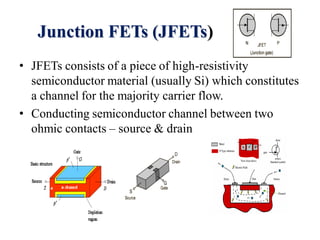
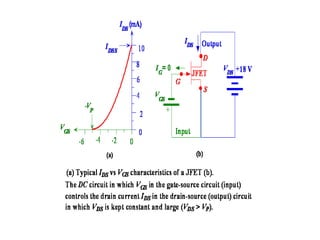
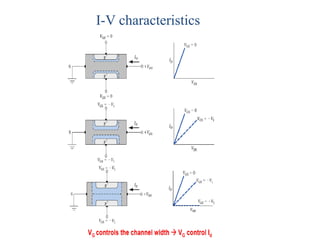
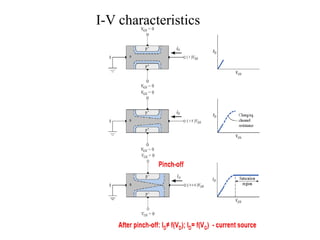
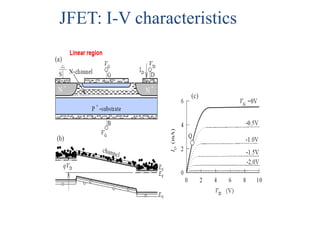
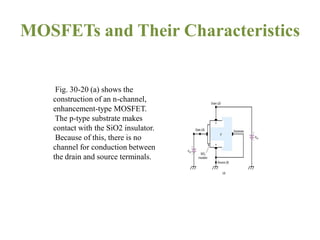
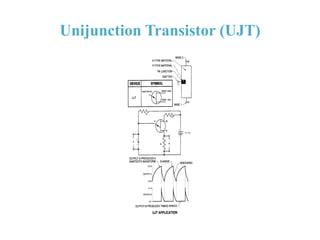
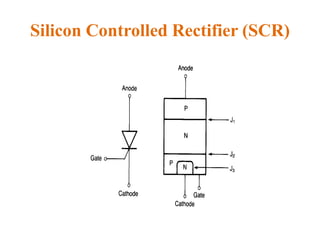
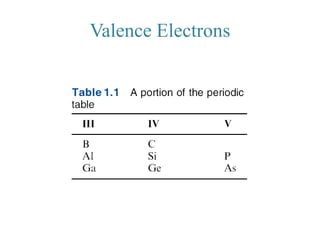
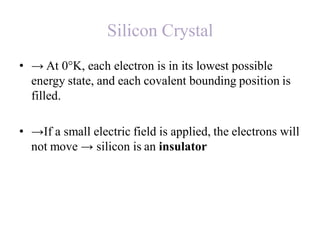
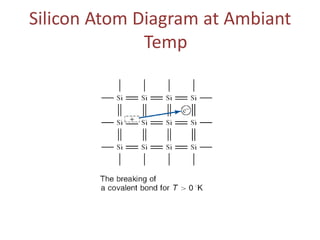
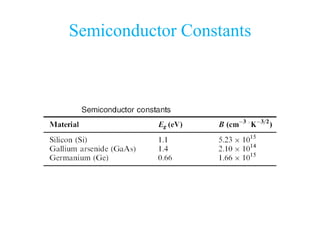
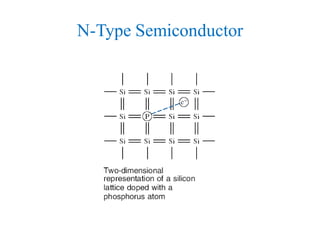
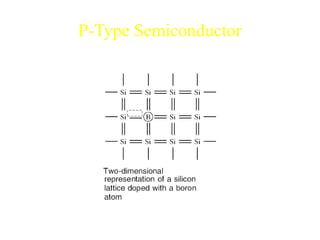
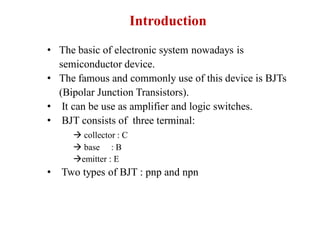
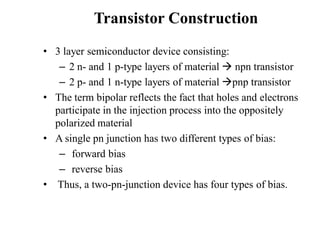
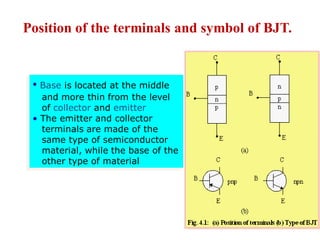
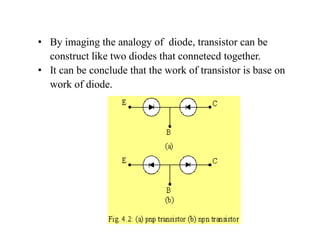
