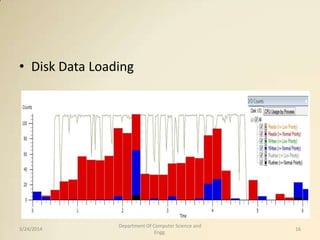
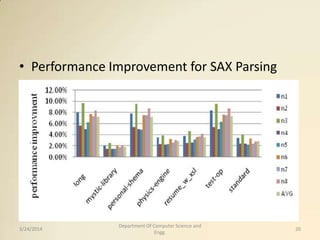
The document proposes accelerating XML parsing through prefetching techniques. It discusses how XML parsing consists of character conversion, lexical analysis, and syntactic analysis, which introduces significant overhead. It then presents different prefetching techniques that could be applied to bridge the speed gap between CPU and memory and reduce cache misses. Evaluation shows these techniques can reduce cache misses by up to 80% and improve performance by up to 20%, as well as provide 12.77% energy savings for XML parsing.