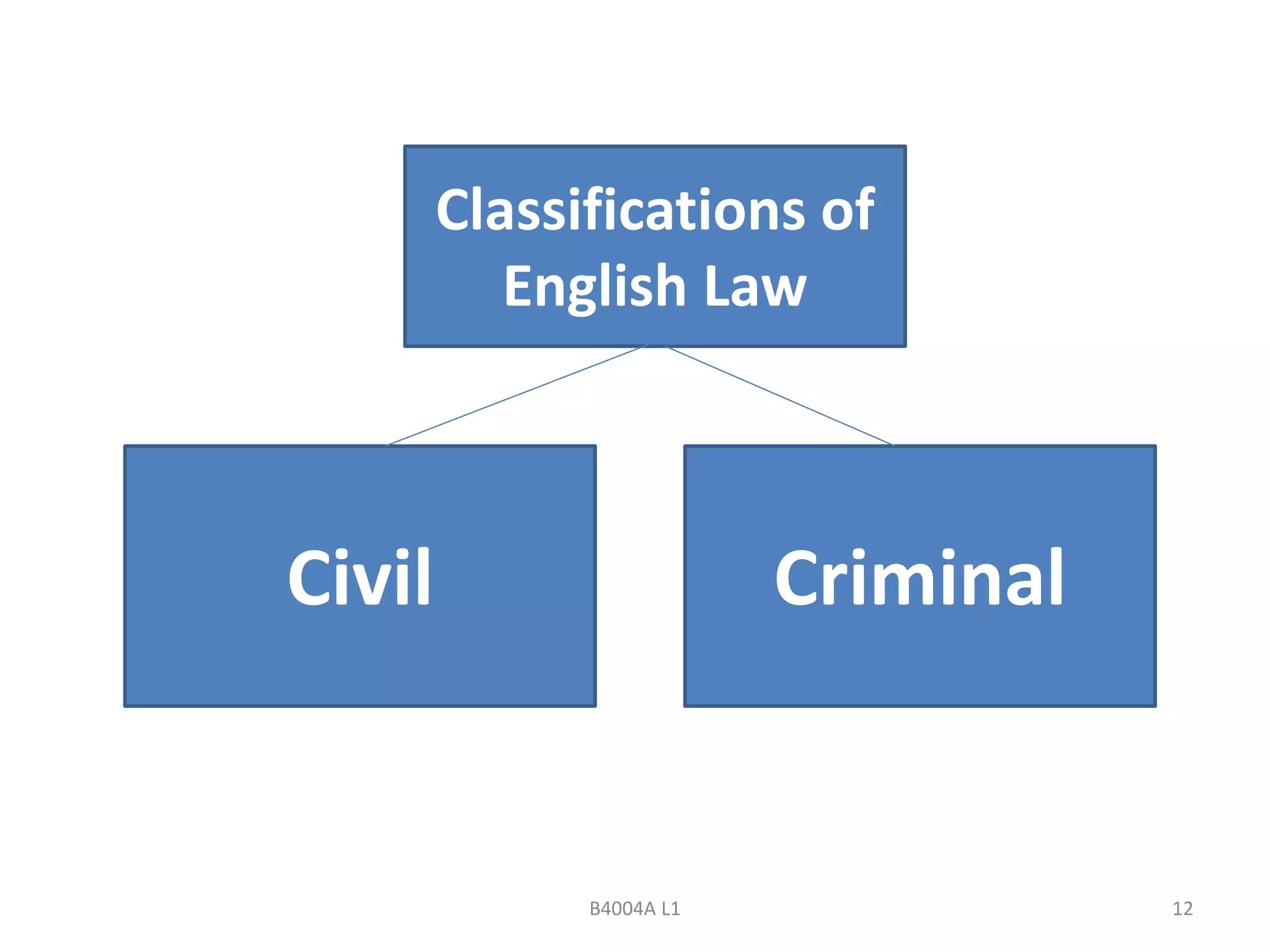
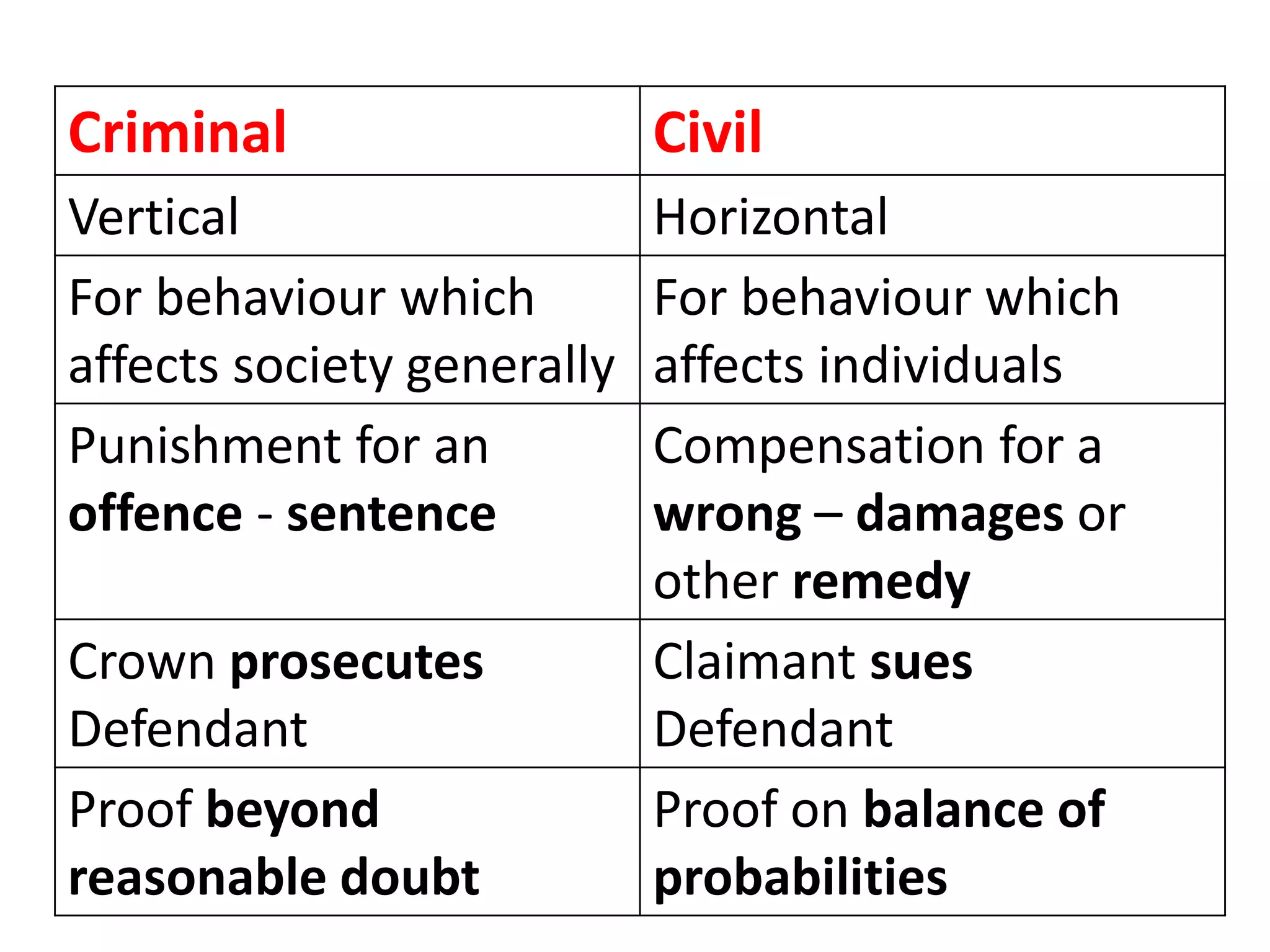
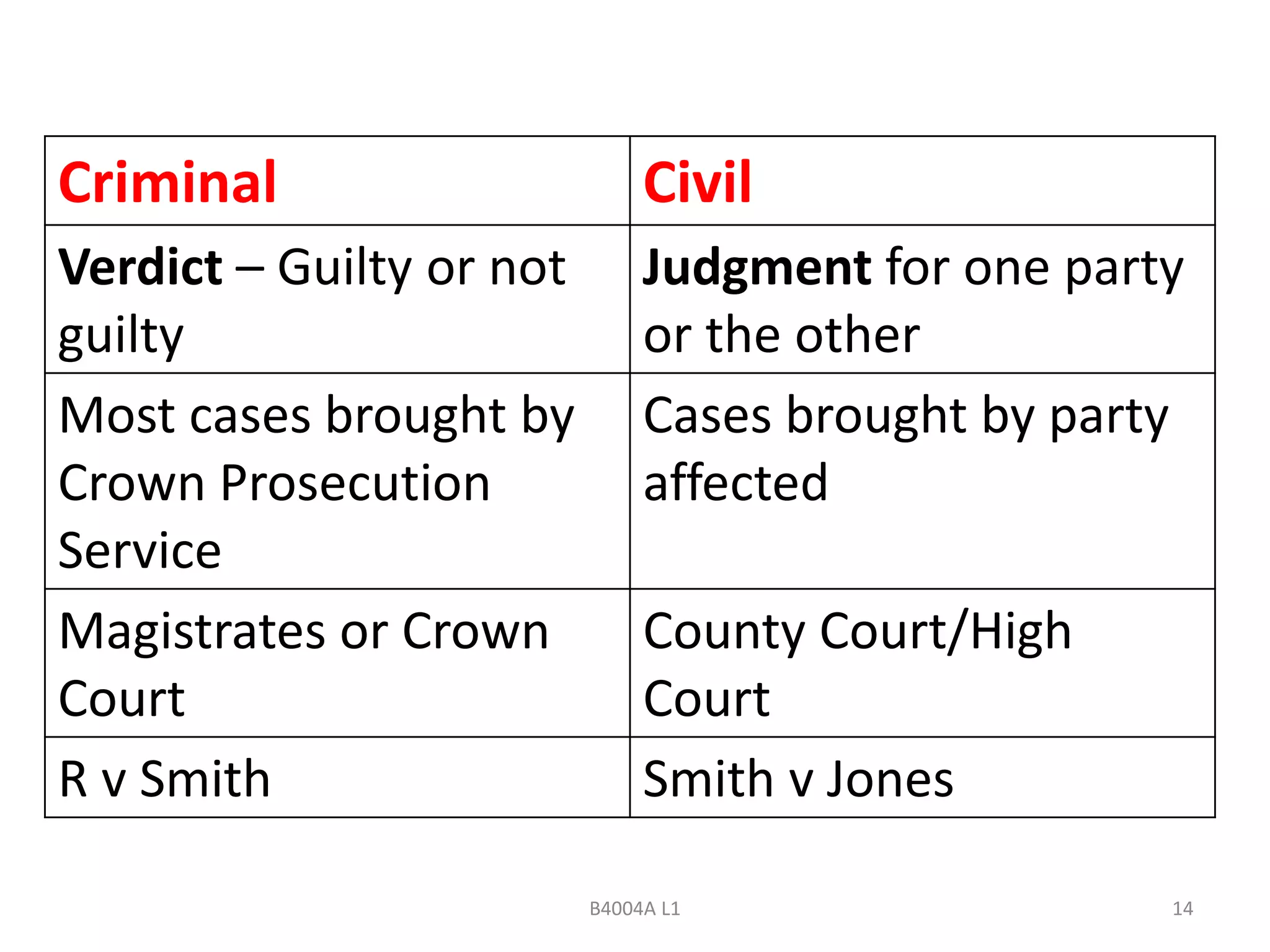
This document provides an introduction to law within the context of business principles. It discusses the meaning and purpose of law, key characteristics of the English legal system, and differences between civil and criminal law. The main areas covered include the rule of law, common law tradition, classifications of public and private law, and differences in how civil versus criminal cases are handled. The goal is to explain the significance of law for business and identify legal areas that most impact commerce.