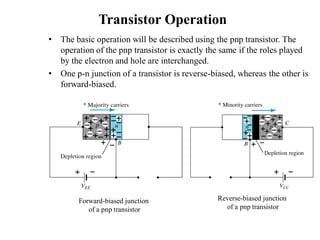
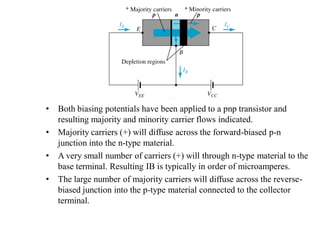
1. The document discusses the atomic structure of semiconductors and how doping creates an excess or deficiency of electrons or holes, turning silicon into an n-type or p-type semiconductor.
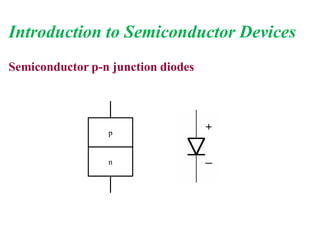
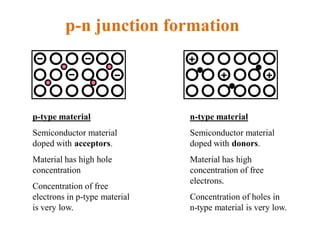
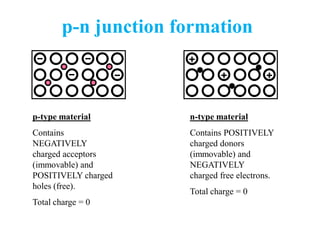
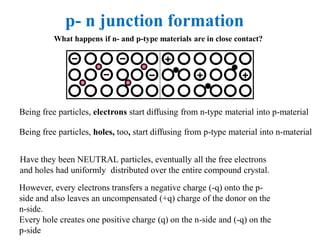
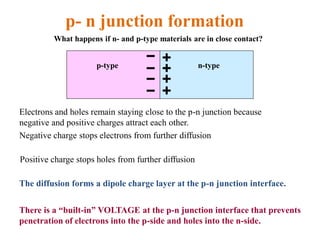
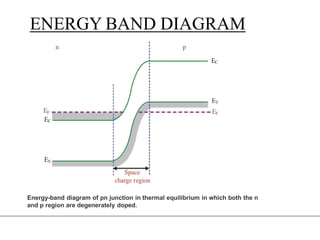
2. When a p-type and n-type semiconductor are joined, electrons from the n-side diffuse into the p-side and holes from the p-side diffuse into the n-side, leaving an area devoid of charge carriers called the depletion region.
