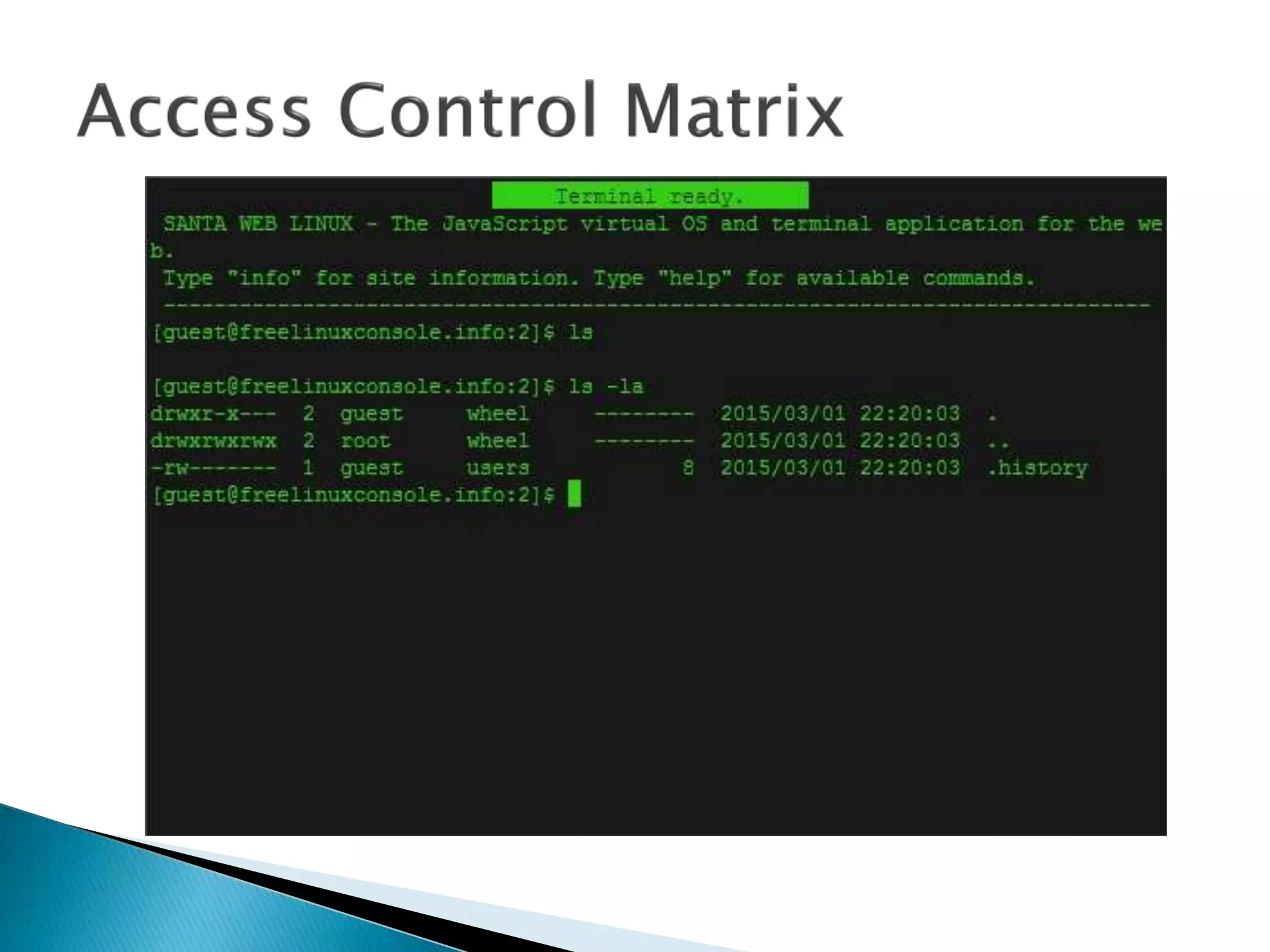
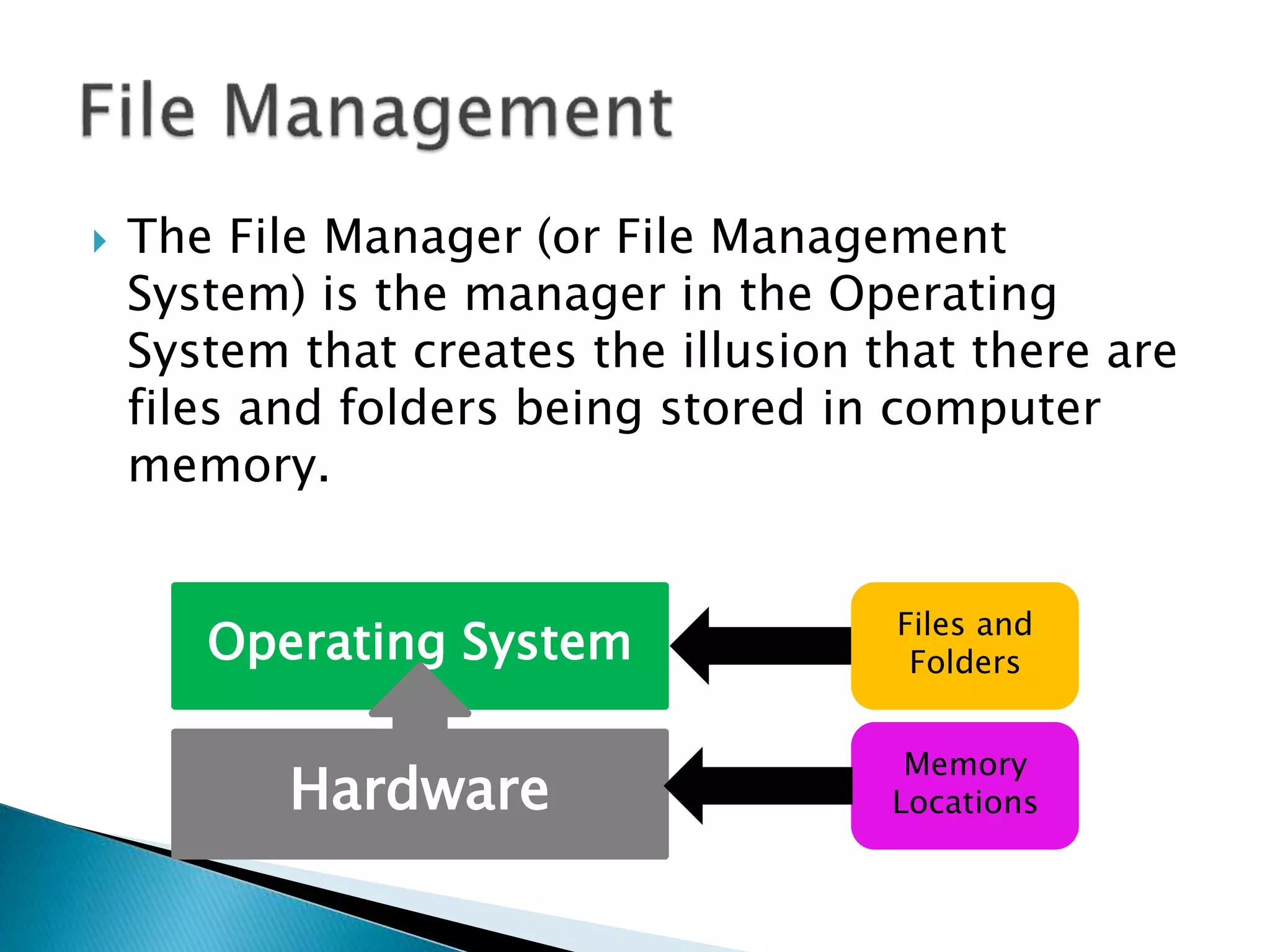
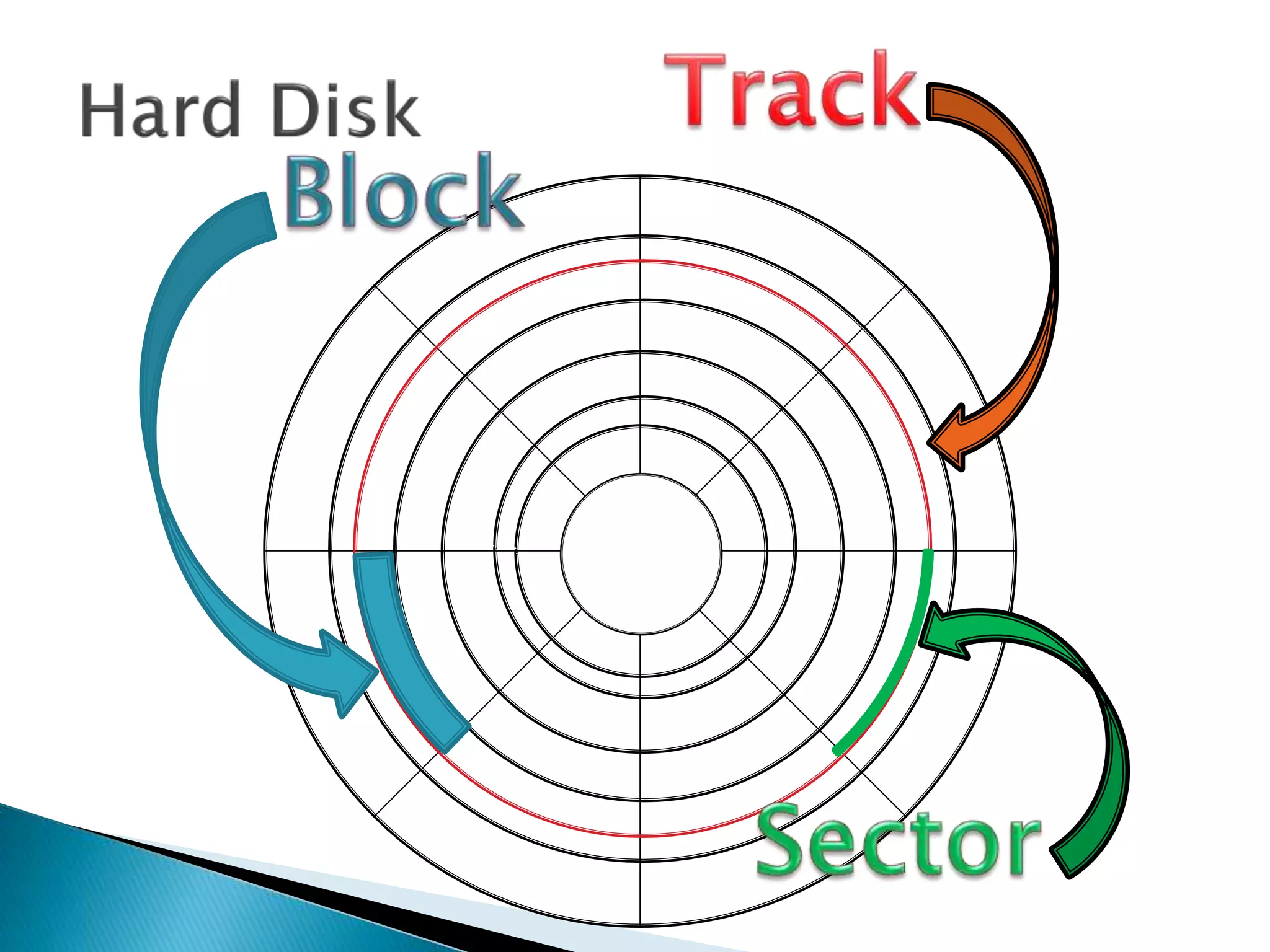
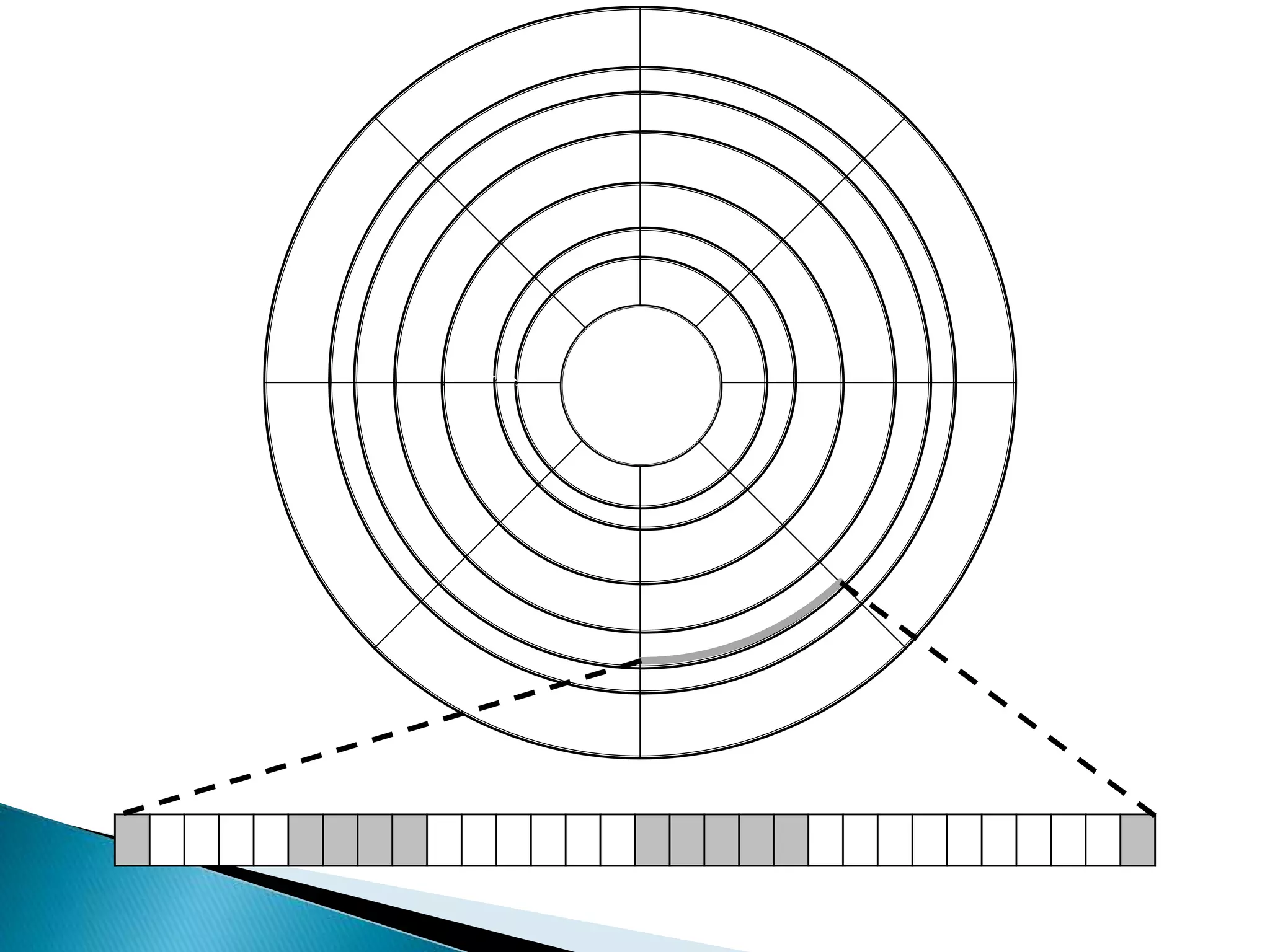
