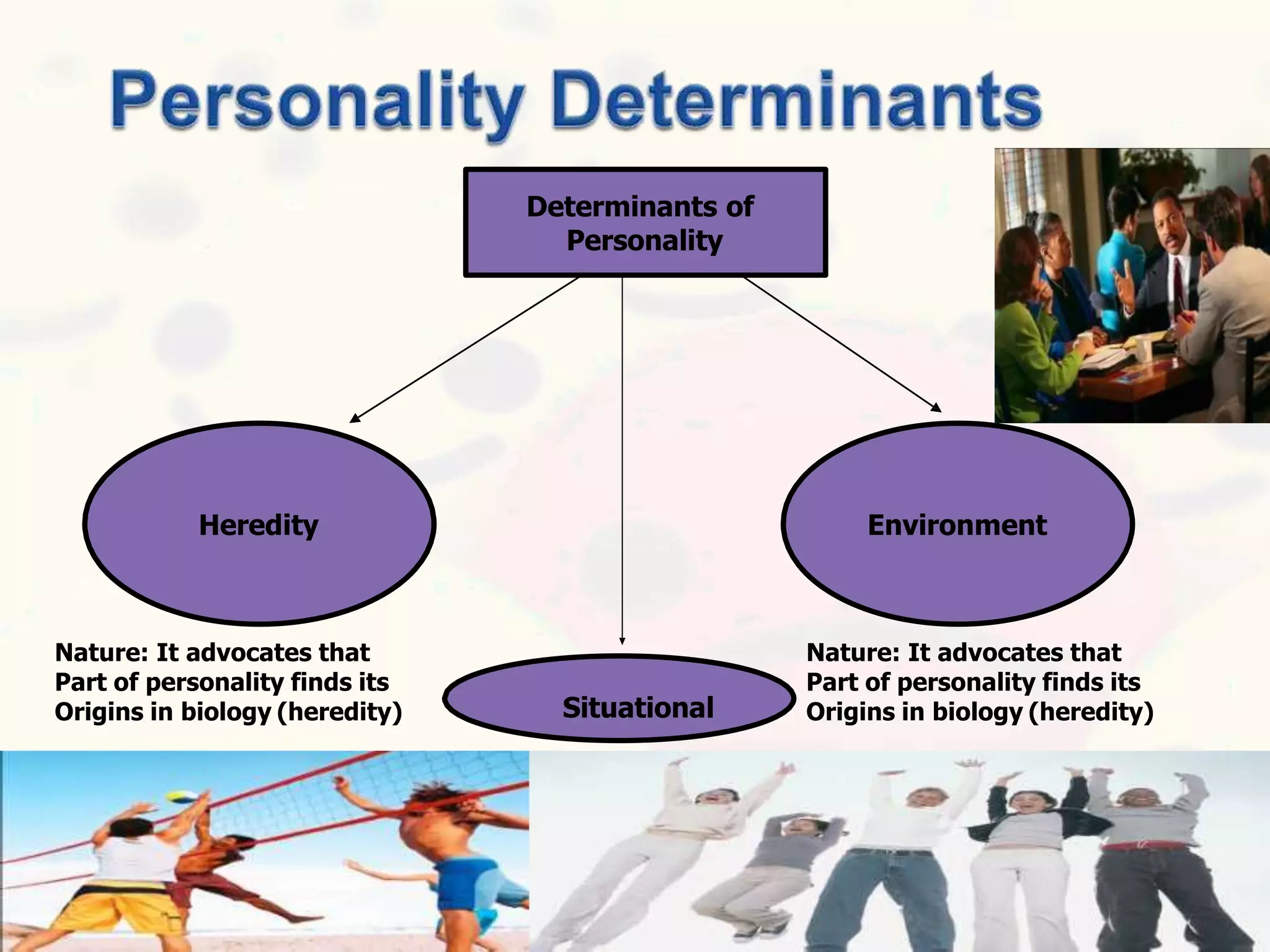
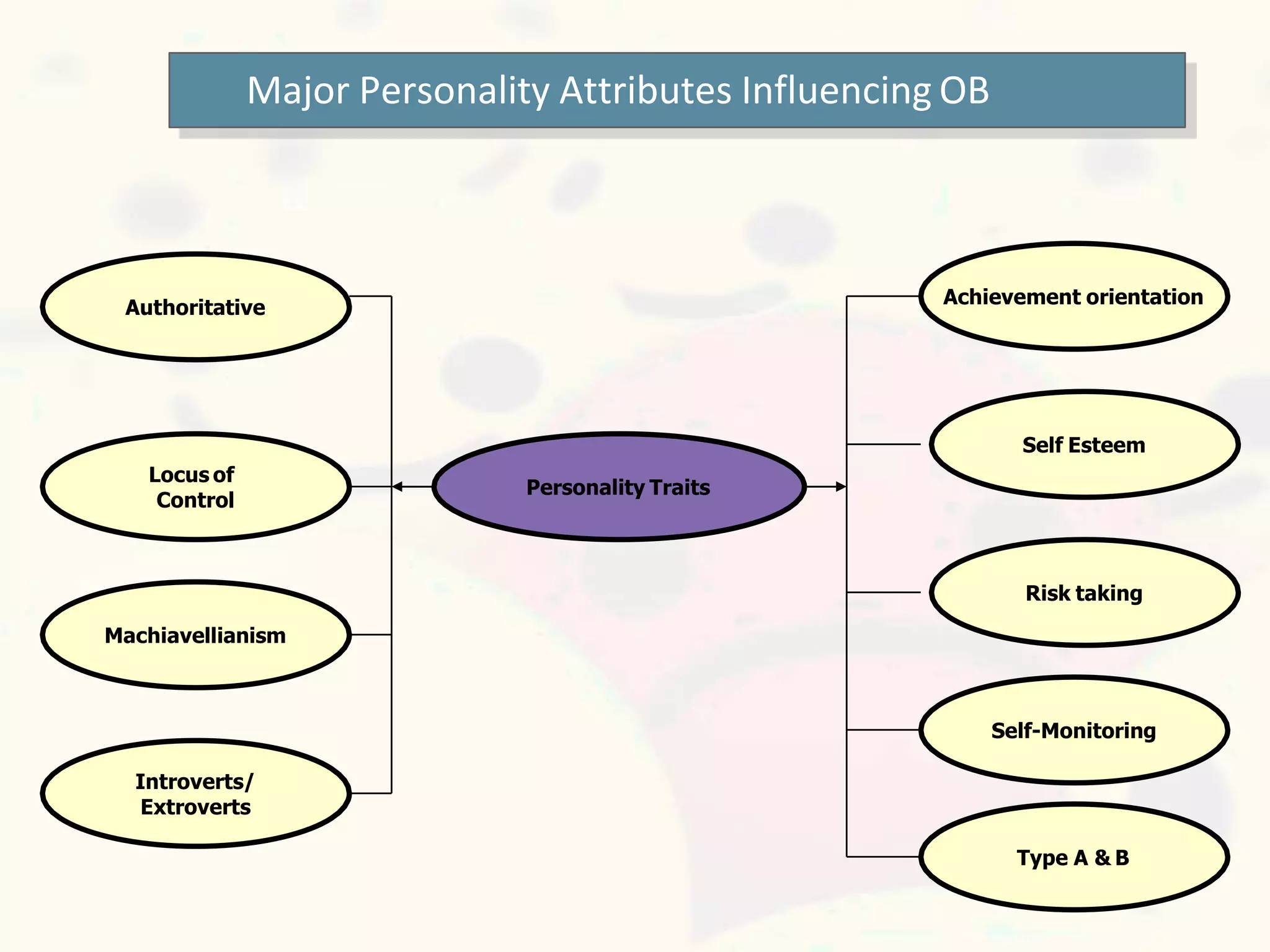
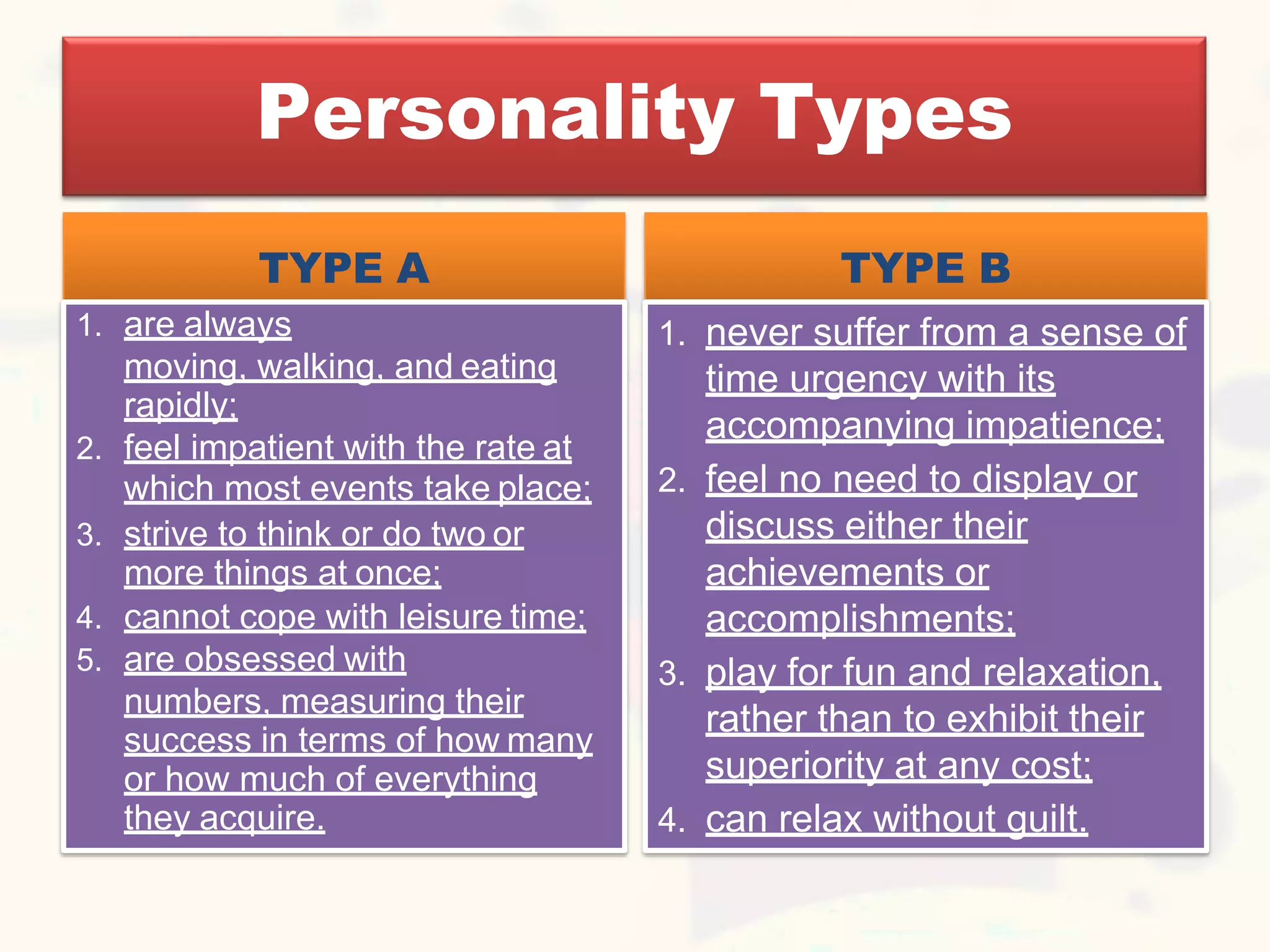
