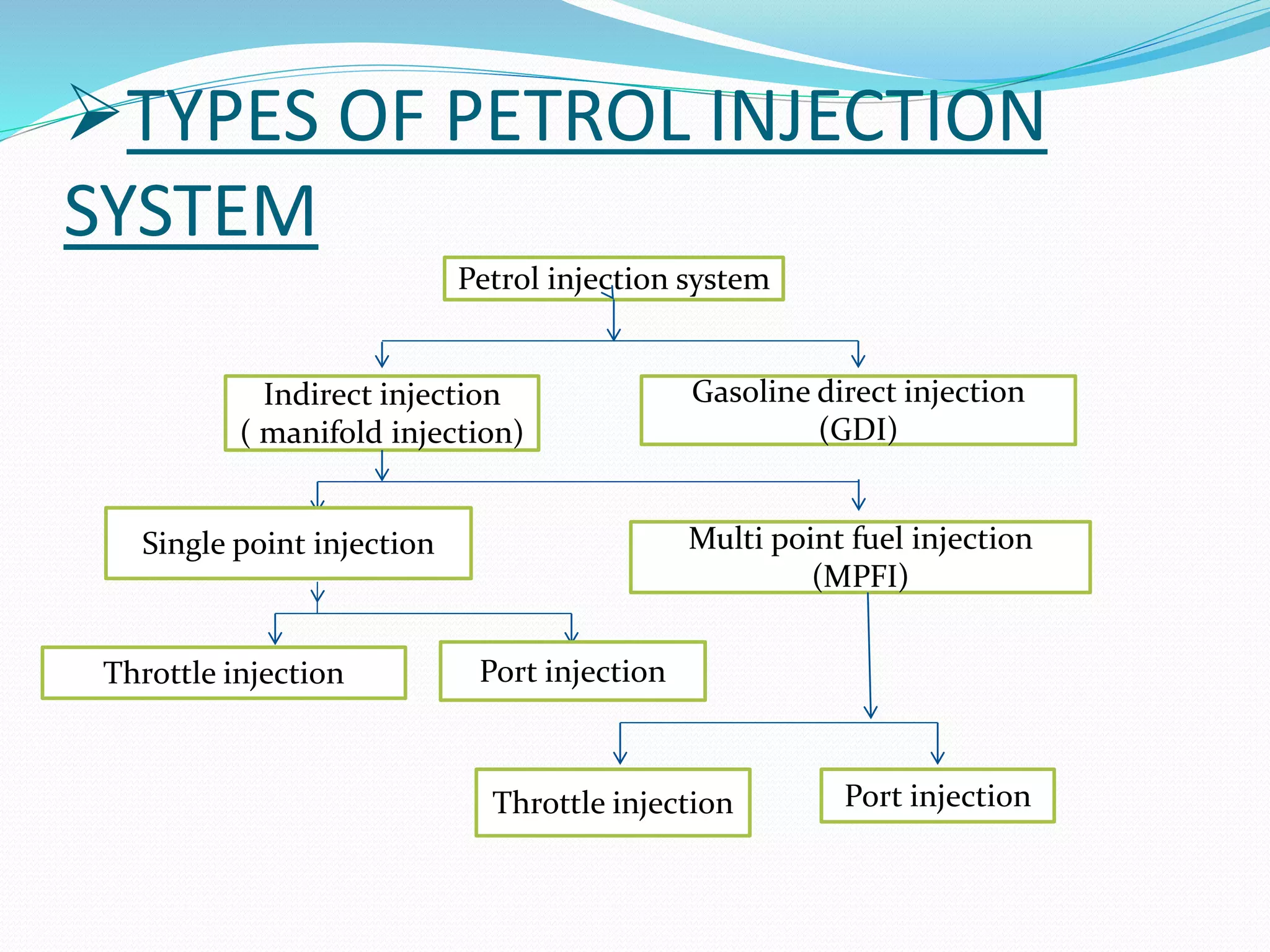
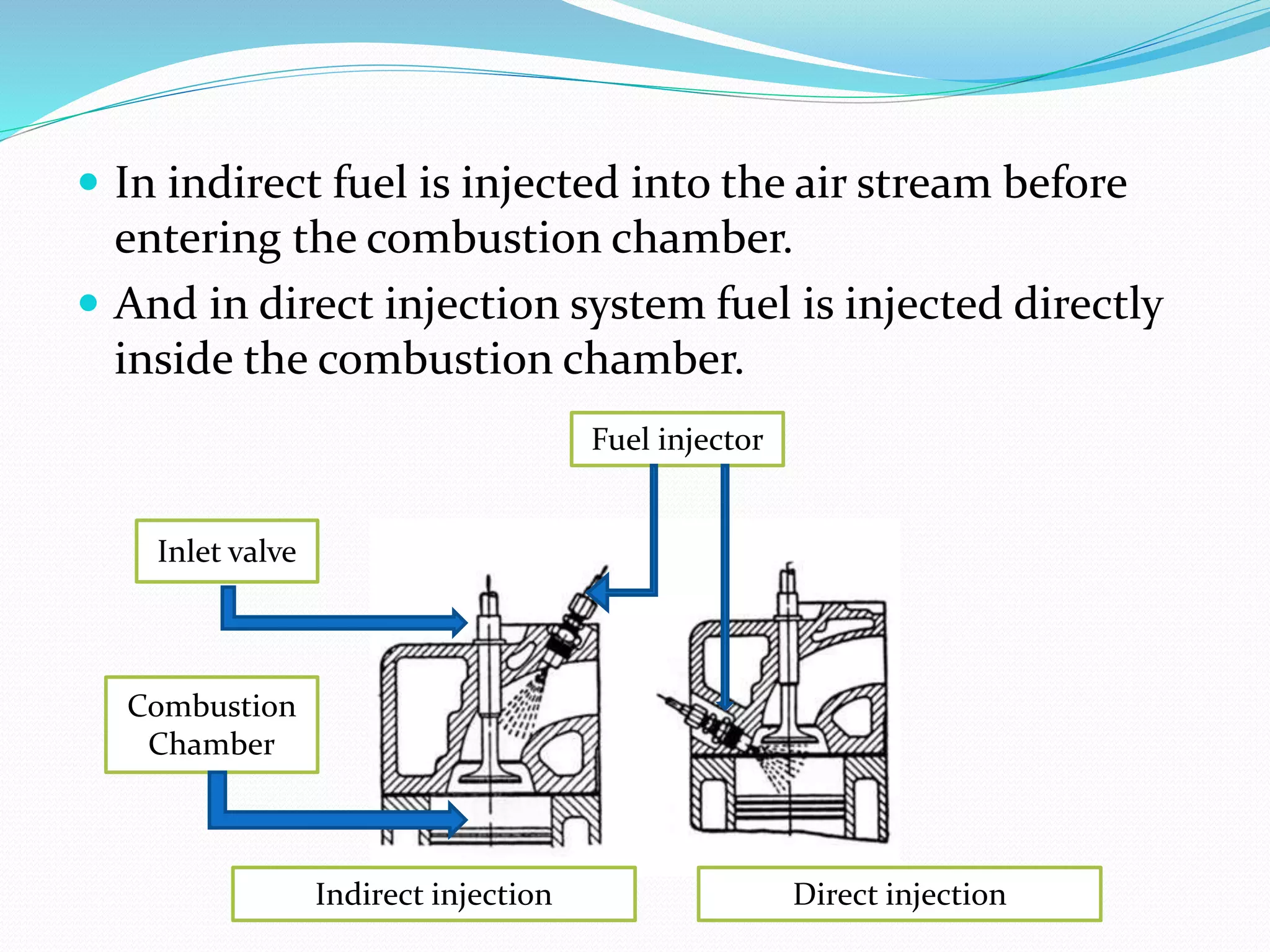
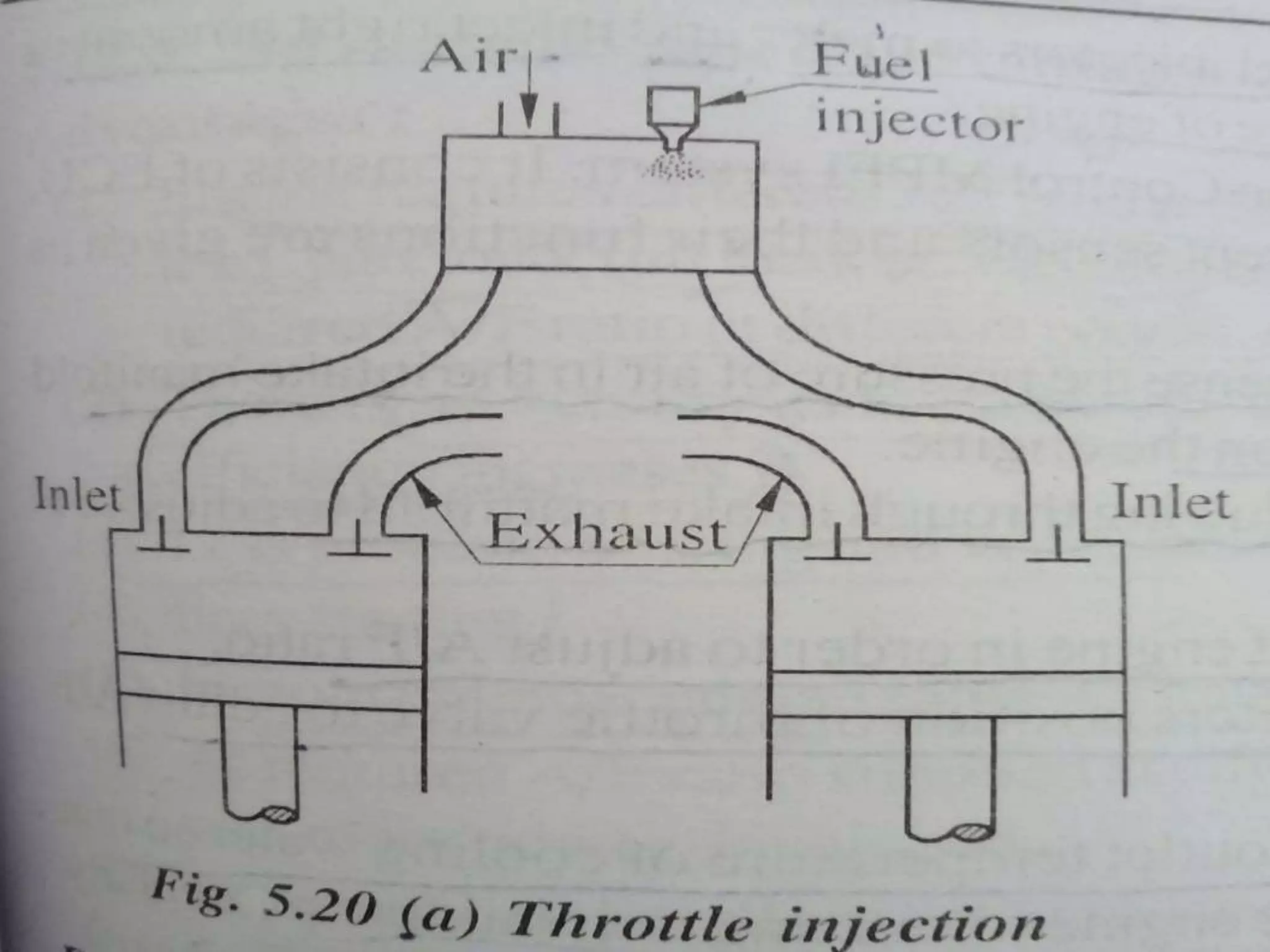
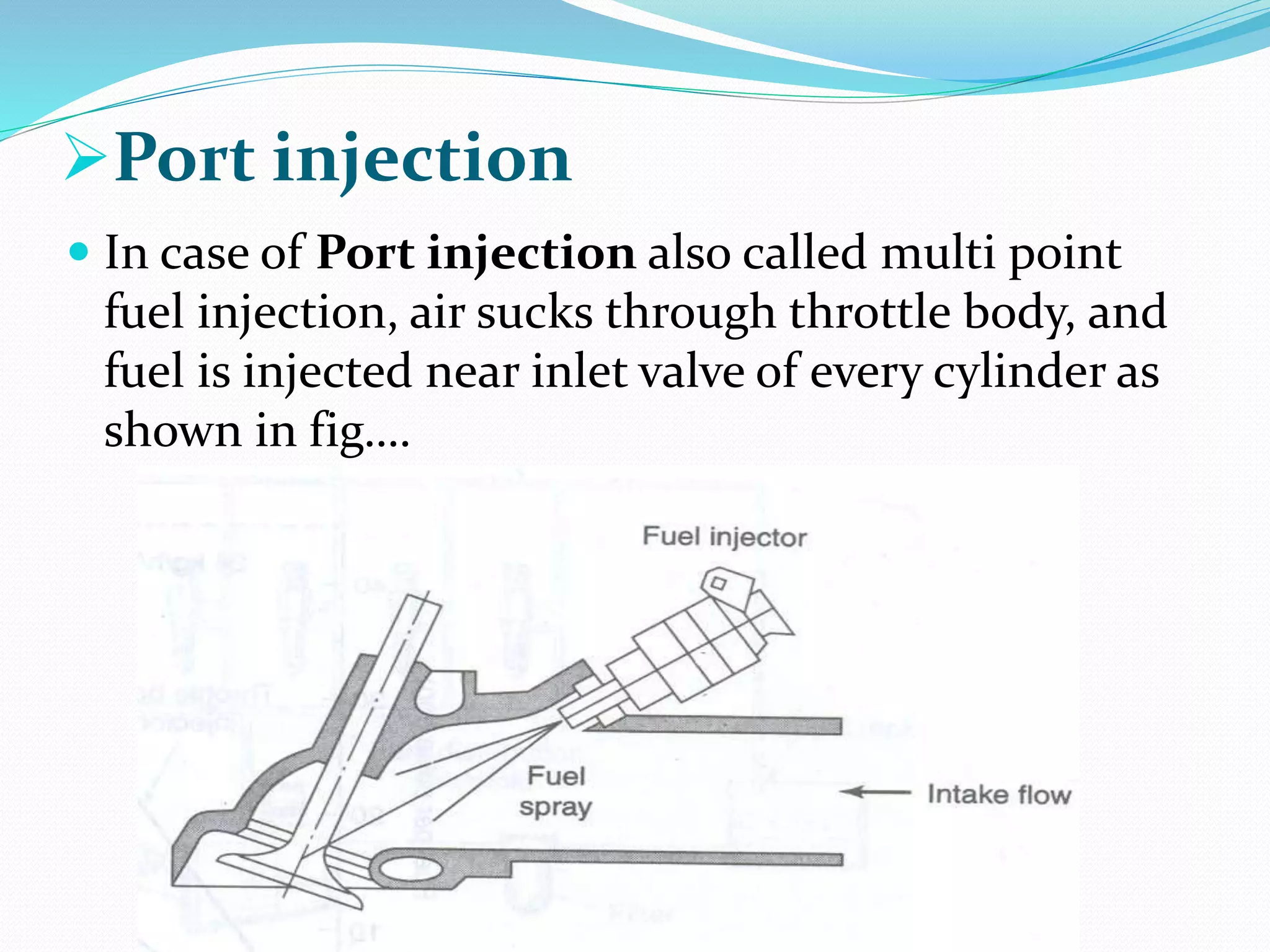