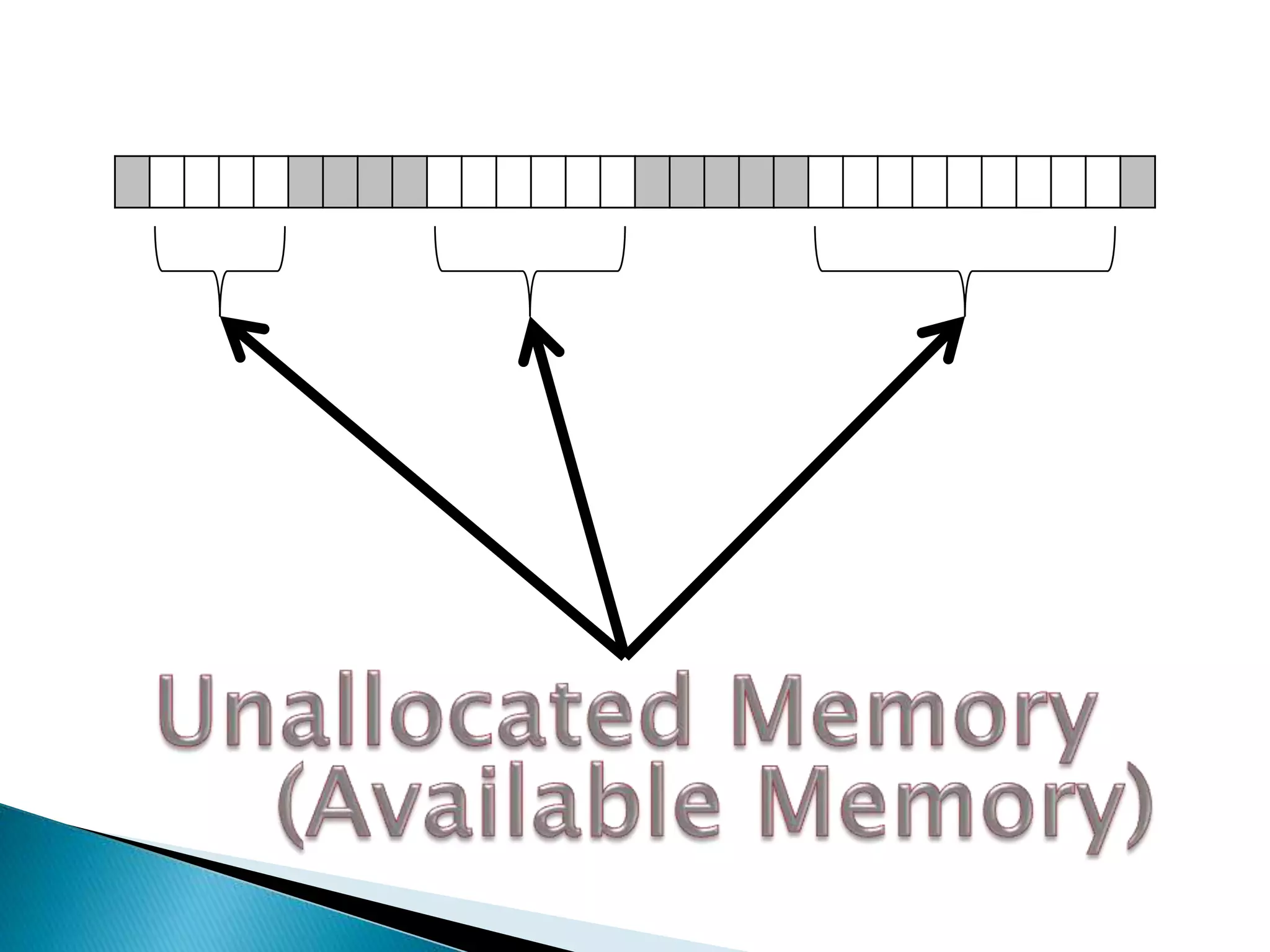
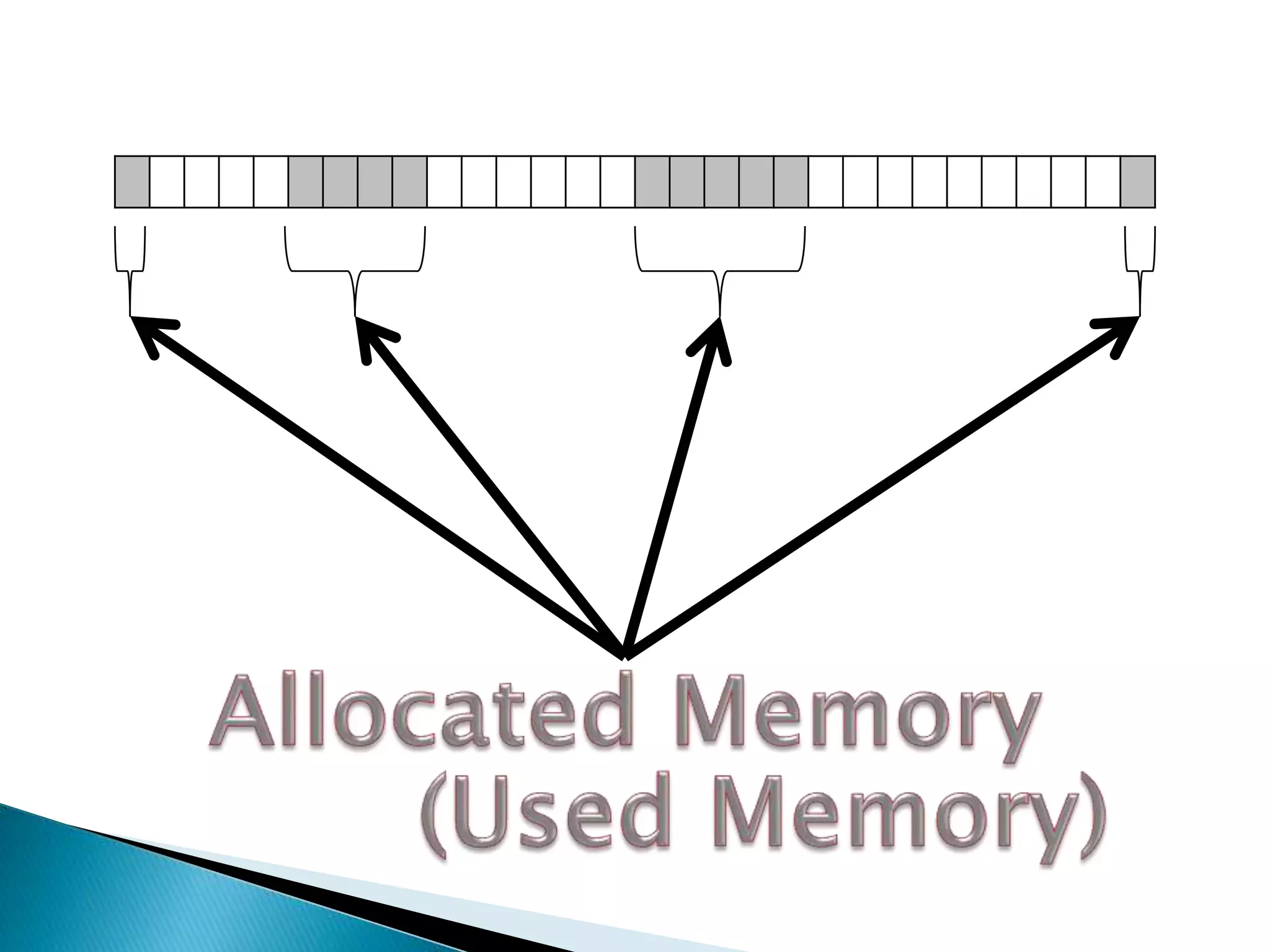
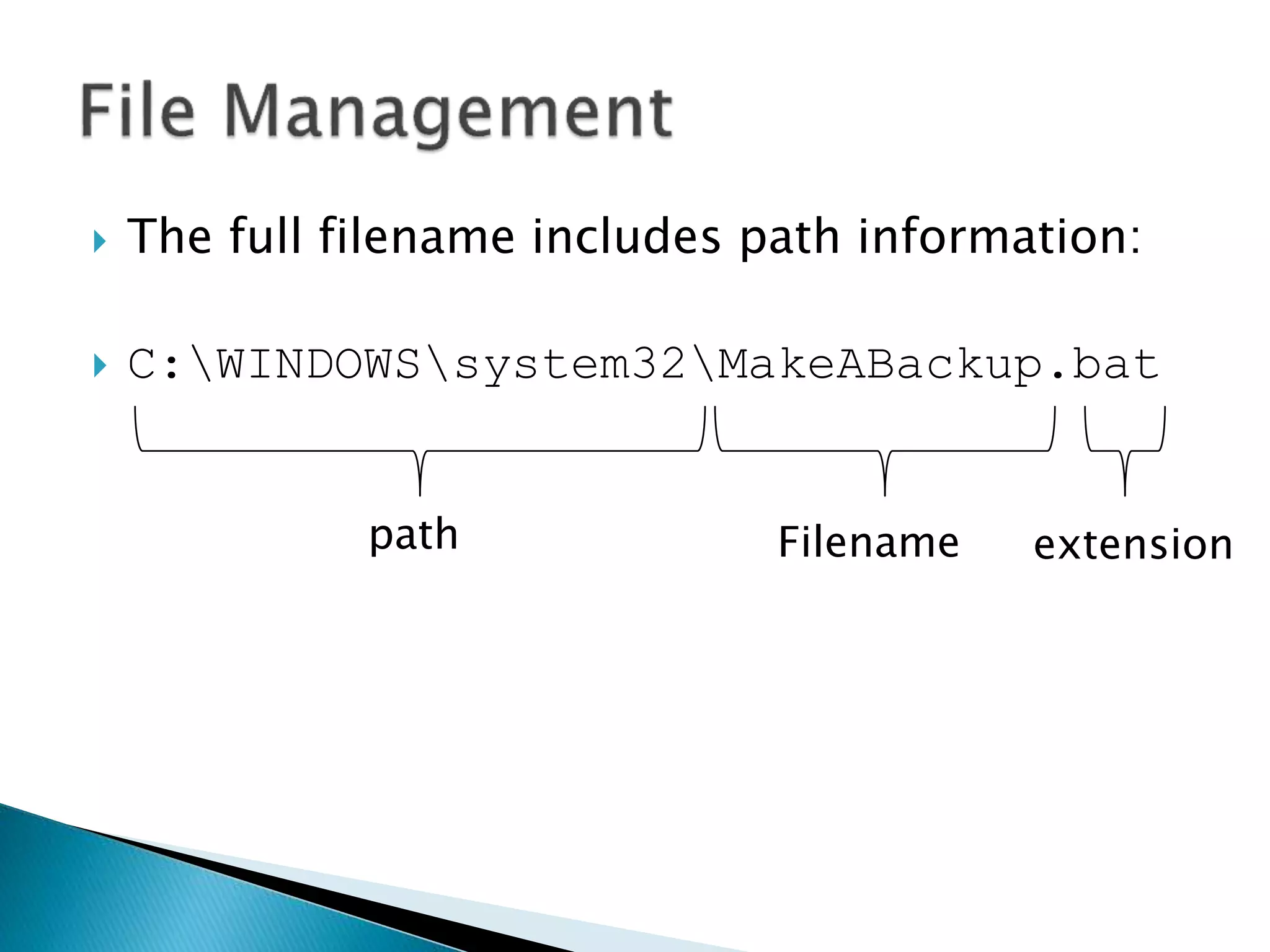