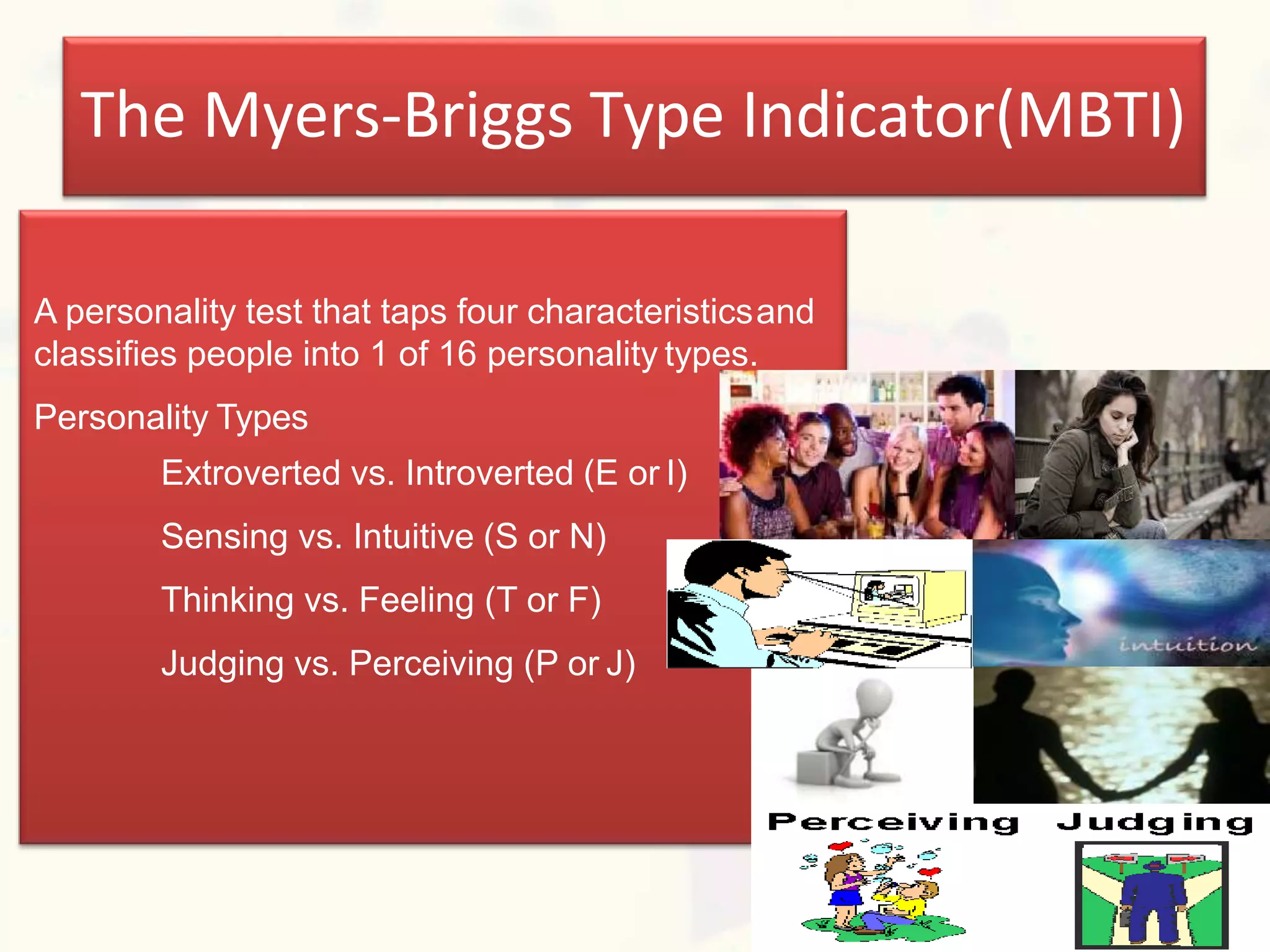
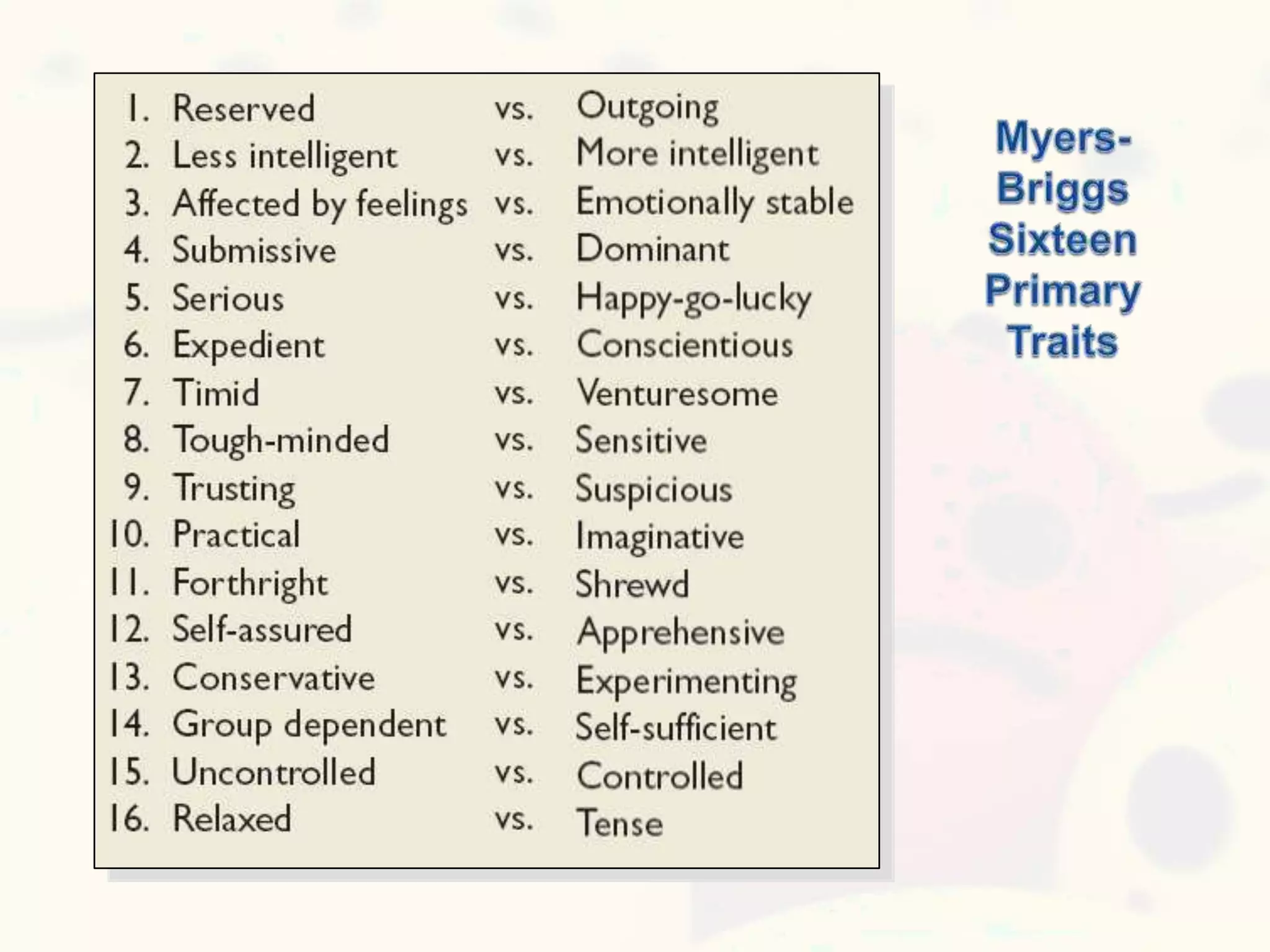
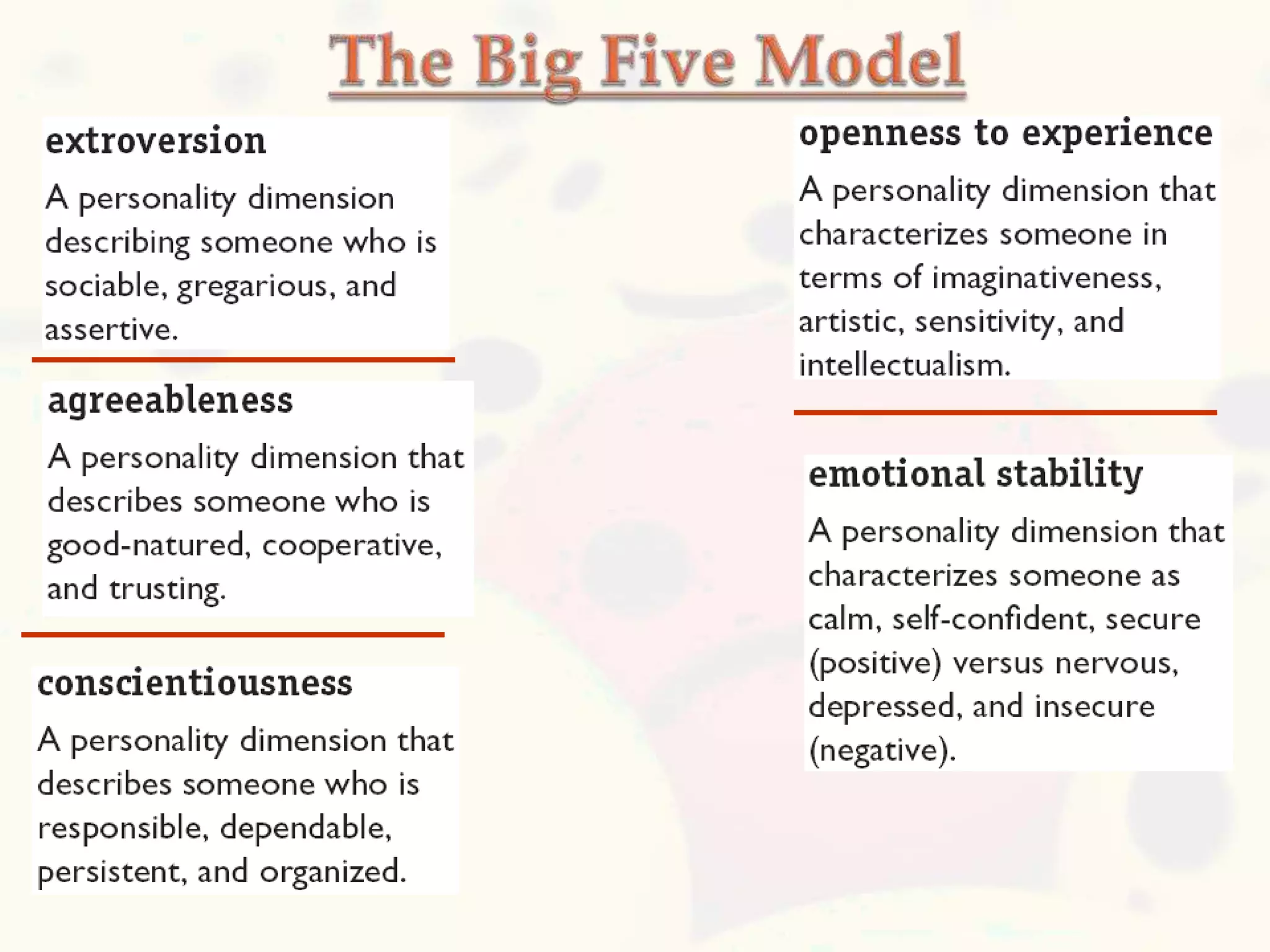
