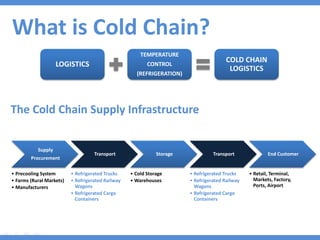
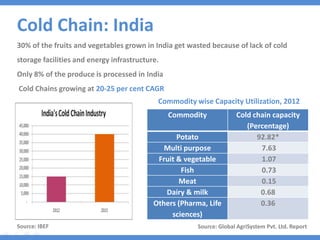
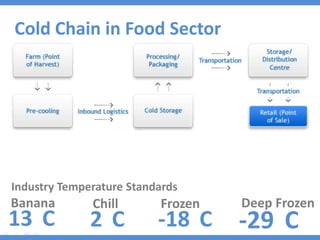
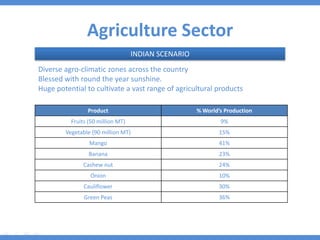
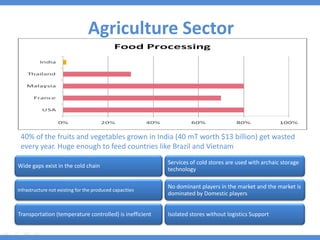
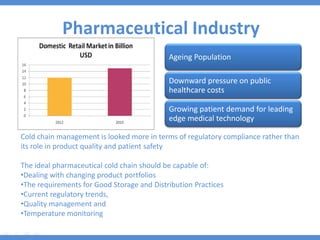
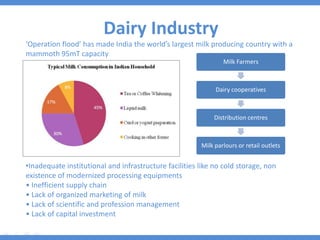
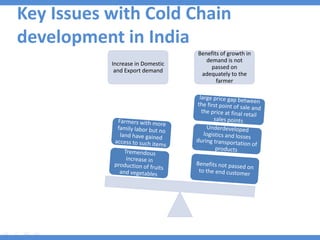
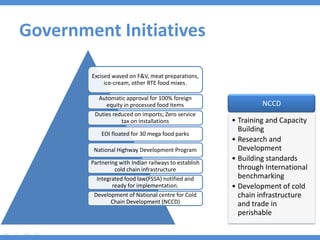
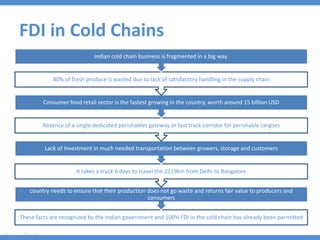
The document discusses the current state and development of cold chains in India, highlighting the significant waste of agricultural produce due to inadequate infrastructure and inefficiencies in the supply chain. It outlines the challenges faced in various industries, including pharmaceuticals and food, while presenting government initiatives aimed at promoting cold chain investment and modernization. The document also emphasizes the need for improved logistics, technology standards, and foreign investment to enhance the cold chain system's effectiveness in supporting India's agricultural sector.