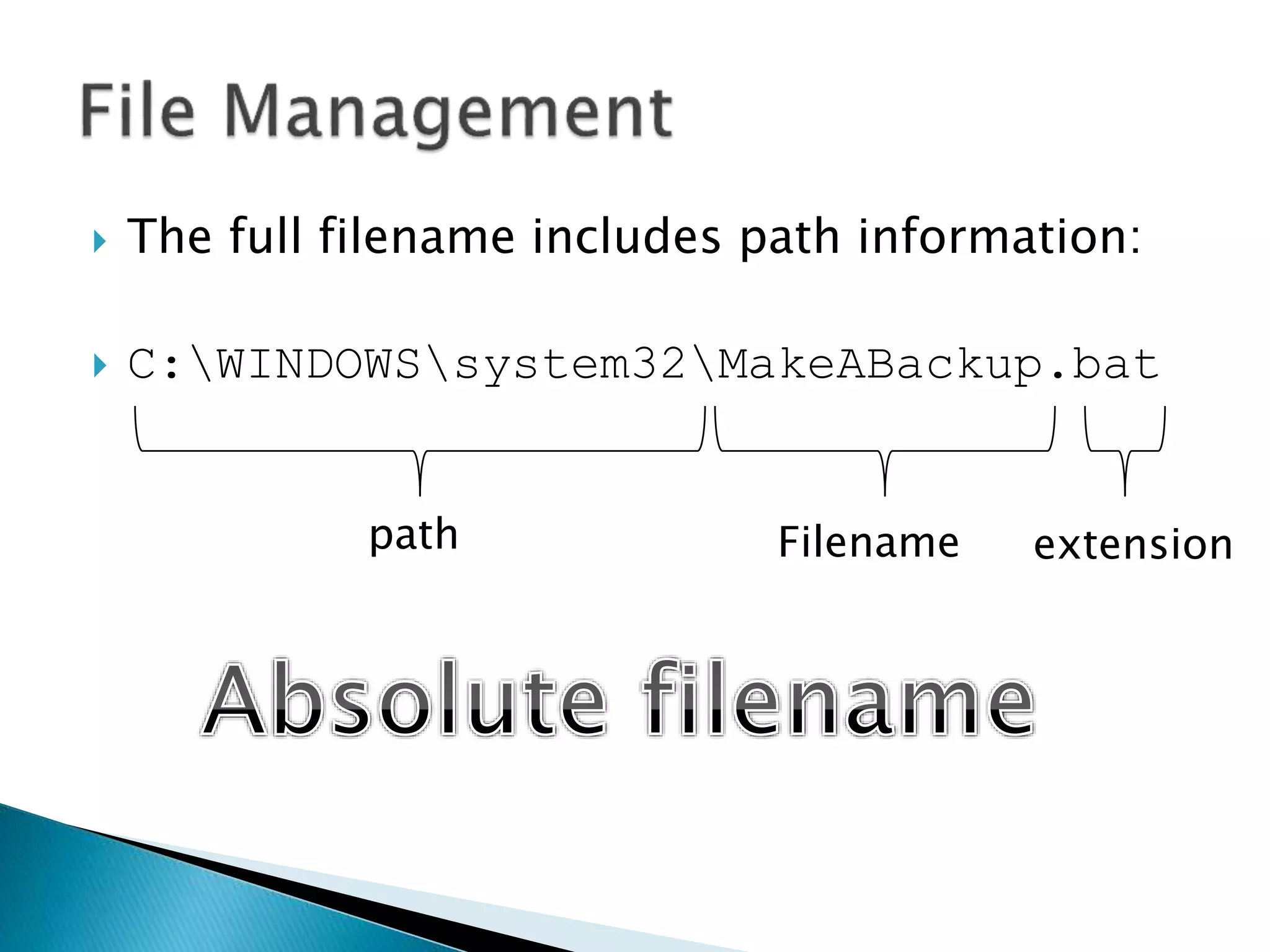
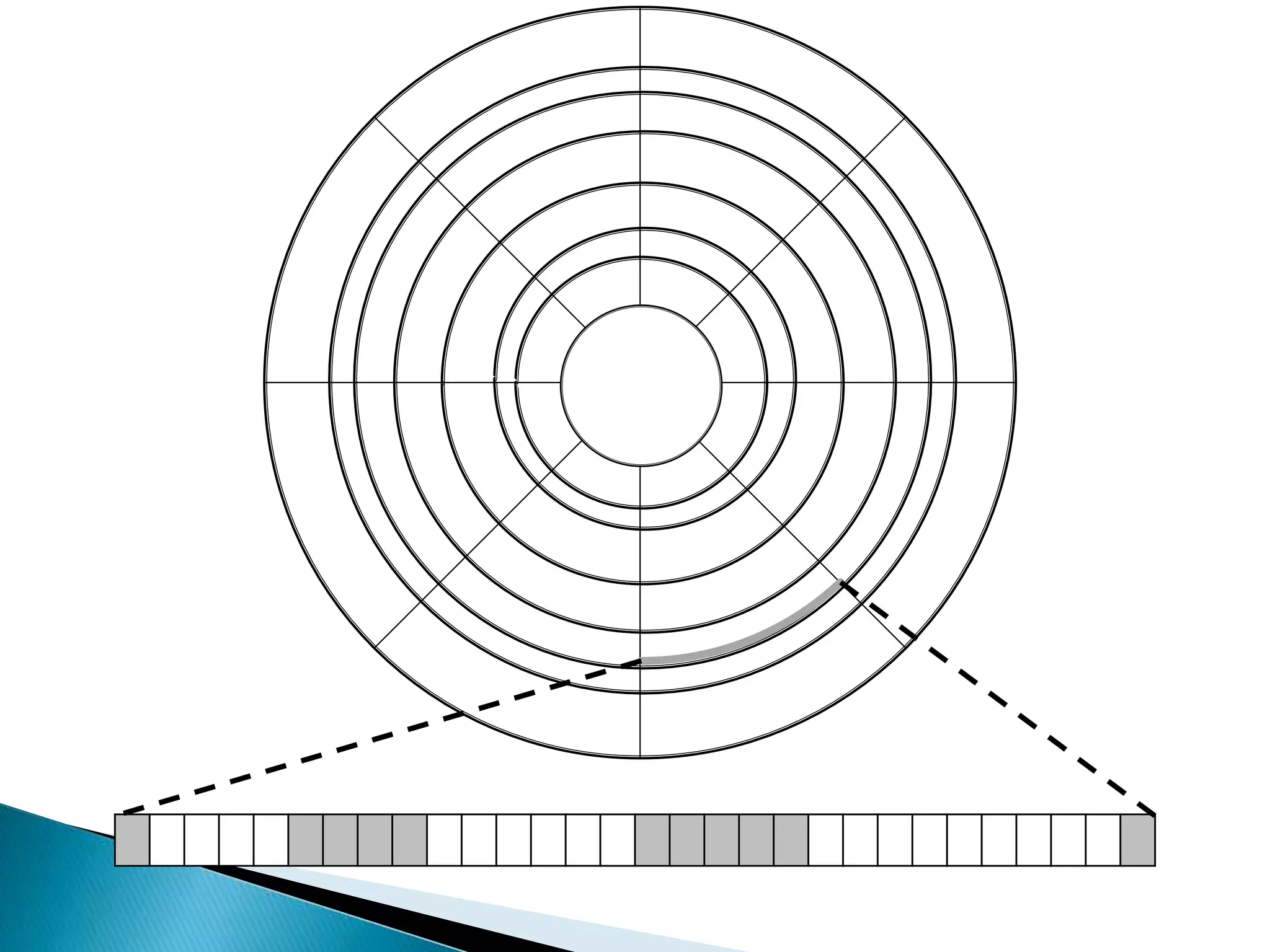
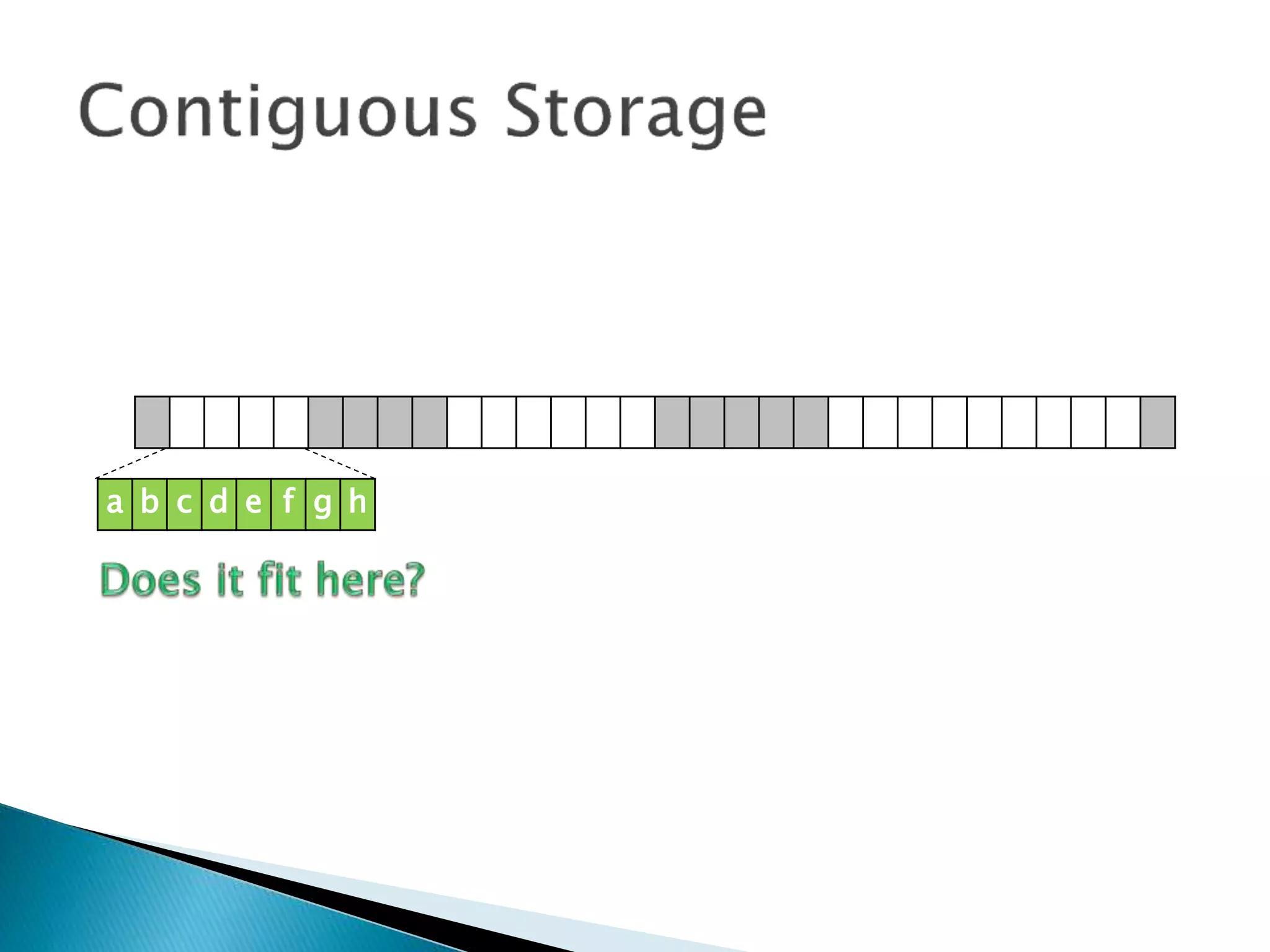
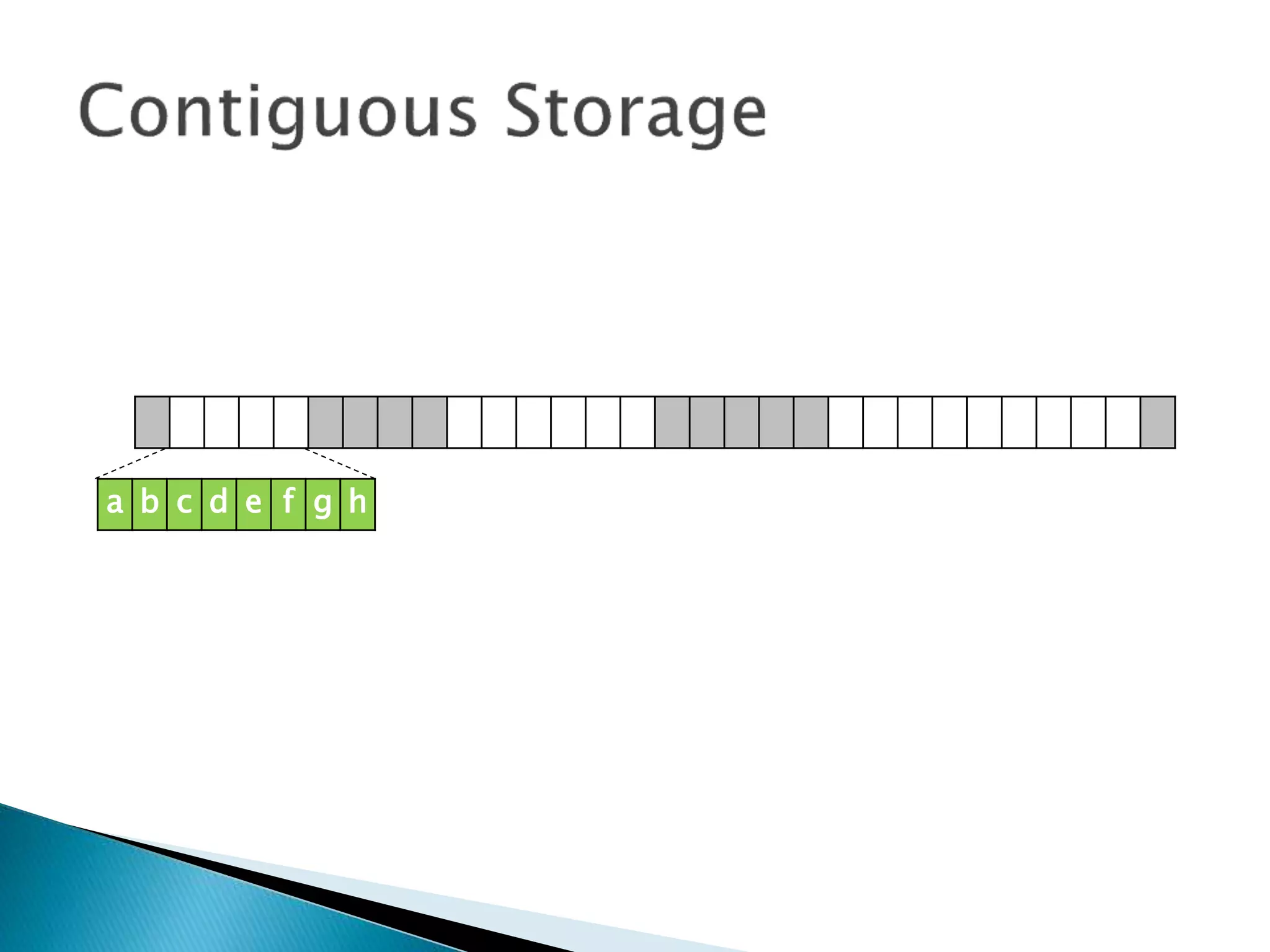