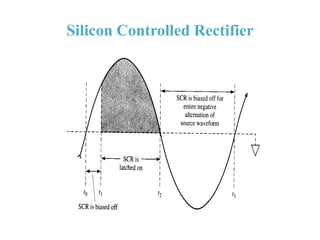
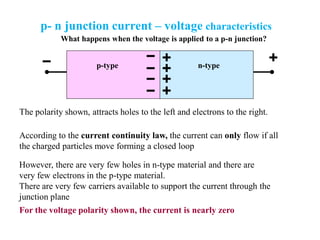
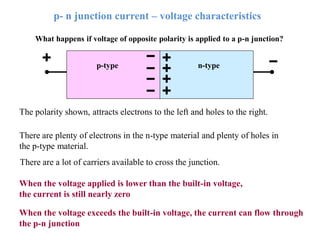
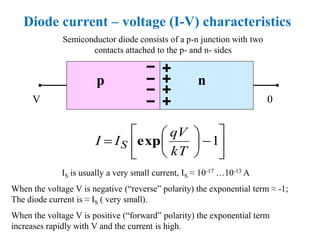
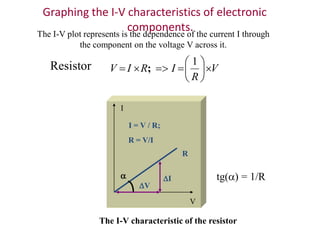
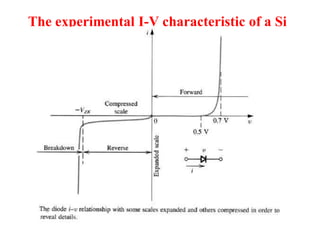
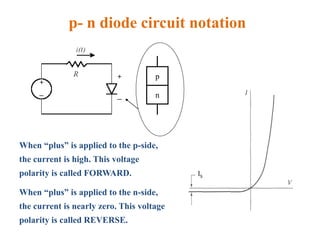
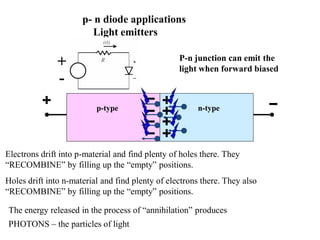
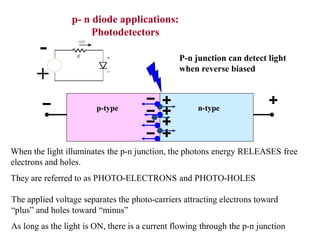
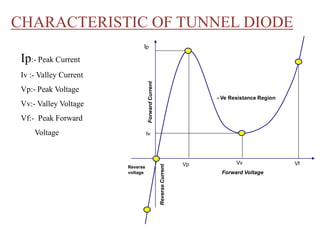
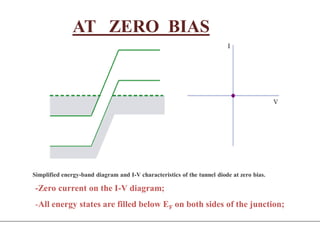
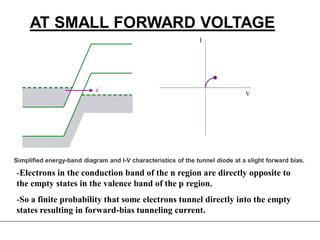
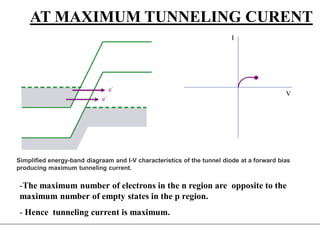
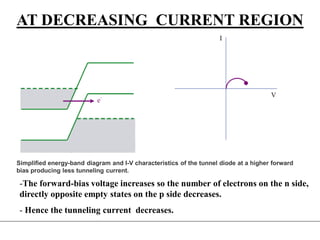
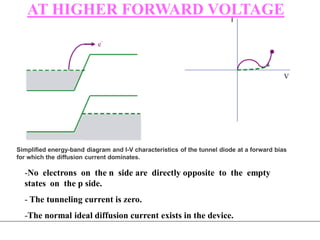
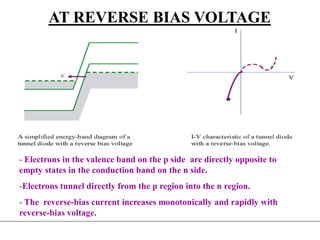
