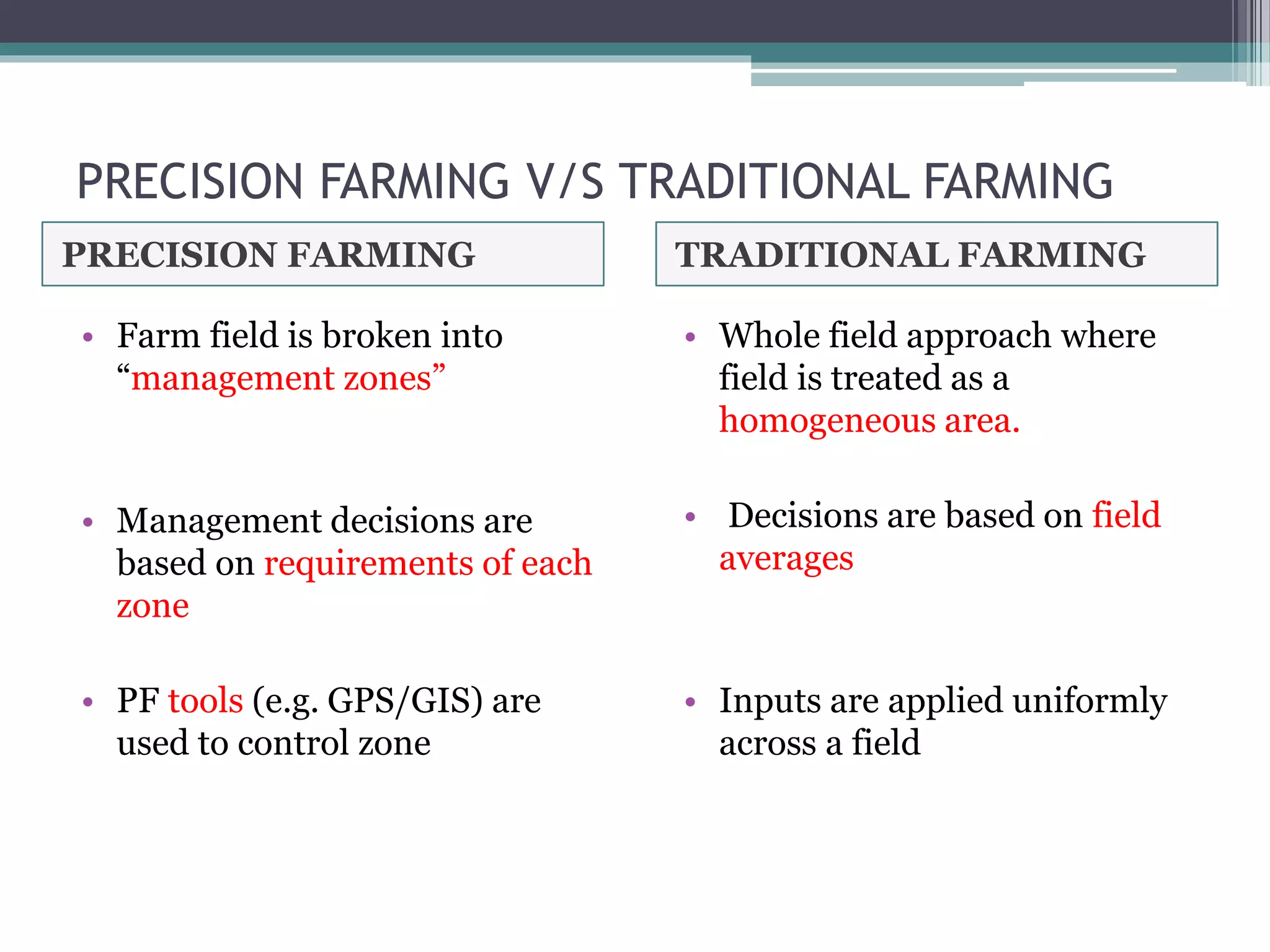
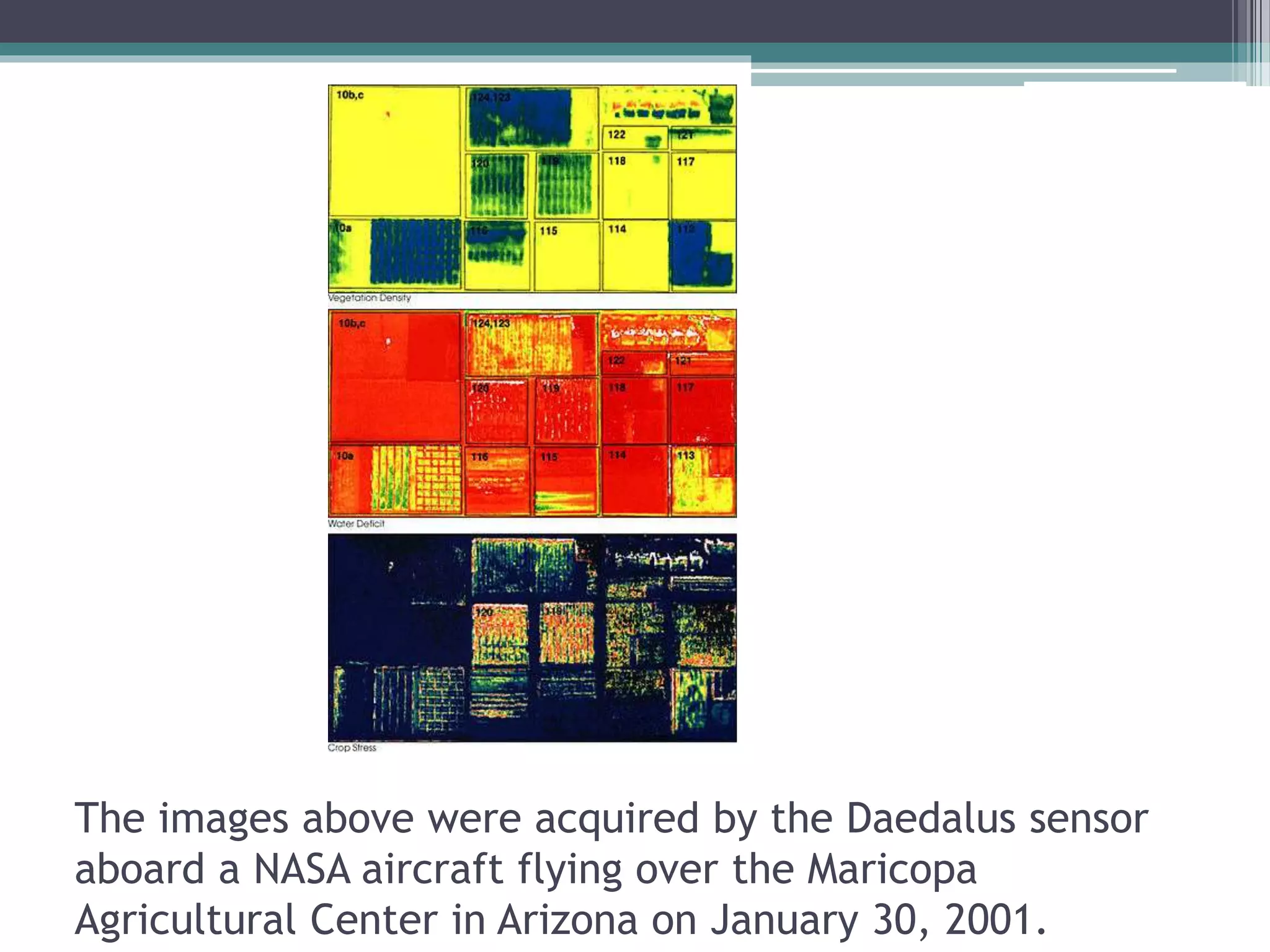
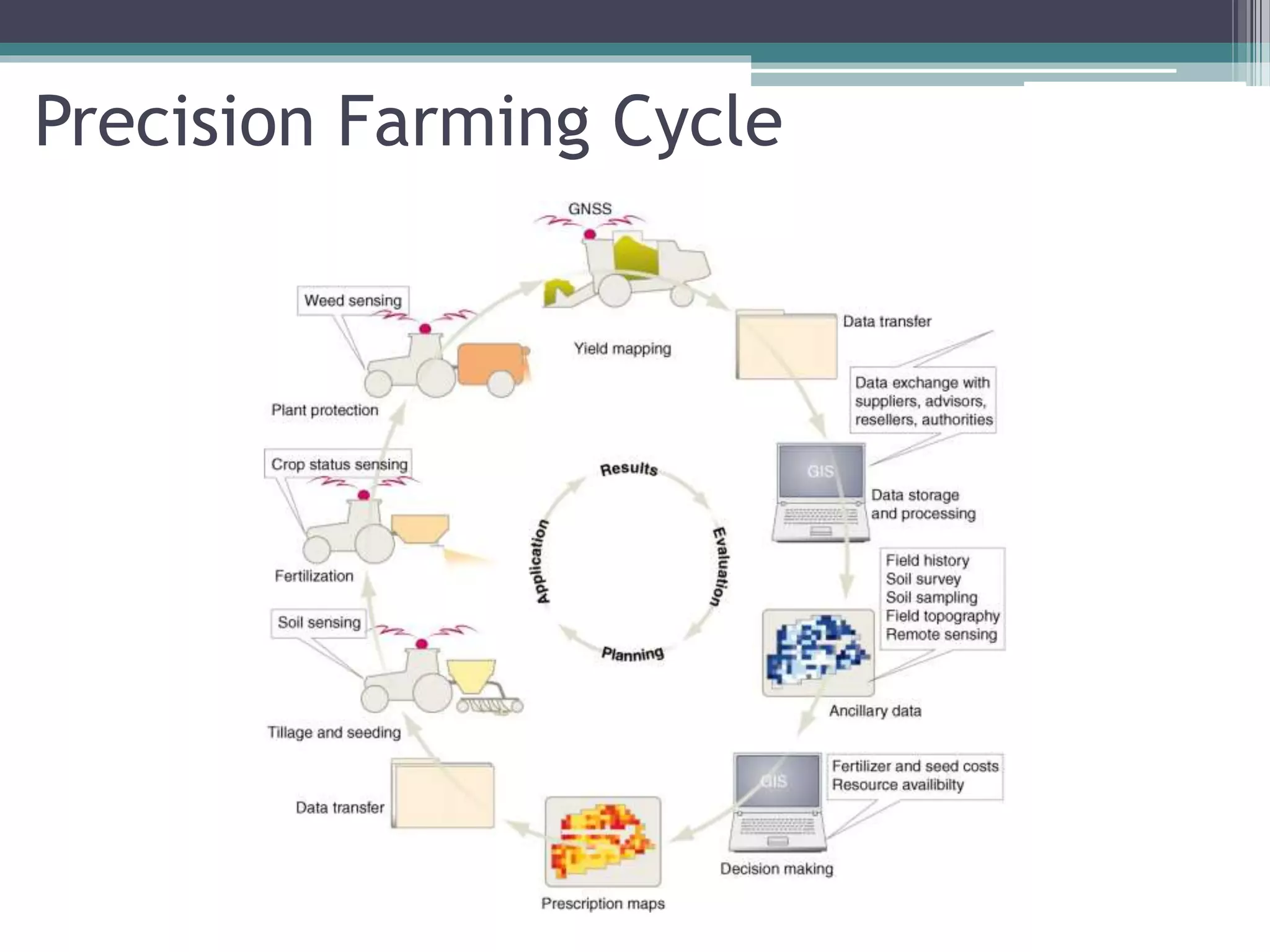
Precision farming uses technology like GPS, GIS, remote sensing, and variable rate application to optimize crop production by accounting for spatial and temporal variability within fields. It involves accessing variability through soil sampling and mapping, then managing that variability using tools like variable rate technology, site-specific planting, and nutrient management. This contrasts with traditional farming which treats entire fields uniformly without consideration for variability. The goal of precision farming is to improve crop yields and quality while reducing costs, waste, and environmental impact.