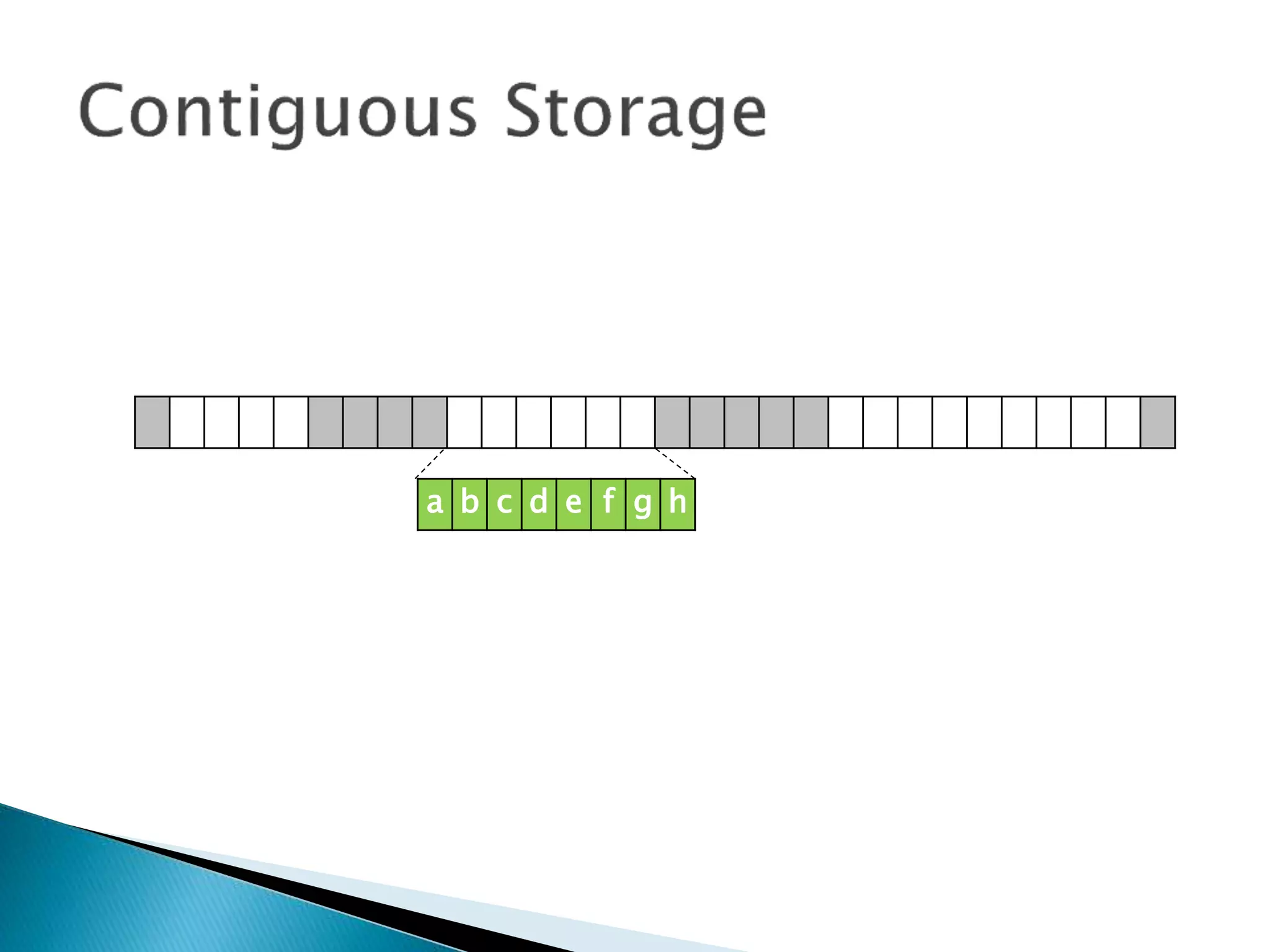
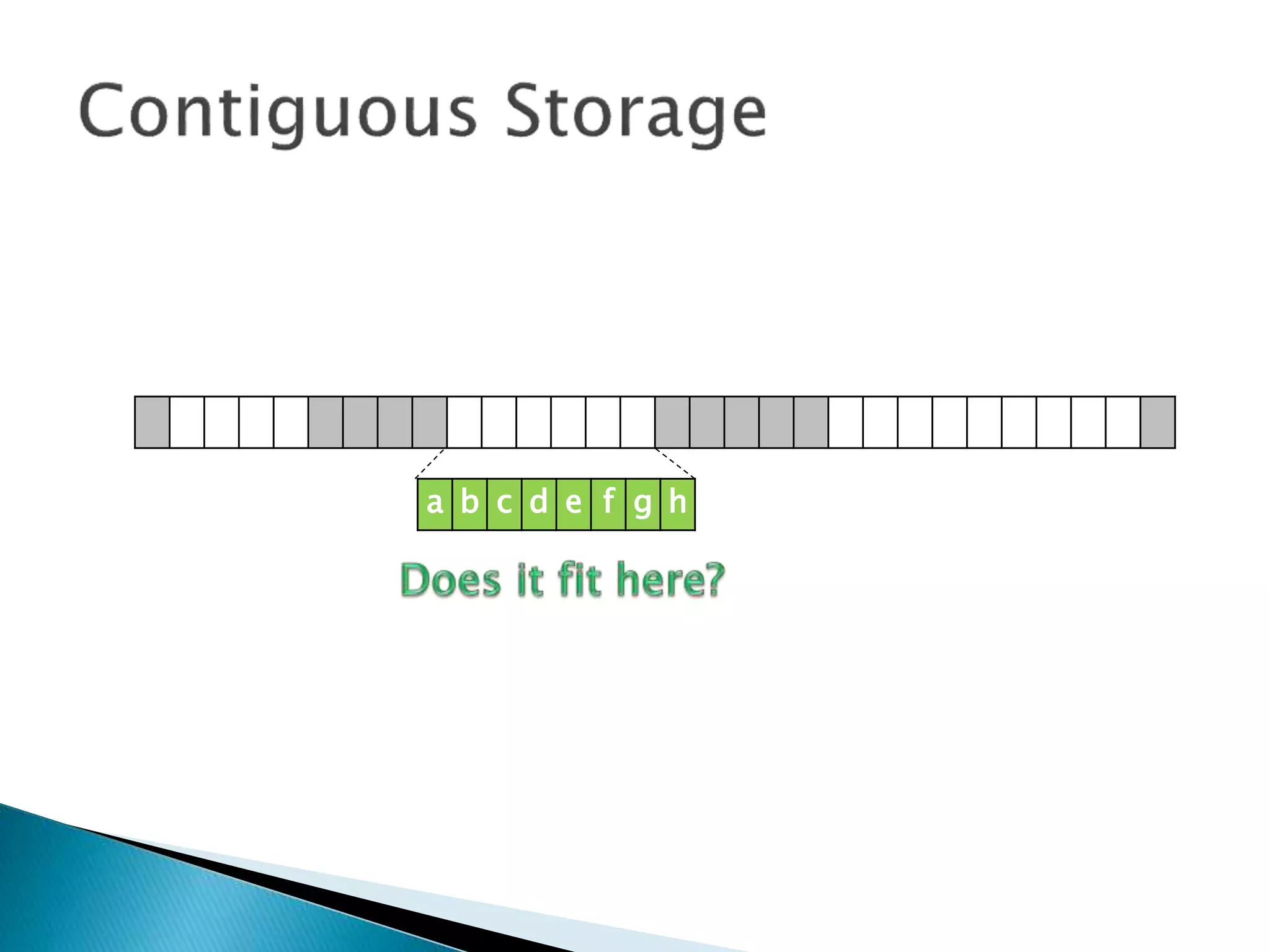
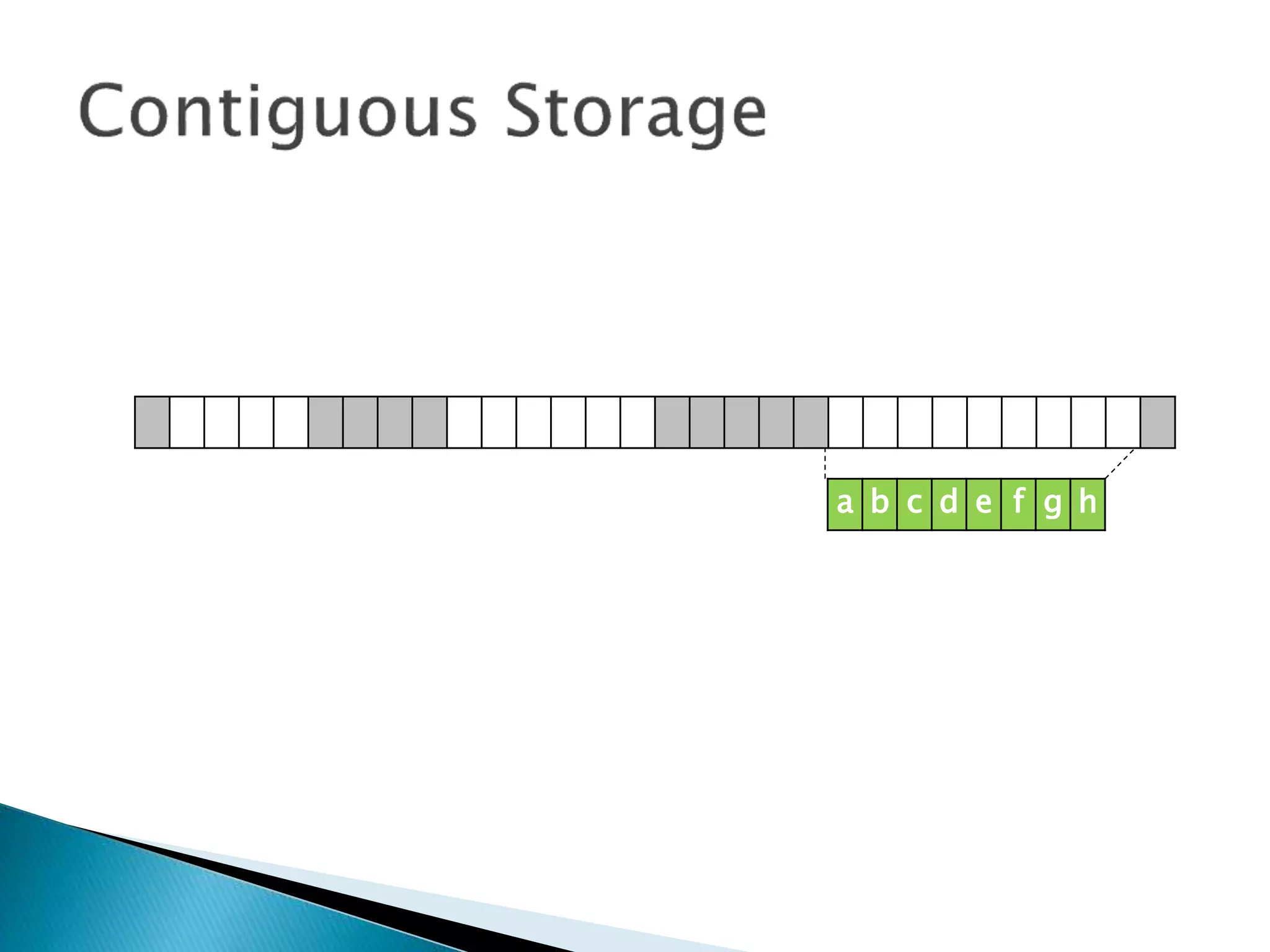
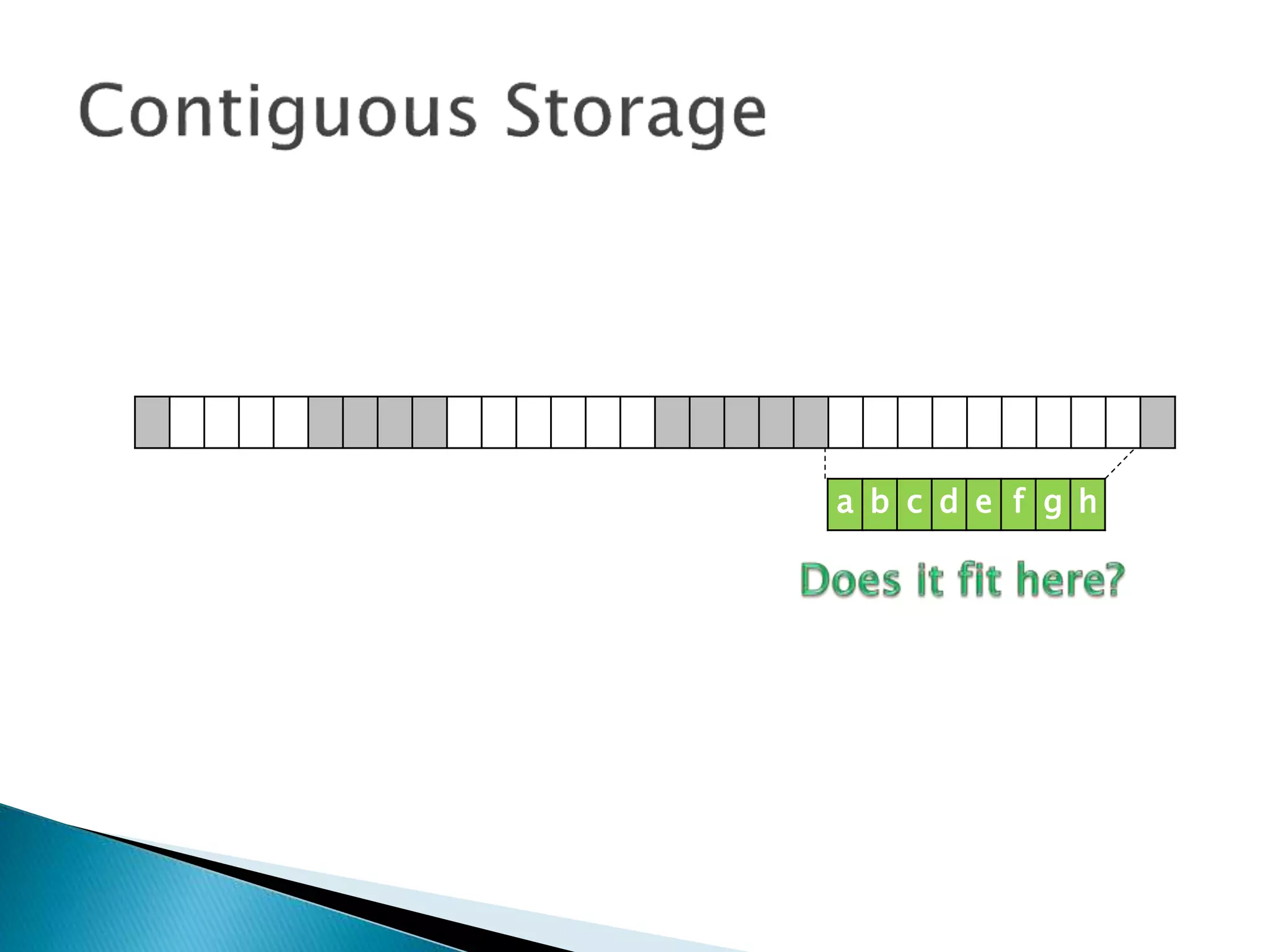
