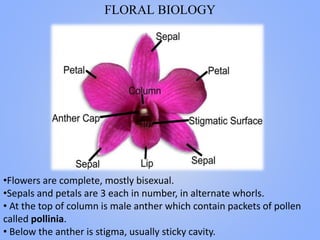
This document provides information on breeding of orchids. It begins with the classification, origin, and description of orchids. It then discusses the vegetative growth, floral biology, and important orchid species. The objectives and methods of orchid breeding are outlined, including hybridization, mutation breeding, polyploidy breeding, and biotechnology. Specific hybrids resulting from these methods are presented for various orchid genera. International ruling varieties are also listed.