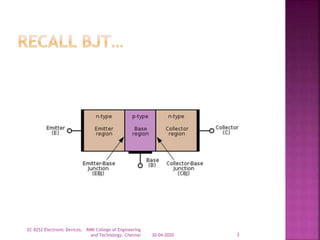
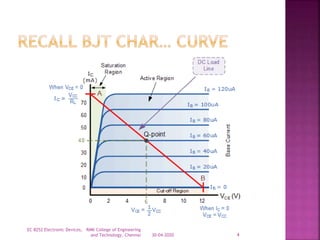
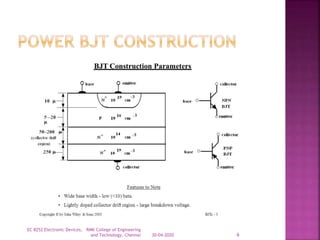
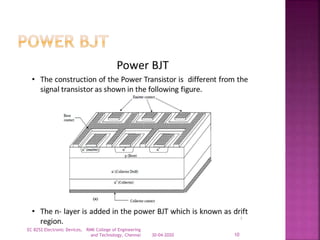
The document discusses power bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). It notes that power BJTs have a vertically oriented four-layer structure to increase their cross-sectional area and allow for high voltage blocking and current carrying capacity. Key layers include a heavily doped emitter, moderately doped base, lightly doped collector drift region, and highly doped collector. The drift region increases the breakdown voltage but also increases resistance. Power BJTs are used in applications like switched mode power supplies, inverters, motor controllers due to their high power handling capability.