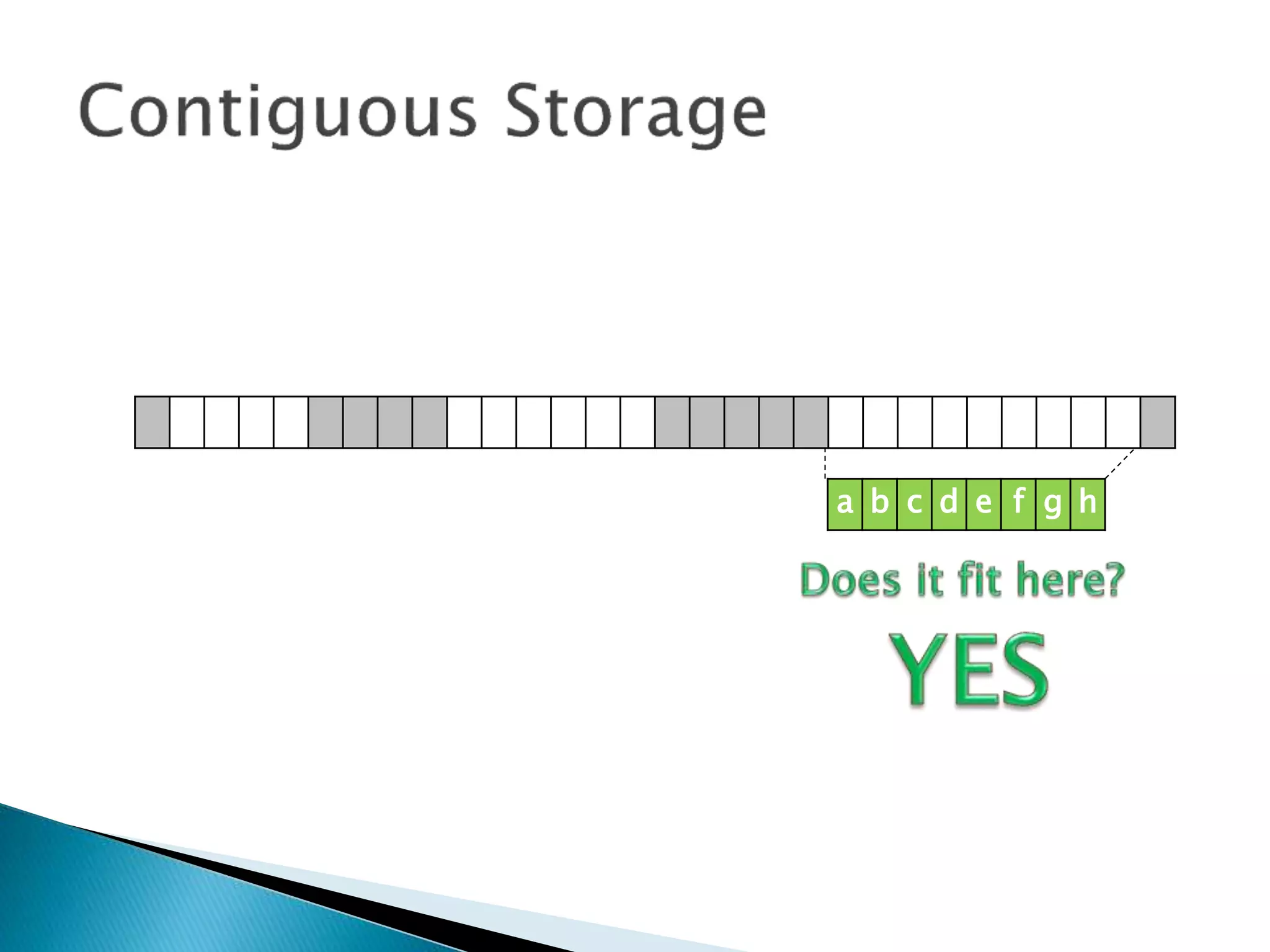
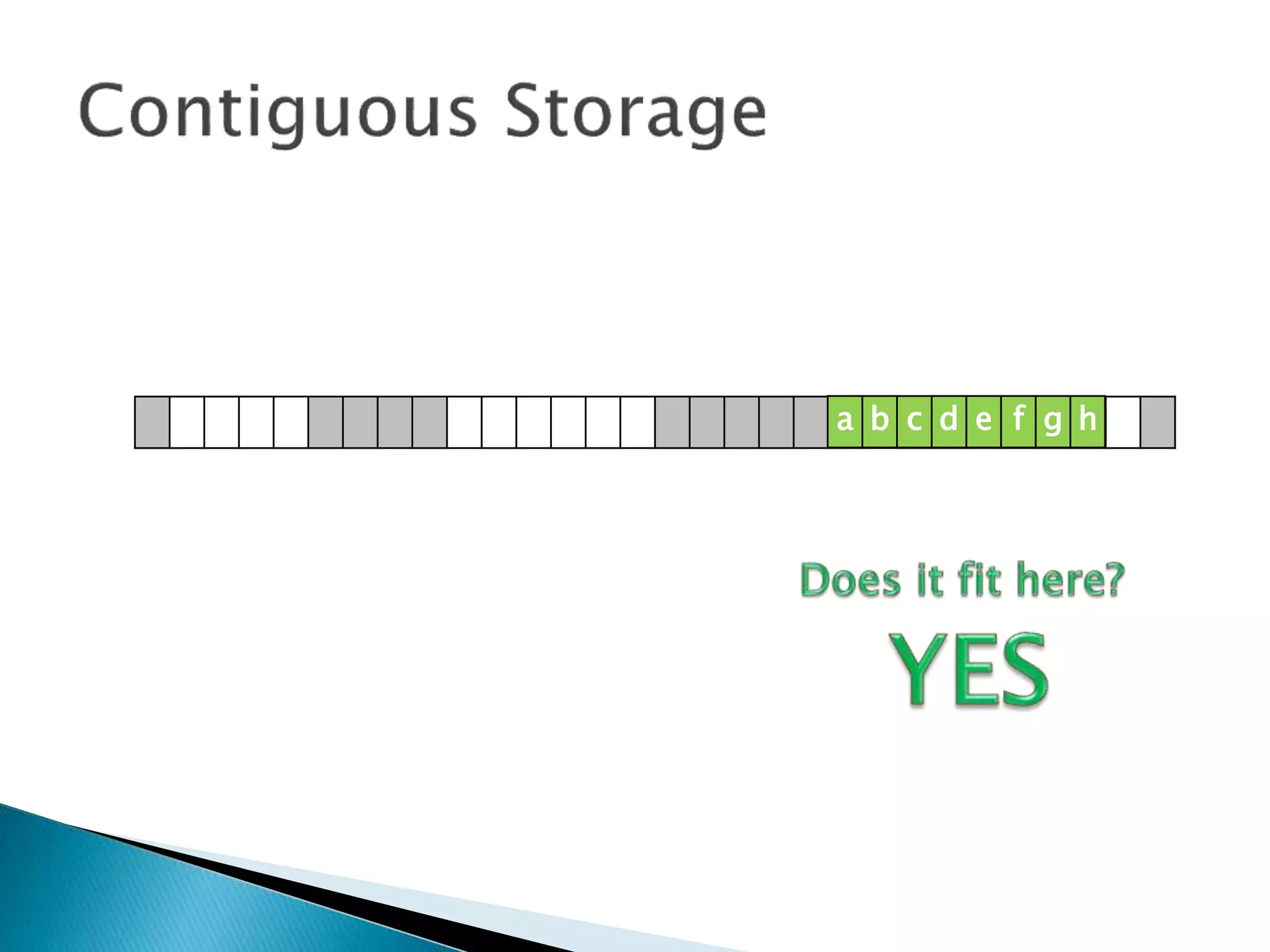
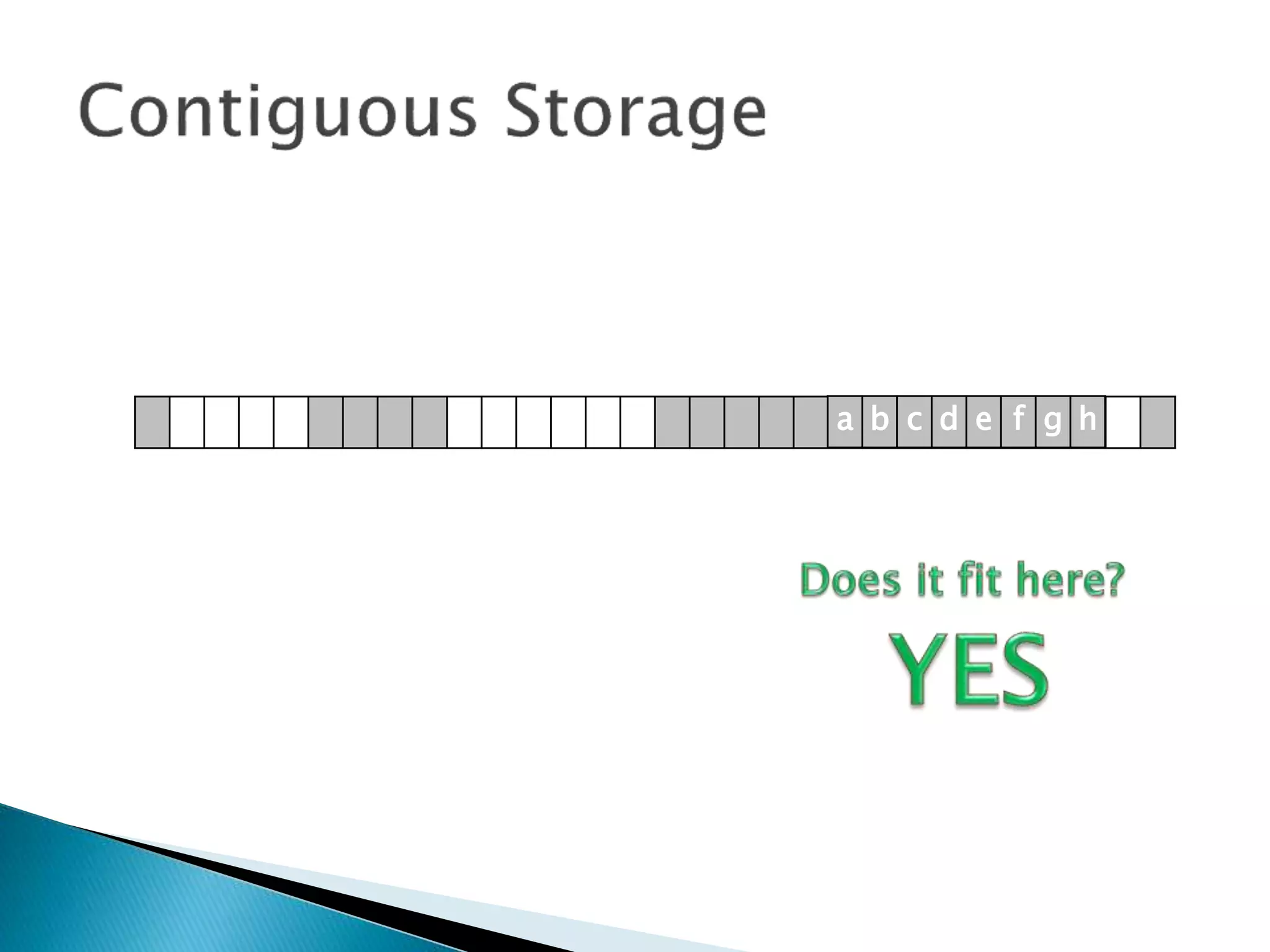
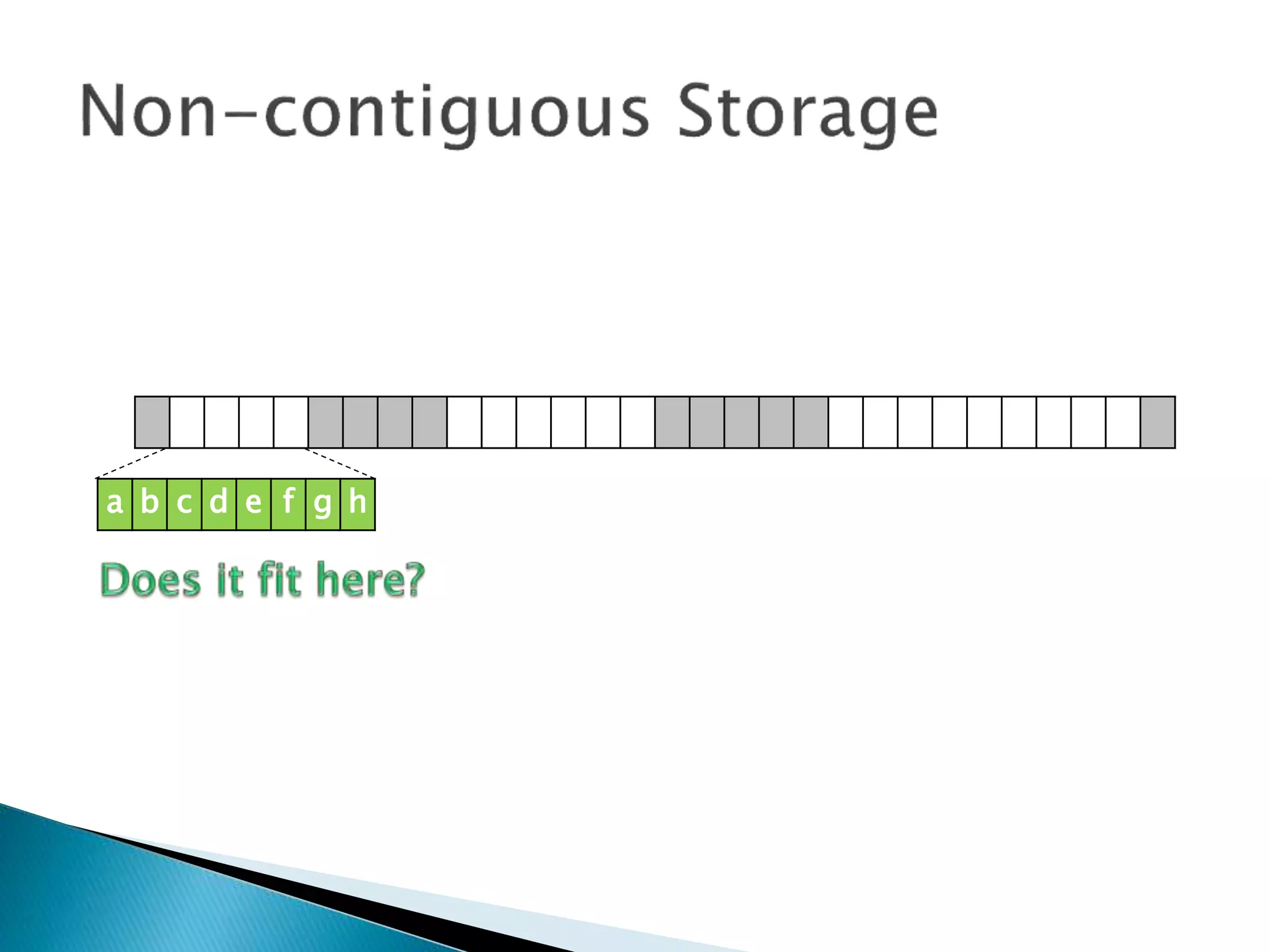
