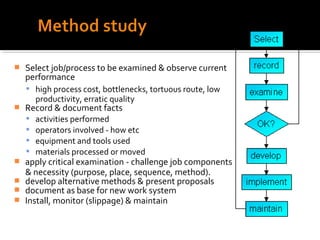
Work study and work measurement are techniques used to analyze jobs and improve efficiency. Work study involves systematically examining work processes to identify opportunities for more efficient procedures. This includes analyzing factors that impact efficiency and seeking improvements. Work measurement determines the time required to complete tasks by measuring tasks being performed and setting standard times. The goals are to establish efficient work flows, reduce costs, improve productivity and working conditions, and deliver benefits for employees and customers.