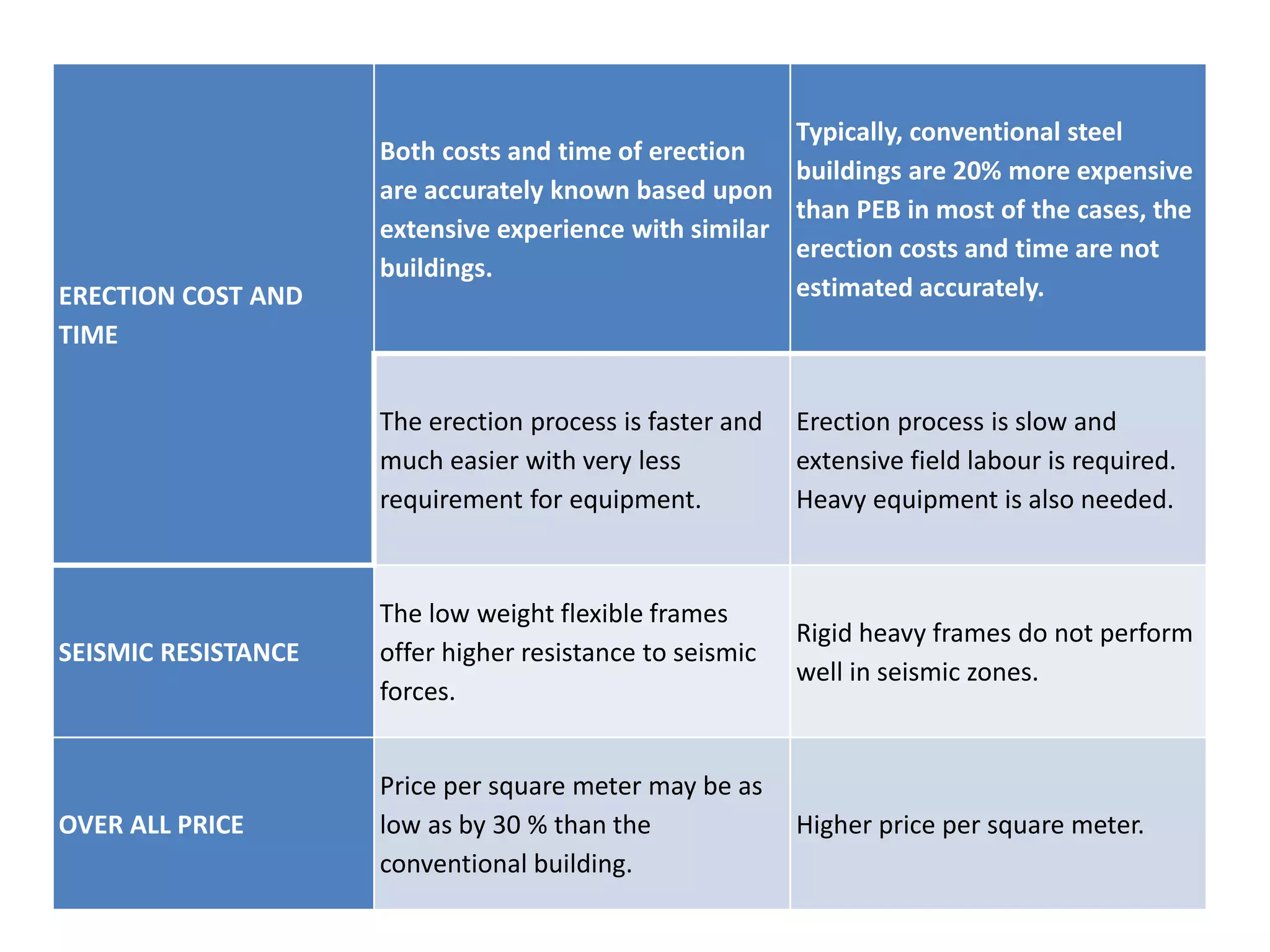
Pre Engineered Buildings (PEBs) provide advantages over conventional construction including reduced construction time of at least 50%, lower costs due to standardized design and factory production, and single source responsibility. PEBs use computerized design and lightweight steel framing. They have become popular for non-residential construction worldwide and in India since the 1990s, though their market is still growing in India.