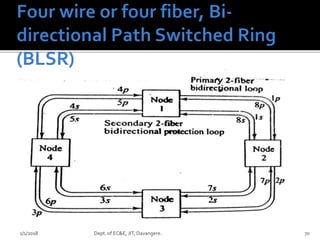
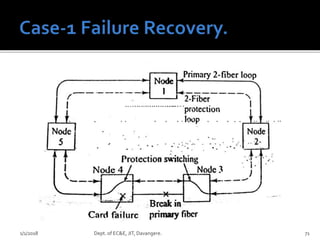
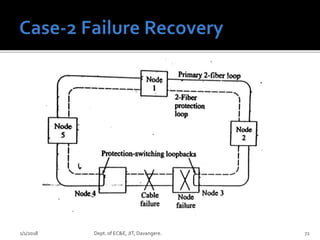
The document discusses optical amplifiers and optical networks. It covers several topics:
- The basic applications and types of optical amplifiers including semiconductor optical amplifiers and erbium-doped fiber amplifiers.
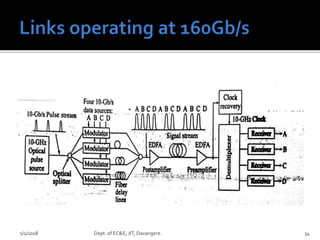
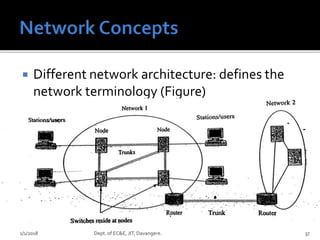
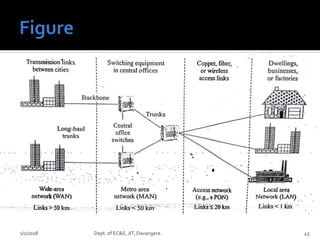
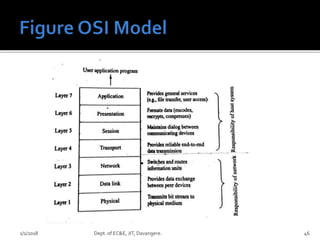
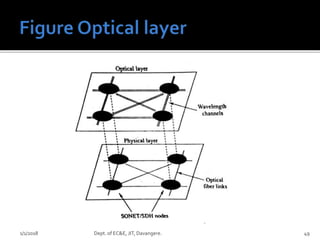
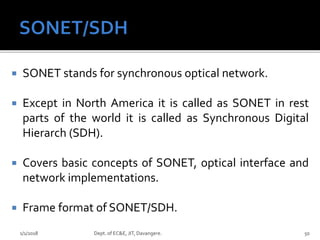
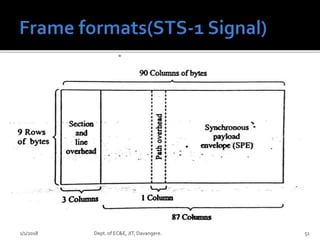
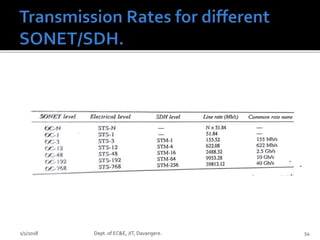
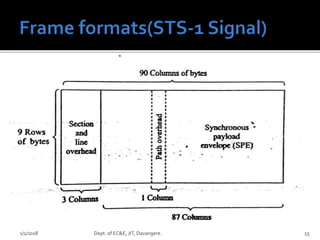
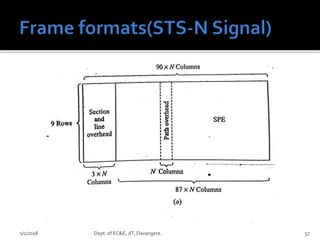
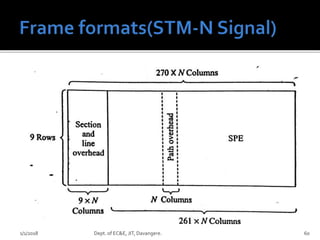
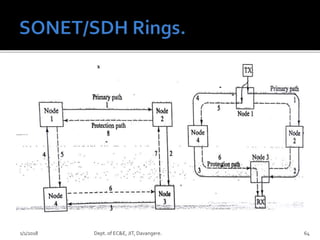
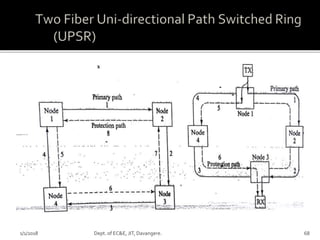
- Key concepts of optical networks including SONET/SDH networks, optical interfaces, and high-speed lightwave transmission.
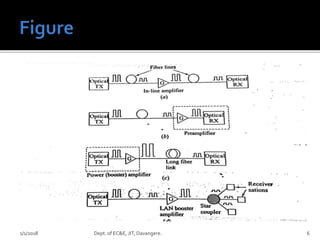
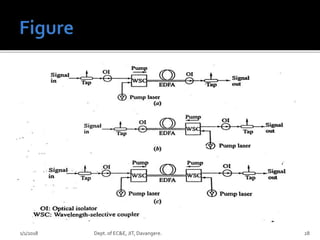
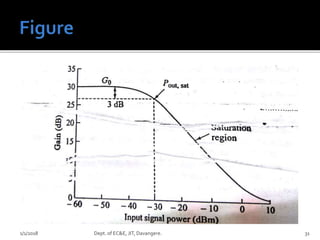
- The operation and applications of different types of optical amplifiers used in optical networks, including inline, pre, and power amplifiers. The document provides details on EDFA, SOA, and Raman amplifiers.