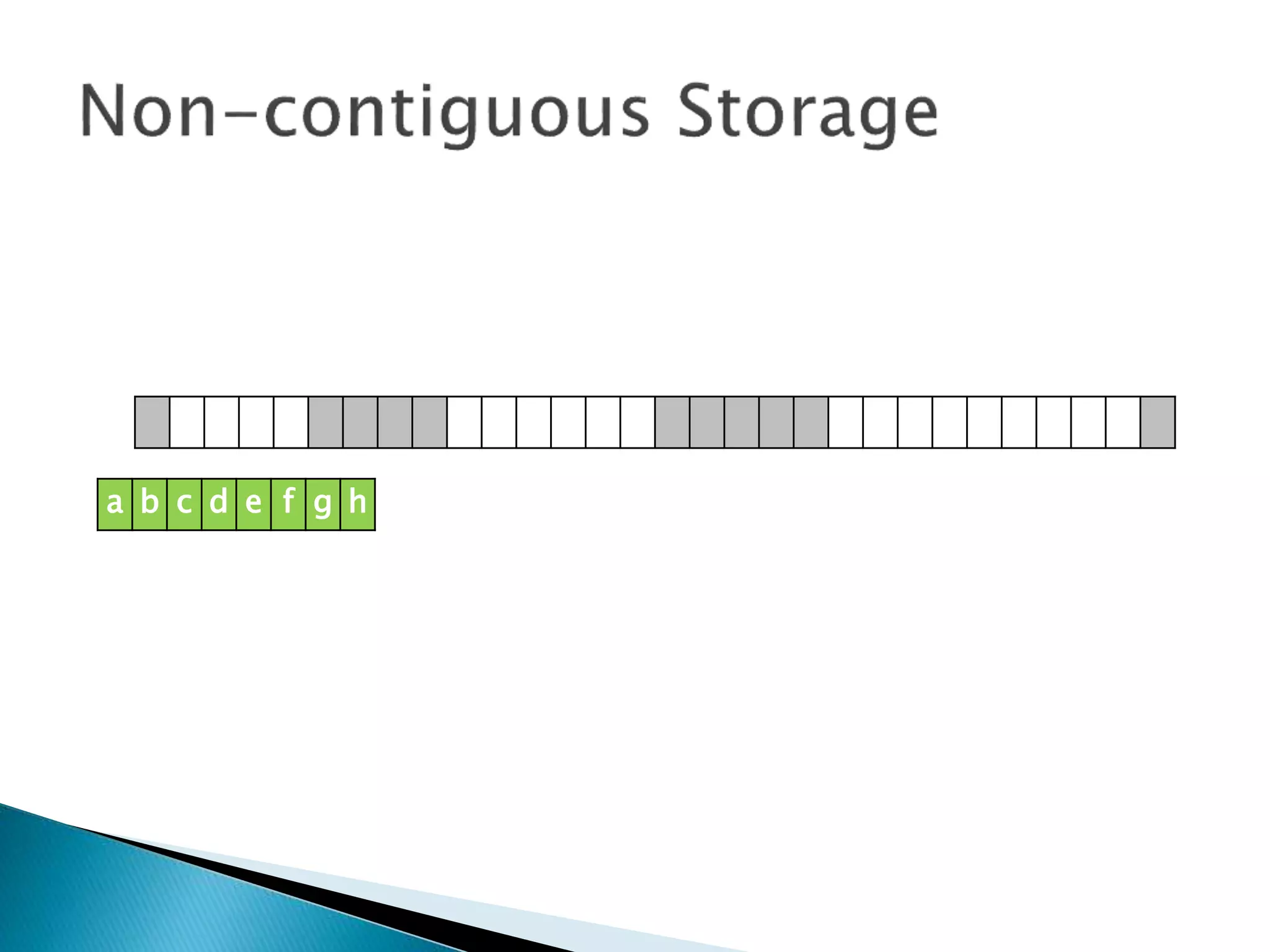
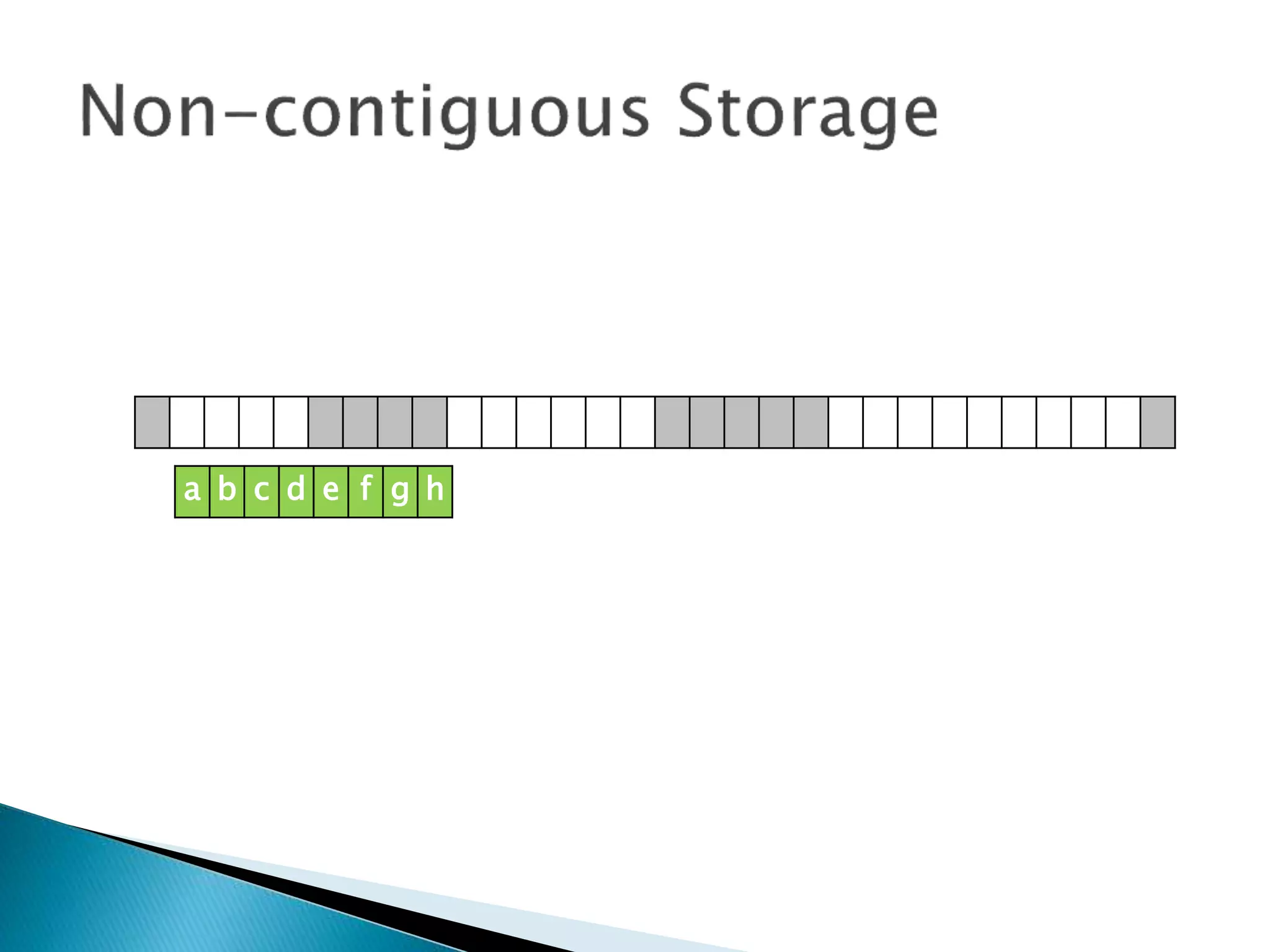
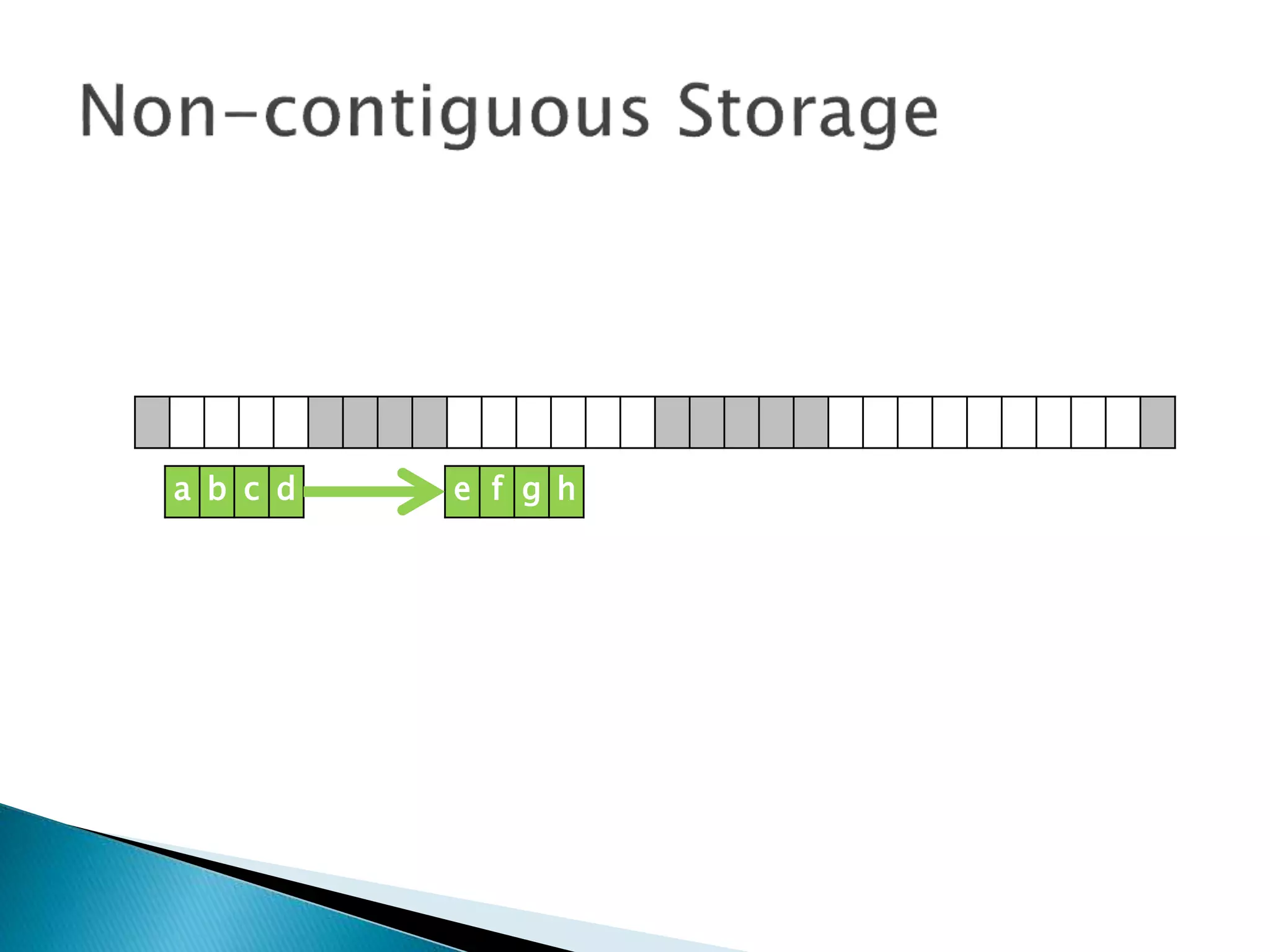