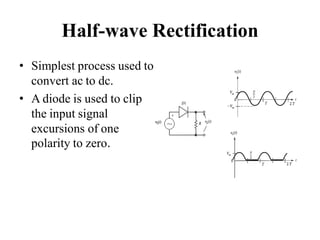
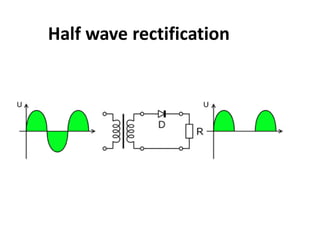
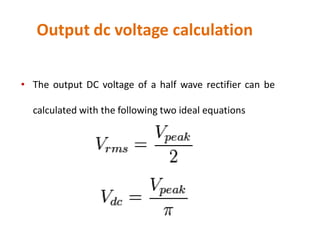
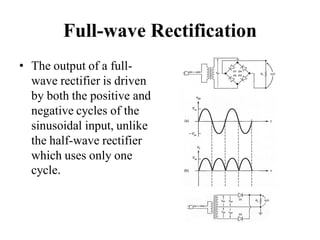
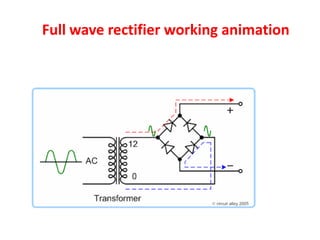
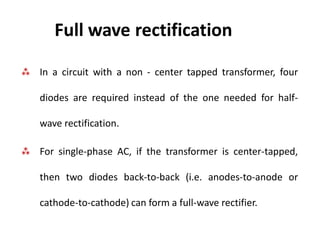
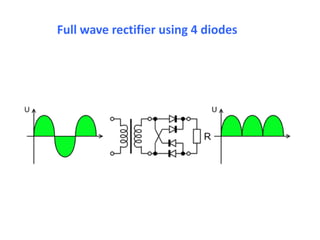
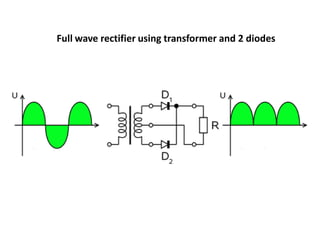
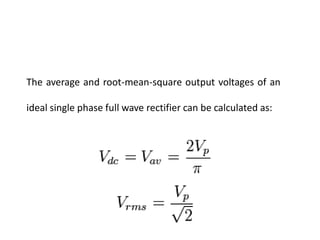
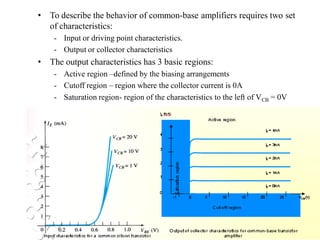
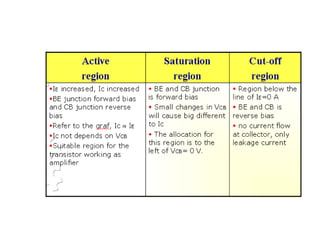
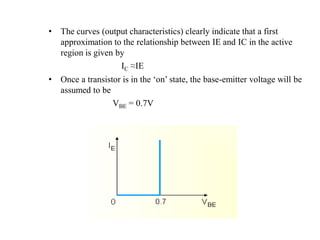
3. A p-n junction diode allows current to flow easily in one direction when forward biased but strongly restricts it in the reverse direction, demonstrated by its characteristic I-V curve.






















