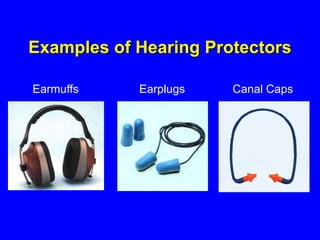
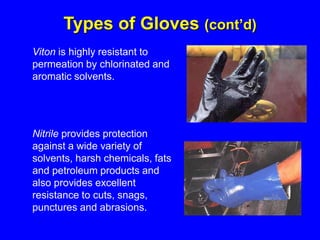
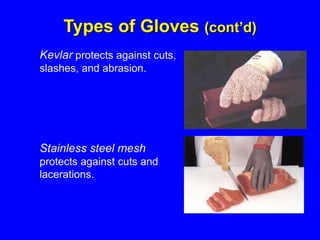
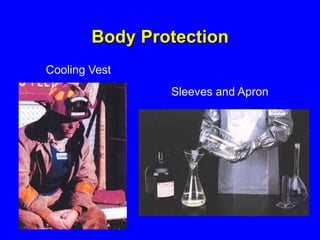
Employers must protect employees from workplace hazards through engineering controls, work practice controls, and if needed, personal protective equipment (PPE). They must assess hazards, select appropriate PPE, inform and train employees on proper PPE use, and require PPE be worn. Examples of PPE include safety glasses, gloves, hard hats, earplugs, steel-toe boots, coveralls, and respirators.