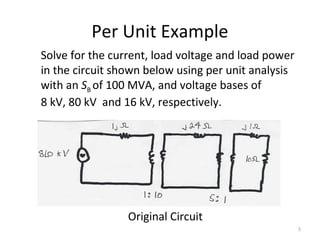
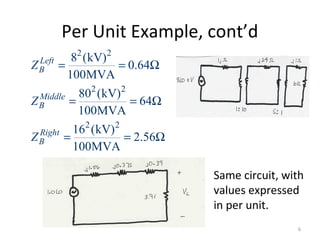
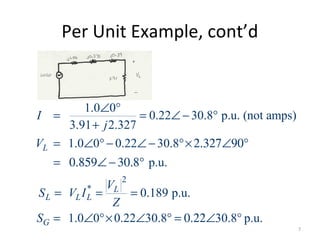
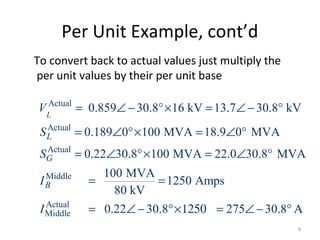
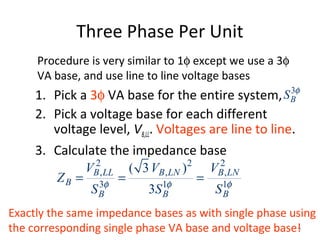
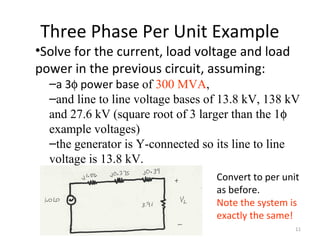
Per unit analysis is used to normalize variables in power systems to avoid difficulties in referring impedances across transformers. It involves choosing base values for voltage, power, impedance and current, then expressing all quantities as ratios of their actual to base values. This allows transformer impedances to be treated as single values regardless of which side they are referred to. It also keeps per unit quantities within a narrow range and clearly shows their relative values. The procedure is demonstrated through an example circuit solved first using single phase and then three phase per unit analysis with the same result.