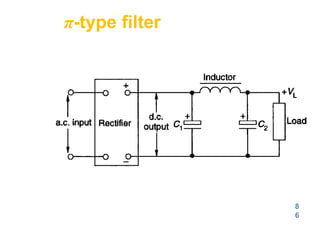
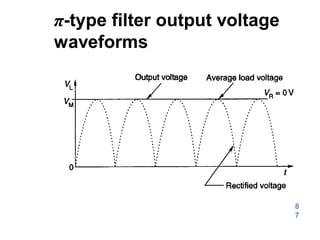
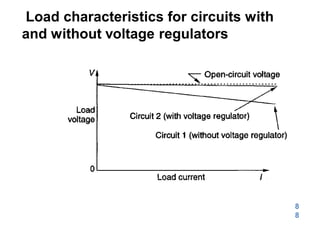
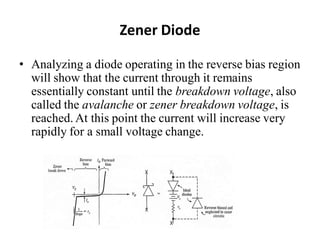

















![148
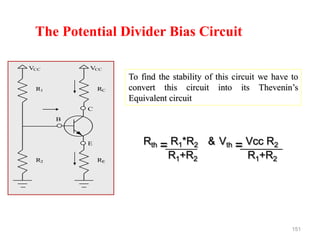
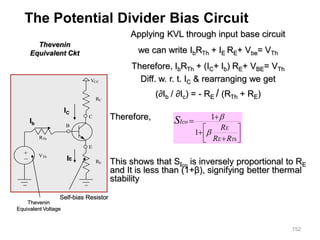
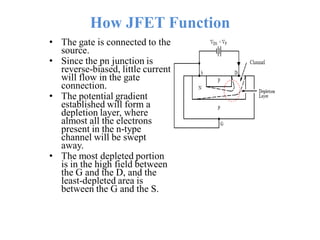
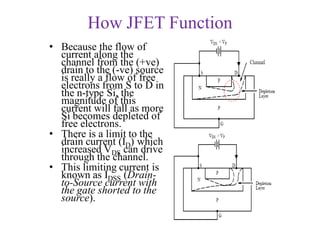
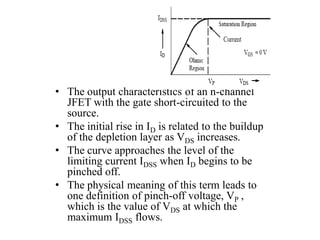
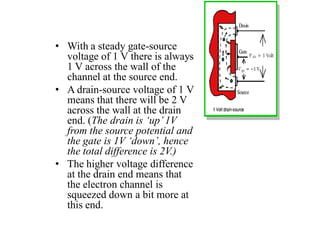
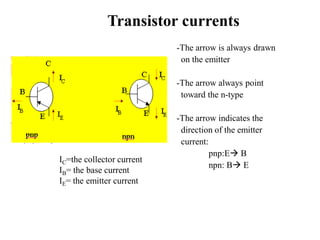
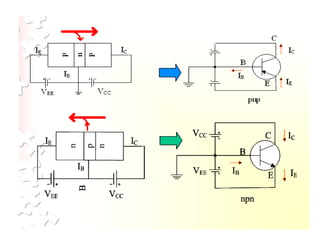
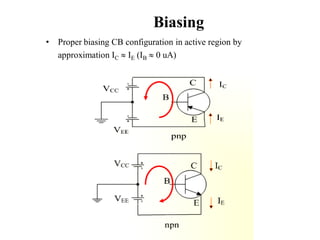
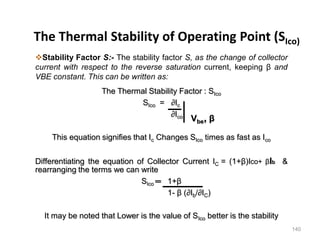
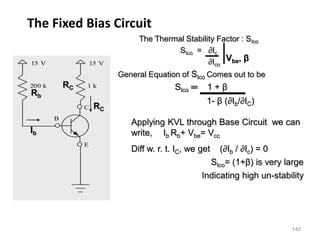
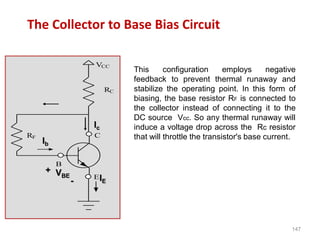
Applying KVL through base circuit
we can write (Ib+ IC) RC + Ib Rf+ Vbe= Vcc
Diff. w. r. t. IC we get
(∂Ib / ∂Ic) = - RC / (Rf + RC)
Therefore, SIco ═ (1+ β)
1+ [βRC/(RC+ Rf)]
Which is less than (1+β), signifying better thermal stability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptedc-221216013810-c4f37ee4/85/ppt_edc-pdf-148-320.jpg)