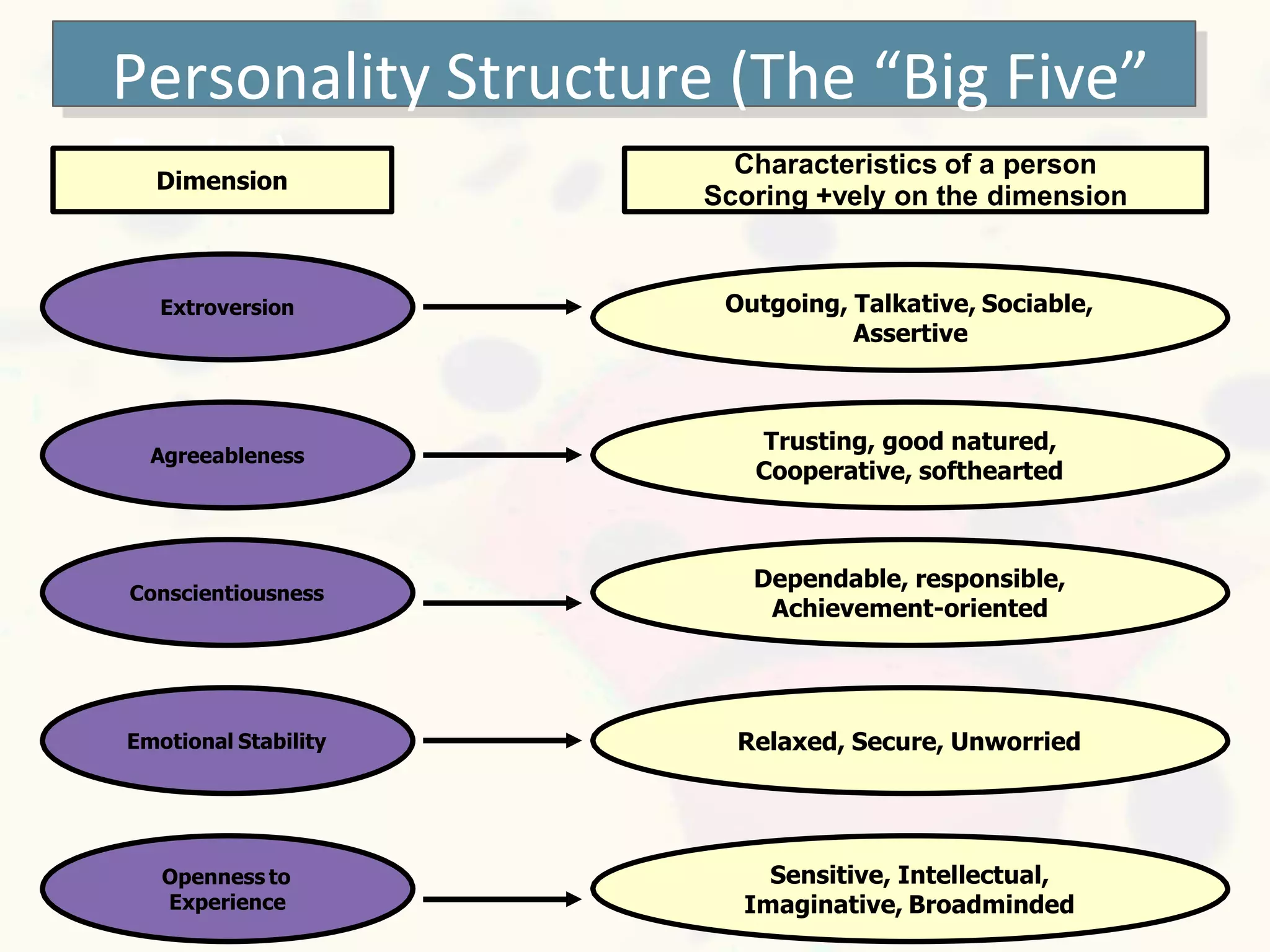
This document discusses personality and personality traits. It defines personality as a relatively stable set of characteristics that influence behavior. It notes that personality is influenced by both heredity and environment. It describes several major personality attributes that influence organizational behavior, including personality traits, locus of control, Machiavellianism, introversion/extroversion, self-esteem, risk-taking, self-monitoring, and achievement orientation. It also discusses personality types like Type A and Type B and various personality traits theories.