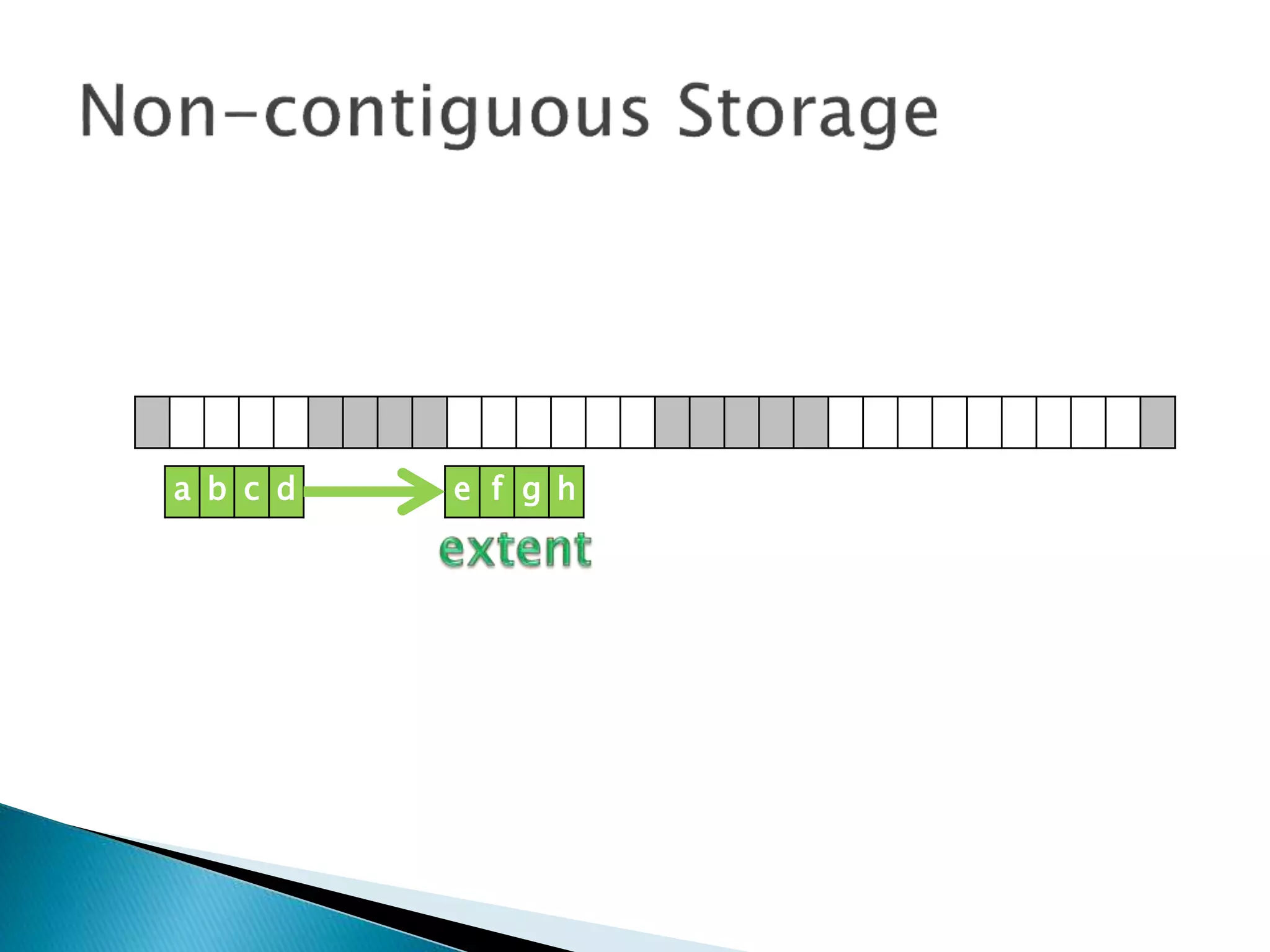
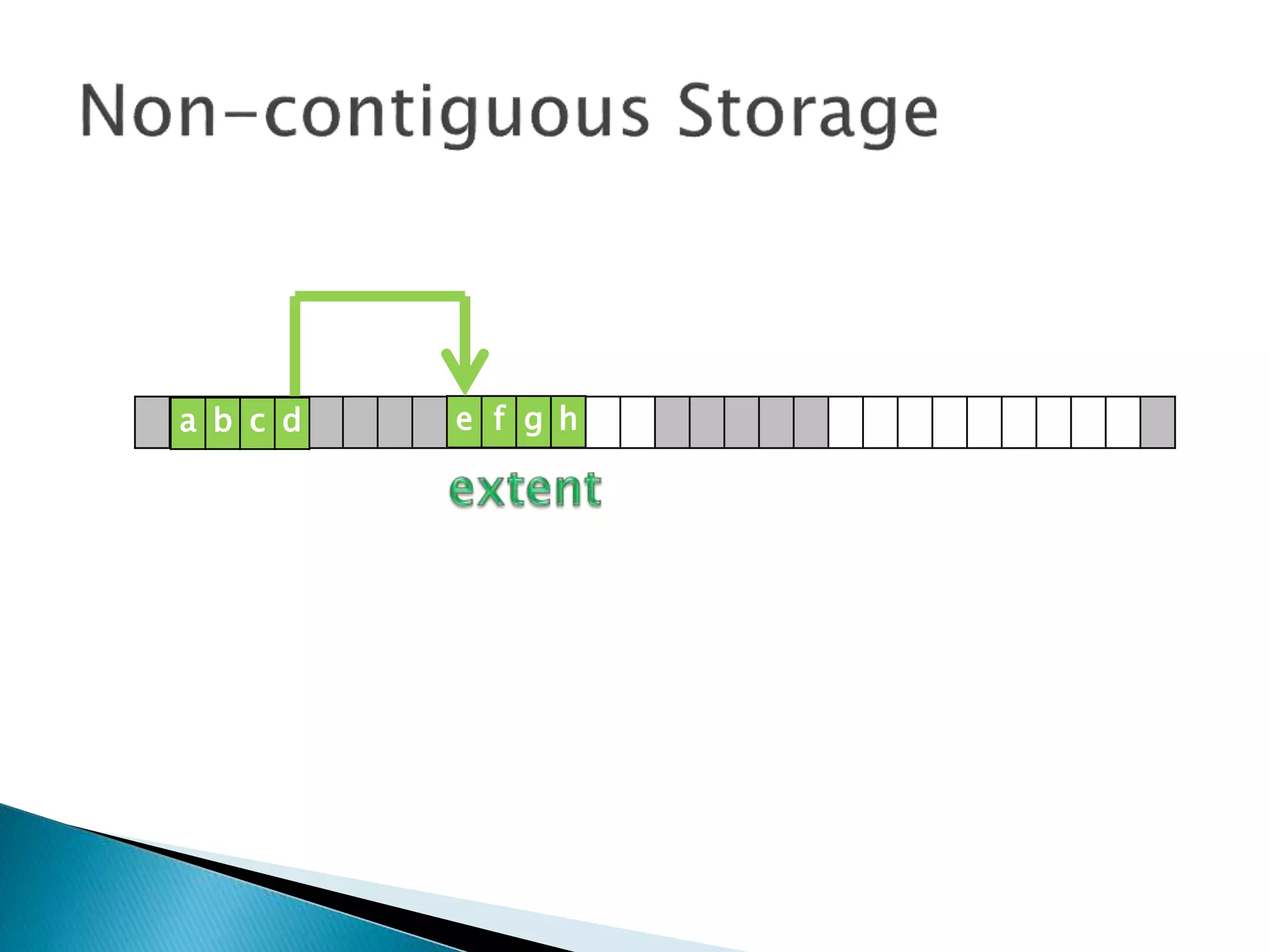
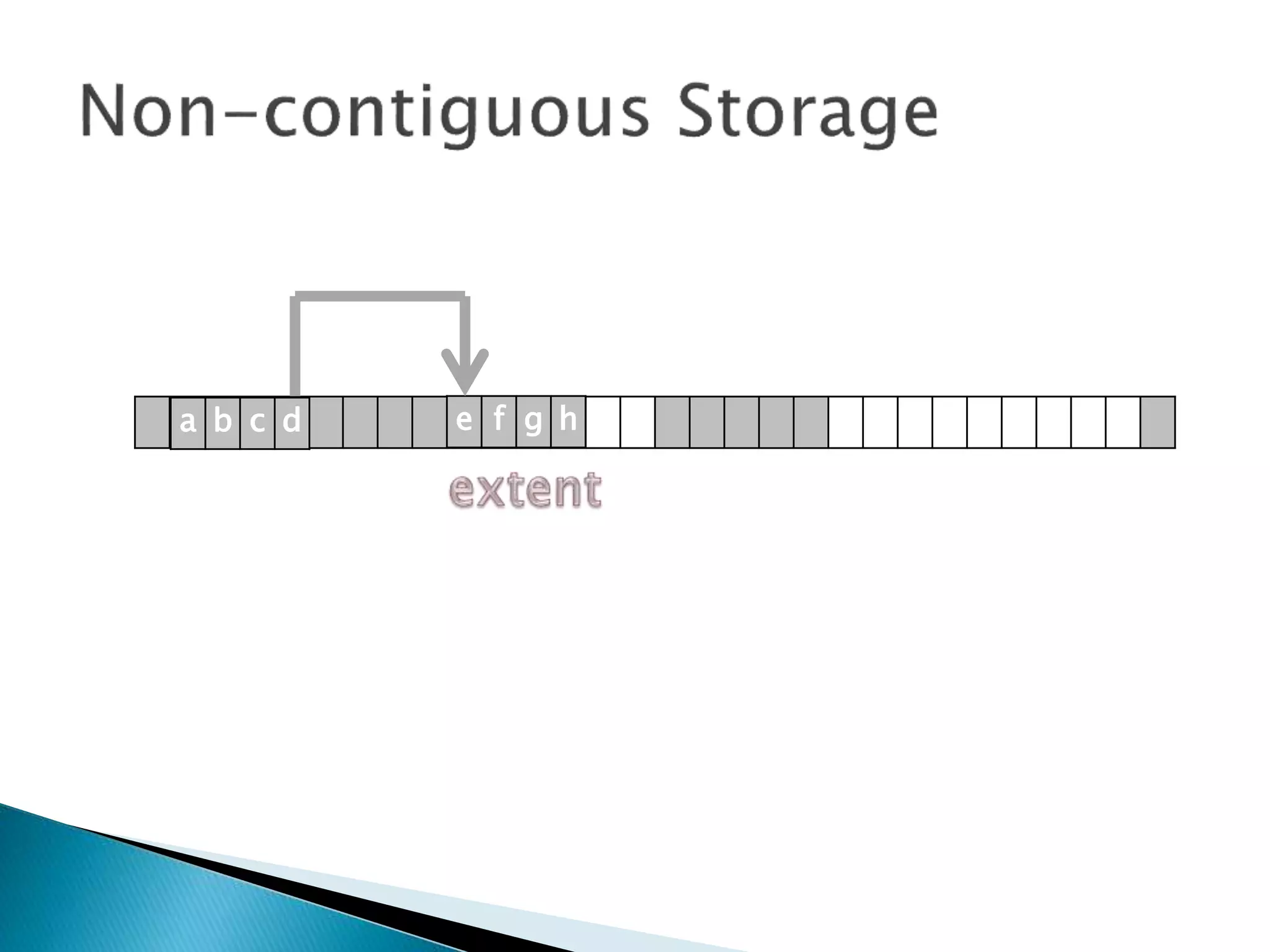
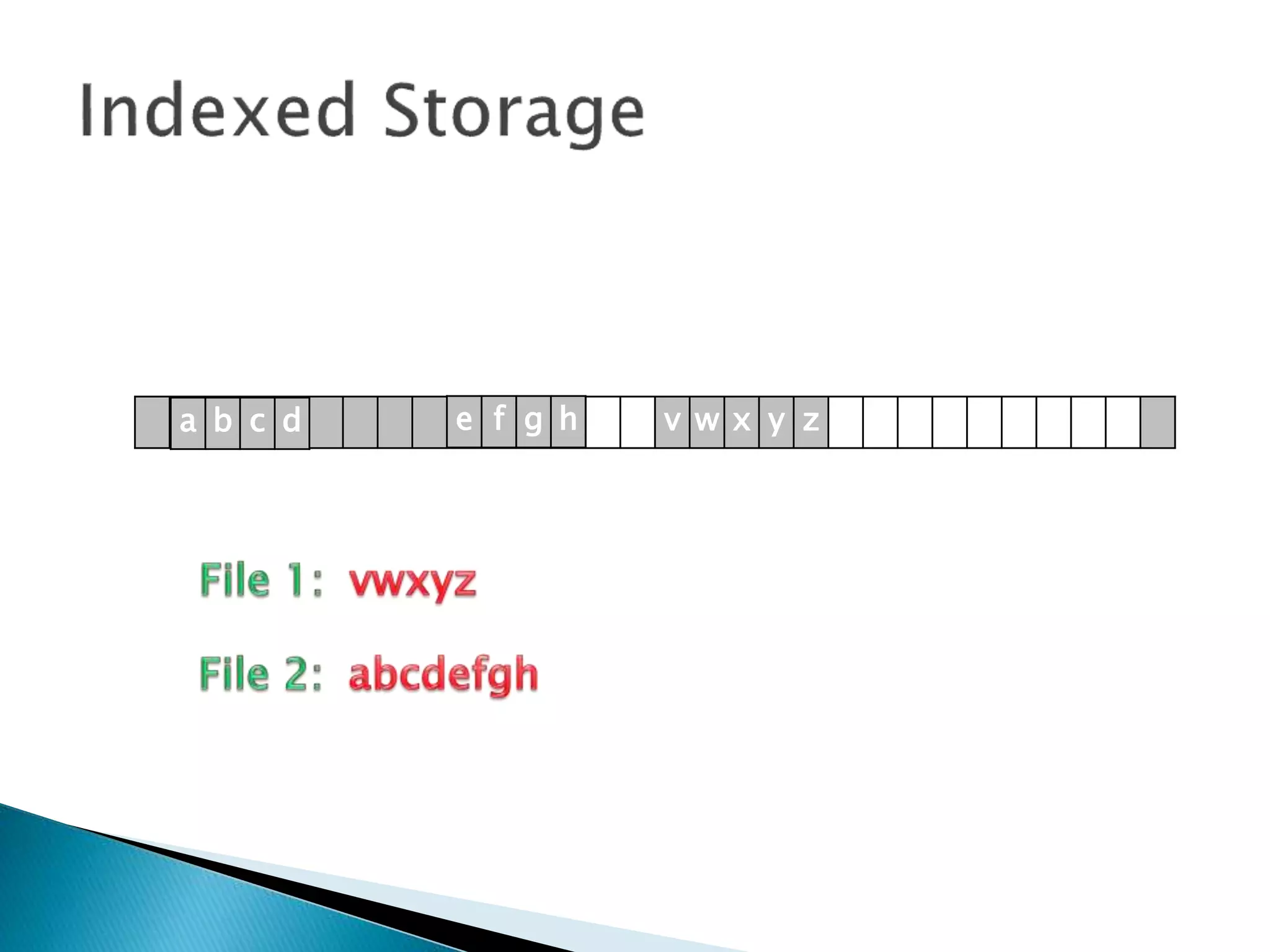
