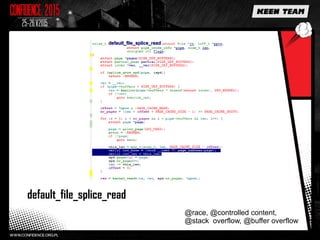
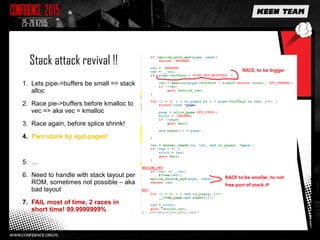
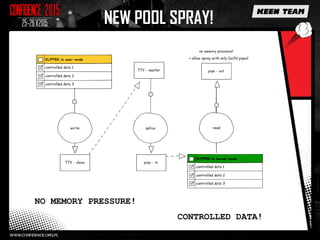
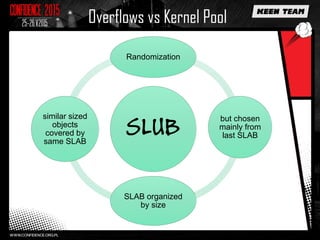
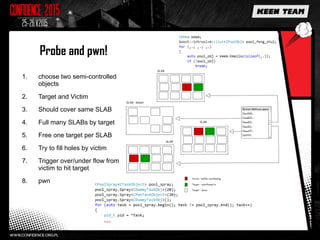
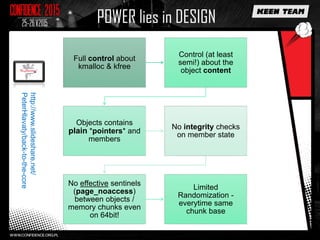
This document discusses various overflow issues that can occur with the splice and vmsplice Linux kernel functions. It describes stack and buffer overflows that can happen due to race conditions when accessing pipe buffers. It also proposes a pool overflow technique using SLUB memory and controlled data read from a TTY device to spray the kernel memory and potentially overflow adjacent objects. Finally, it notes that further research is needed to determine a suitable target and exploit methodology, and hints that pipe buffer sizes may allow overflowing kernel memory allocations.
















![KEEN TEAM - TECHNIQUES
Isolated heap bypass [ blog – MS14-056 ]
CC-shellcoding framework [ nosuchcon ]
Webkit exploitation [ cansecwest ]
VadRoot (vm_area) + PageTable pwn [ syscan ]
Pool spray tech [ confidence ]
1bit flip - kernel escape (kernel code exec) [ recon ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overflow-150525165217-lva1-app6892/85/When-is-something-overflowing-34-320.jpg)