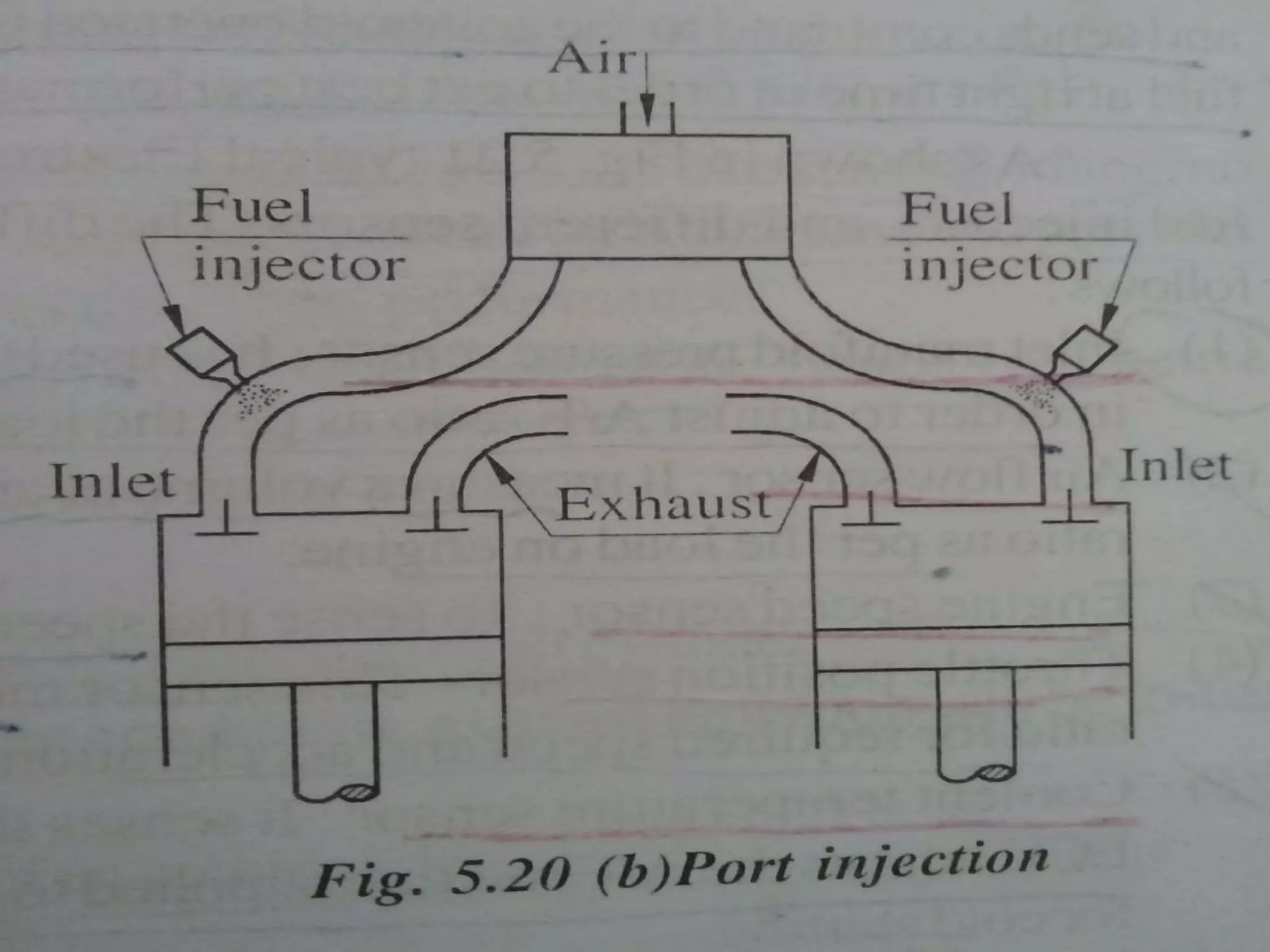
This document discusses various types of fuel injection systems used in automotive engines. It begins by explaining the differences between carburetors and fuel injection systems. It then describes several types of petrol injection systems including single point injection, throttle injection, port injection, and multi-point fuel injection. Direct injection systems are also discussed, along with their advantages such as better vaporization and higher efficiency. The document outlines the components and functioning of multi-point fuel injection systems controlled by an electronic control module. It concludes by listing some advantages and disadvantages of using petrol injection systems compared to carburetors.