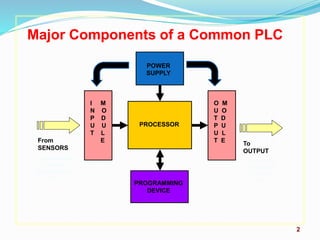
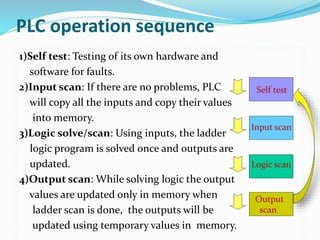
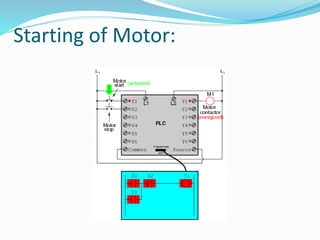
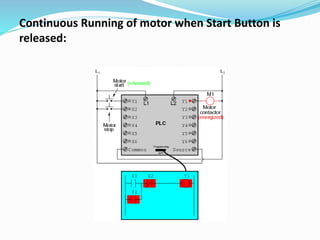
A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is a specialized microprocessor-based computer utilized in industrial environments for process control through programmable memory. It operates through a sequence of steps including self-test, input scan, logic solve, and output scan while supporting various programming languages like ladder logic and functional block diagrams. PLCs are favored for their reliability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and are commonly used in diverse industries such as robotics, automotive control, and food processing.