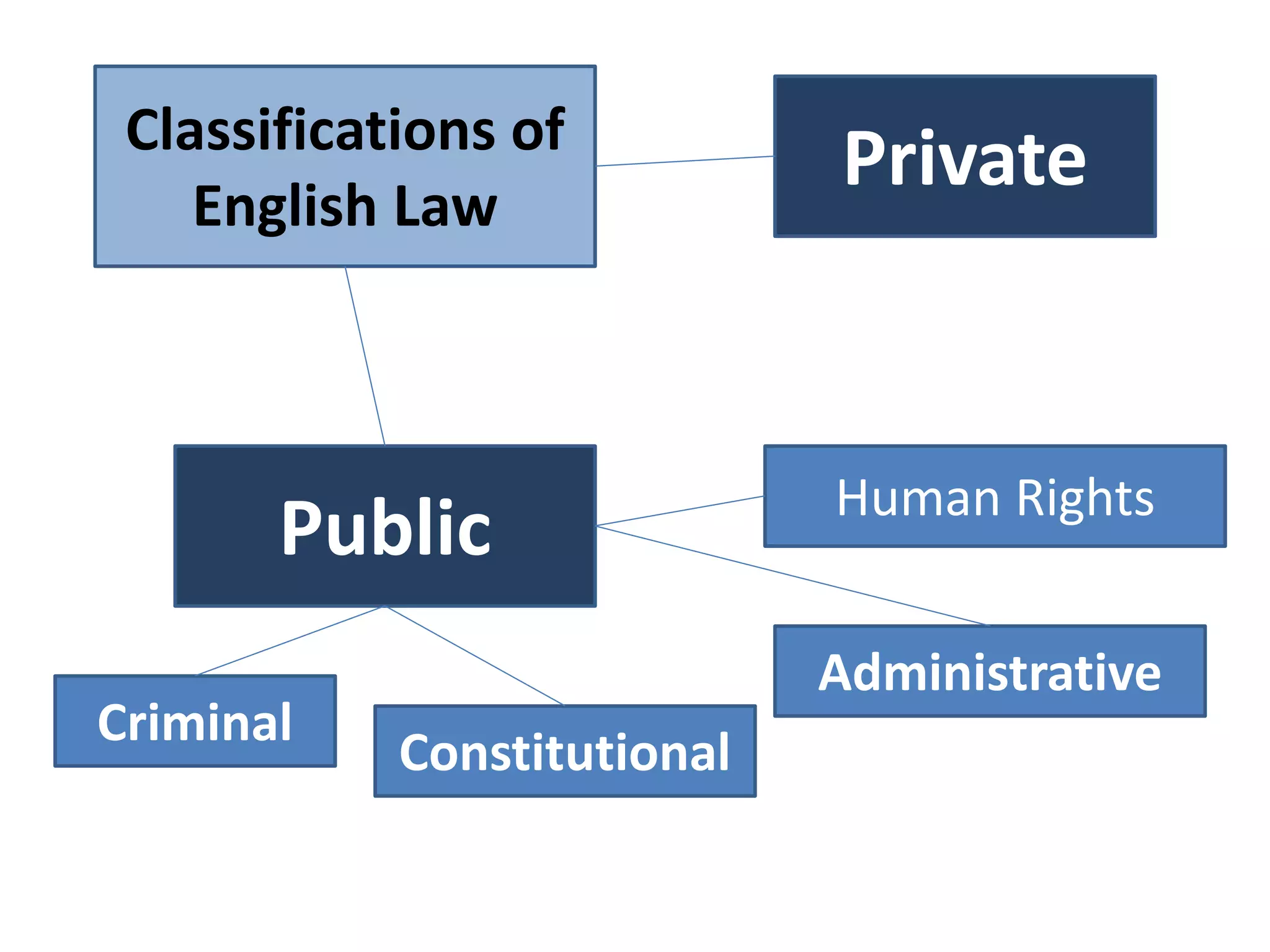
![Private law categories
• Contract Law
• Tort Law
• Property Law – Land Law, Intellectual
Property, Trusts, Succession
• Family Law
• Employment Law
• Company Law
• [EU Law]
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pobstage2lecture7introductionpostoleset-140829042934-phpapp01/75/Pob-stage-2-lecture-7-introduction-post-ole-set-16-2048.jpg)





