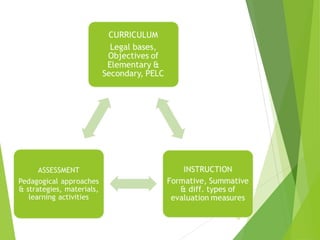
The 2002 Basic Education Curriculum (BEC) establishes official learning goals for elementary, secondary, and alternative learning system education. It emphasizes helping learners become successful readers through interactive approaches. The core subjects are Filipino, English, math, and science, while the experiential area includes citizenship education and health subjects. Instruction can be in English, Filipino, or local mother tongues depending on the educational level and location. Assessment of student learning considers curriculum, instruction, and assessment as an integrated system.