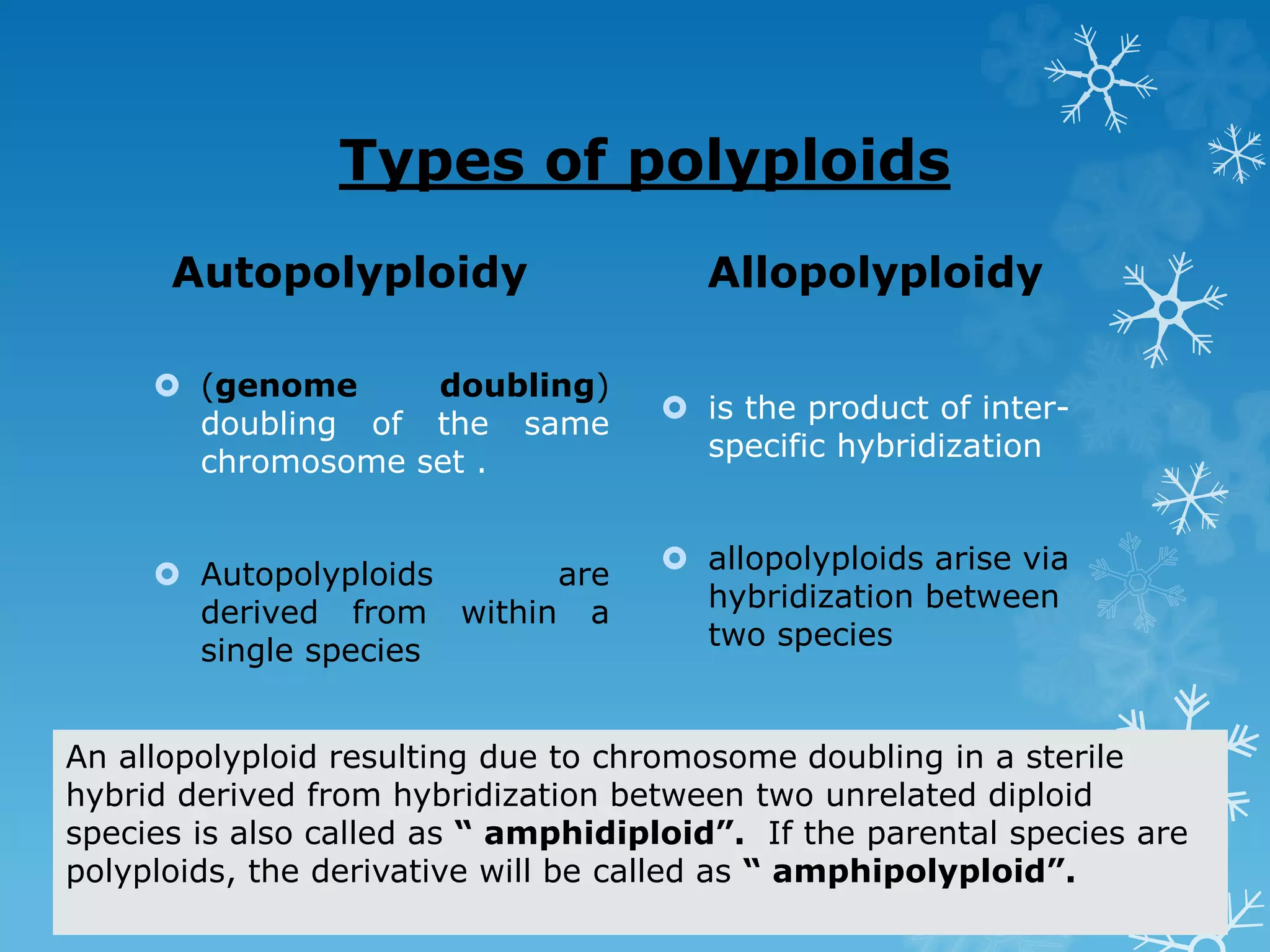
This document discusses polyploidy and its applications in plant breeding. It begins by defining polyploidy as having three or more sets of chromosomes, which can occur naturally or through induction. Examples of polyploid plants include wheat, strawberries, and plant endosperm. Polyploidy can originate through somatic doubling during mitosis, non-reduction during meiosis producing unreduced gametes, polyspermy, or endoreplication. Artificial polyploids have been created to study natural allopolyploids or develop new crop species, such as the synthetic allopolyploid Raphanobrassica. Breeding autopolyploids and allopolyploids can bridge