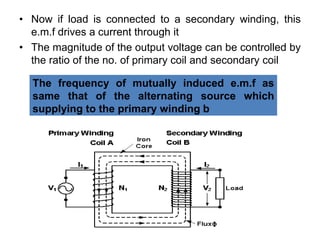
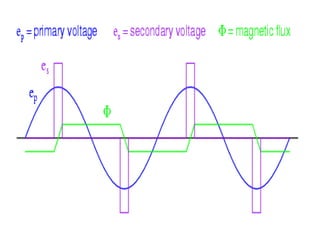
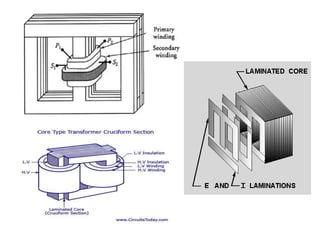
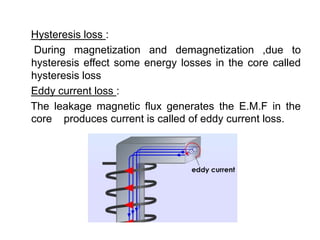
The document discusses transformers, including their structure, working principle, construction, losses, and applications. A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two coils, a primary and secondary winding, wrapped around an iron core. When alternating current flows through the primary, it induces a magnetic field that transfers energy to the secondary coil without direct electrical connection, inducing voltage in the secondary. Transformers are used widely in power transmission and distribution to change voltage levels for efficient transmission or usage. They allow flexible adaptation of voltage for different applications while maintaining frequency.