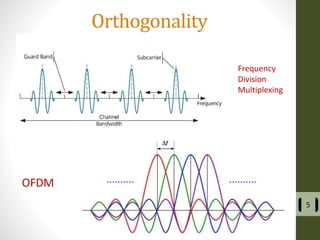
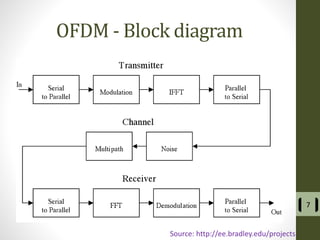
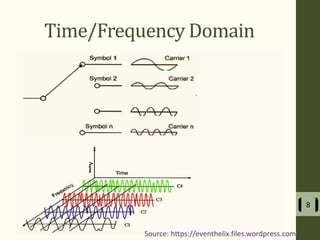
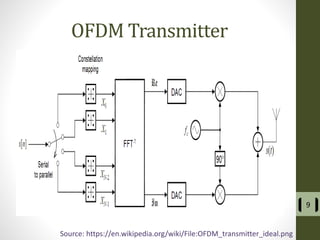
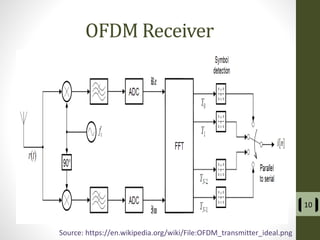
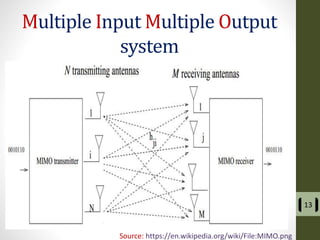
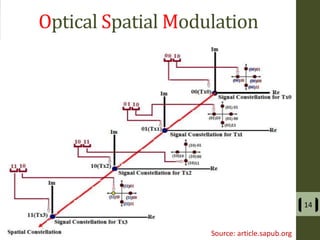
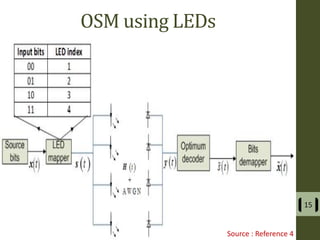
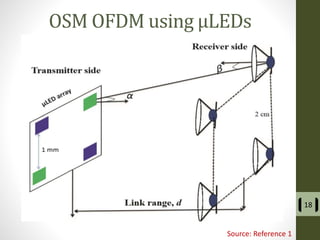
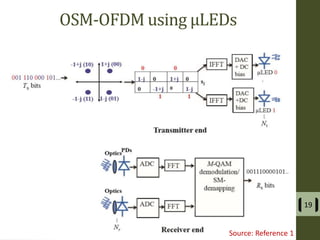
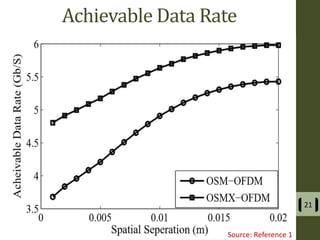
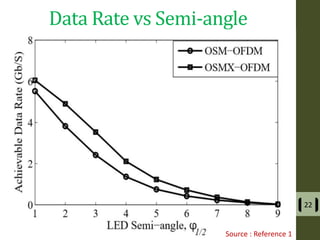
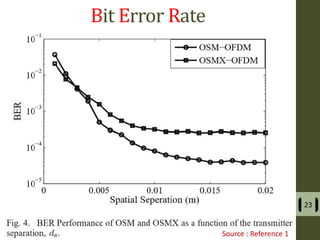
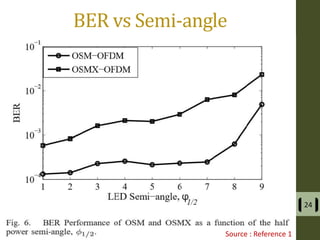
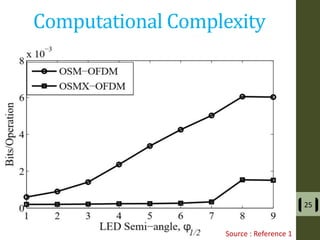
The document presents a detailed examination of optical spatial modulation OFDM using micro LEDs, covering key concepts such as OFDM, visible light communication, and multi-input multi-output systems. It highlights the advantages of micro LEDs over traditional LEDs, including faster flicker rates and higher quantum efficiencies, and discusses the achieved data rates and bit error rates associated with this technology. The findings indicate that osm-OFDM using micro LEDs can achieve a data rate of up to 5.5 Gb/s, outperforming other methods in terms of computational complexity.