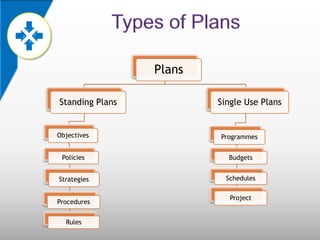
The document defines planning as determining a course of action to achieve desired results. It is a process that involves looking to the future and selecting actions. Planning provides a framework for managing, motivating, and controlling an organization. It is a prerequisite for effective management. Planning bridges the gap between current and desired states by deciding what to do, how to do it, where, and by whom. Planning helps organizations choose the right path and improves efficiency, coordination, decision-making, and innovation. Plans can be standing, single-use, objectives, policies, strategies, procedures, rules, programs, budgets or schedules. Planning occurs on long-term and short-term horizons and at strategic, operational, and functional levels. The