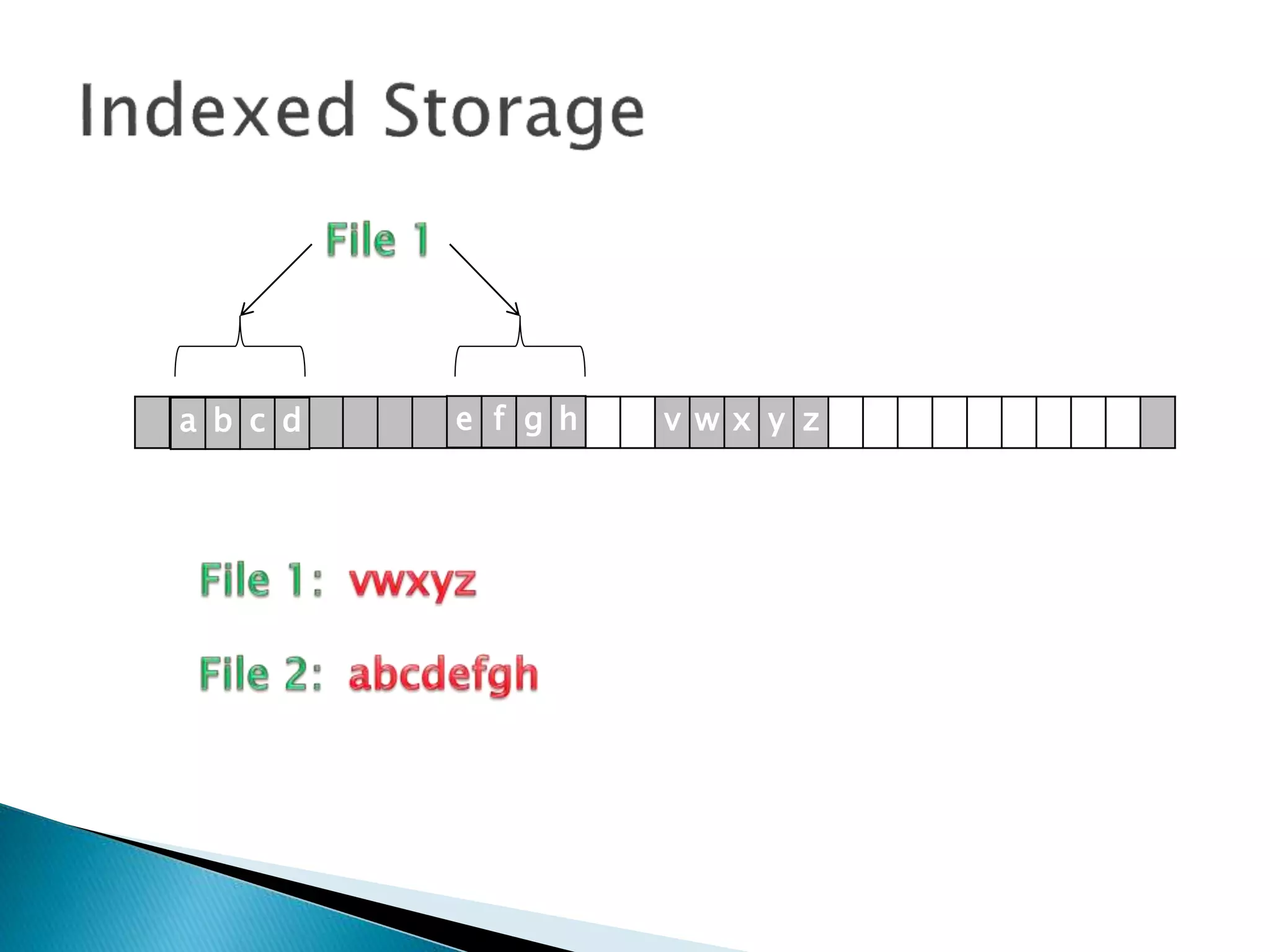
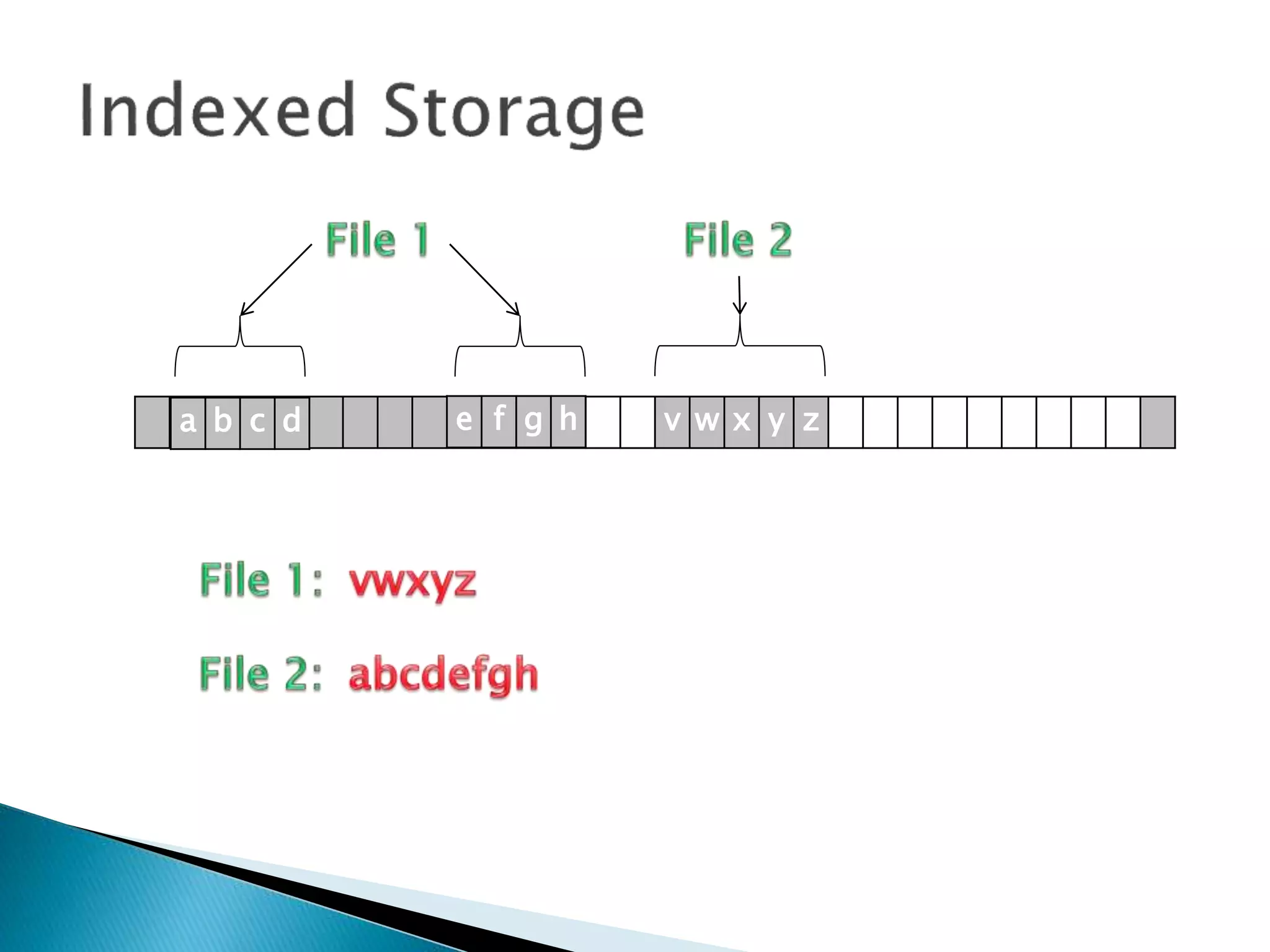
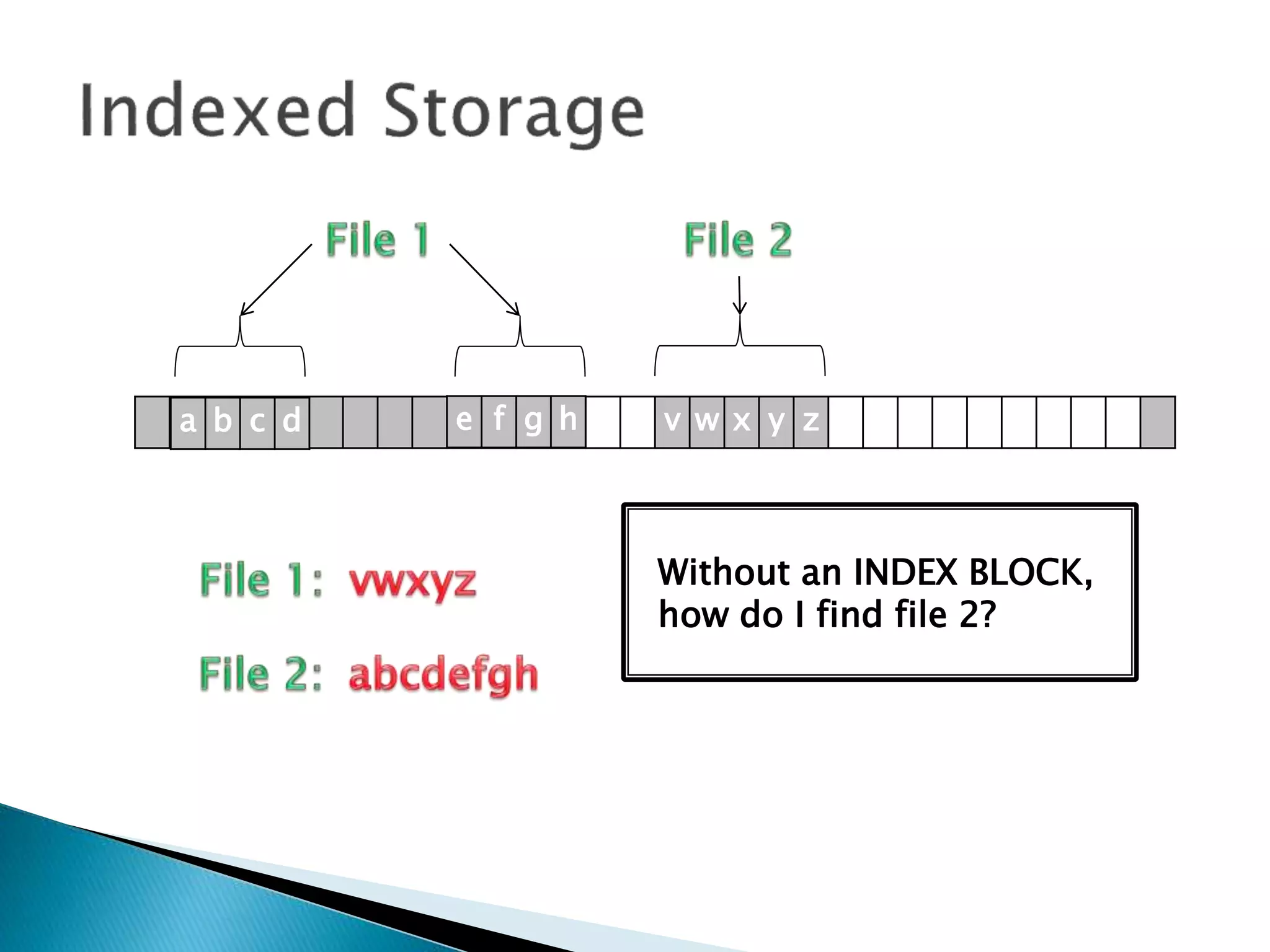
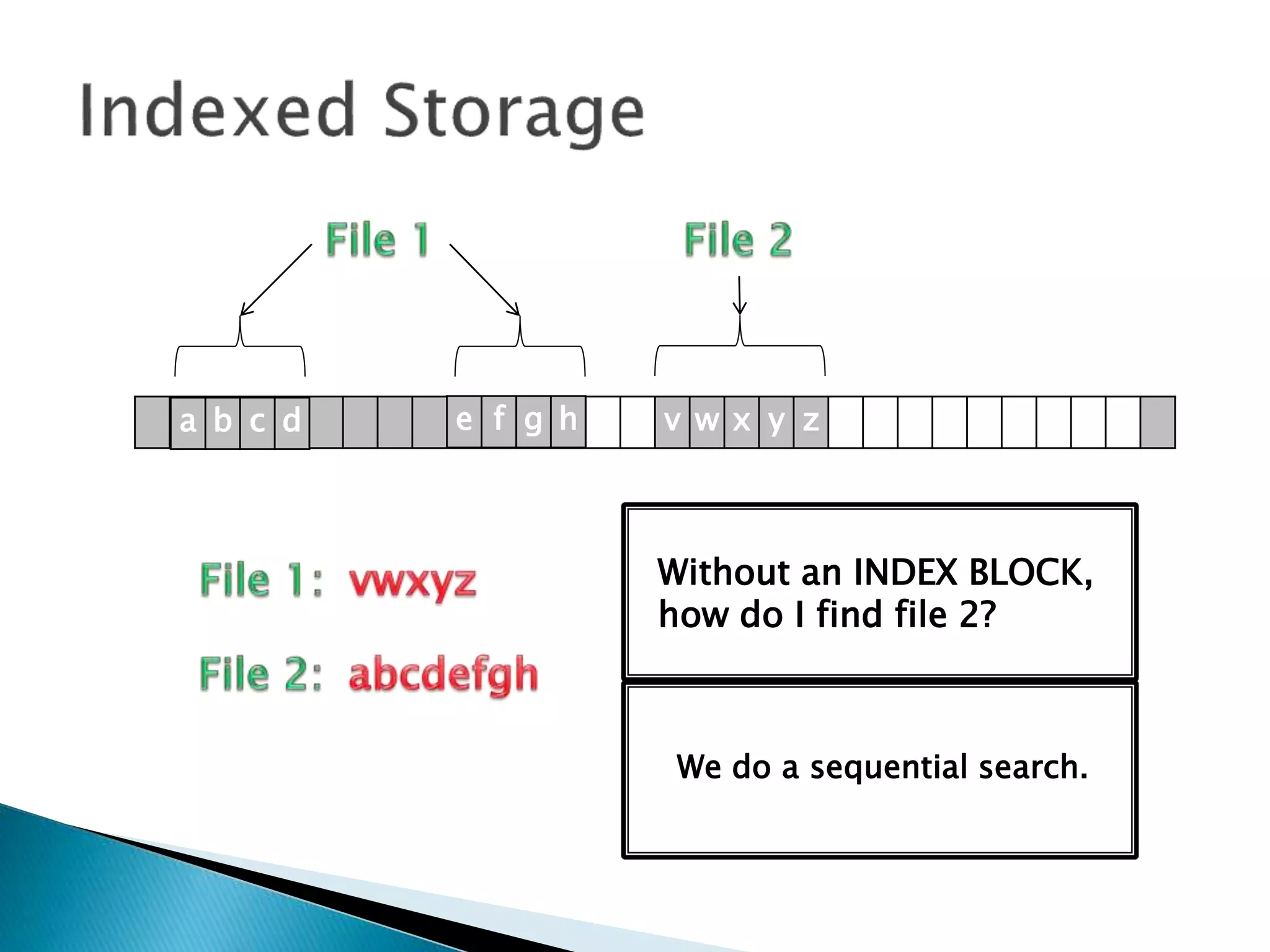
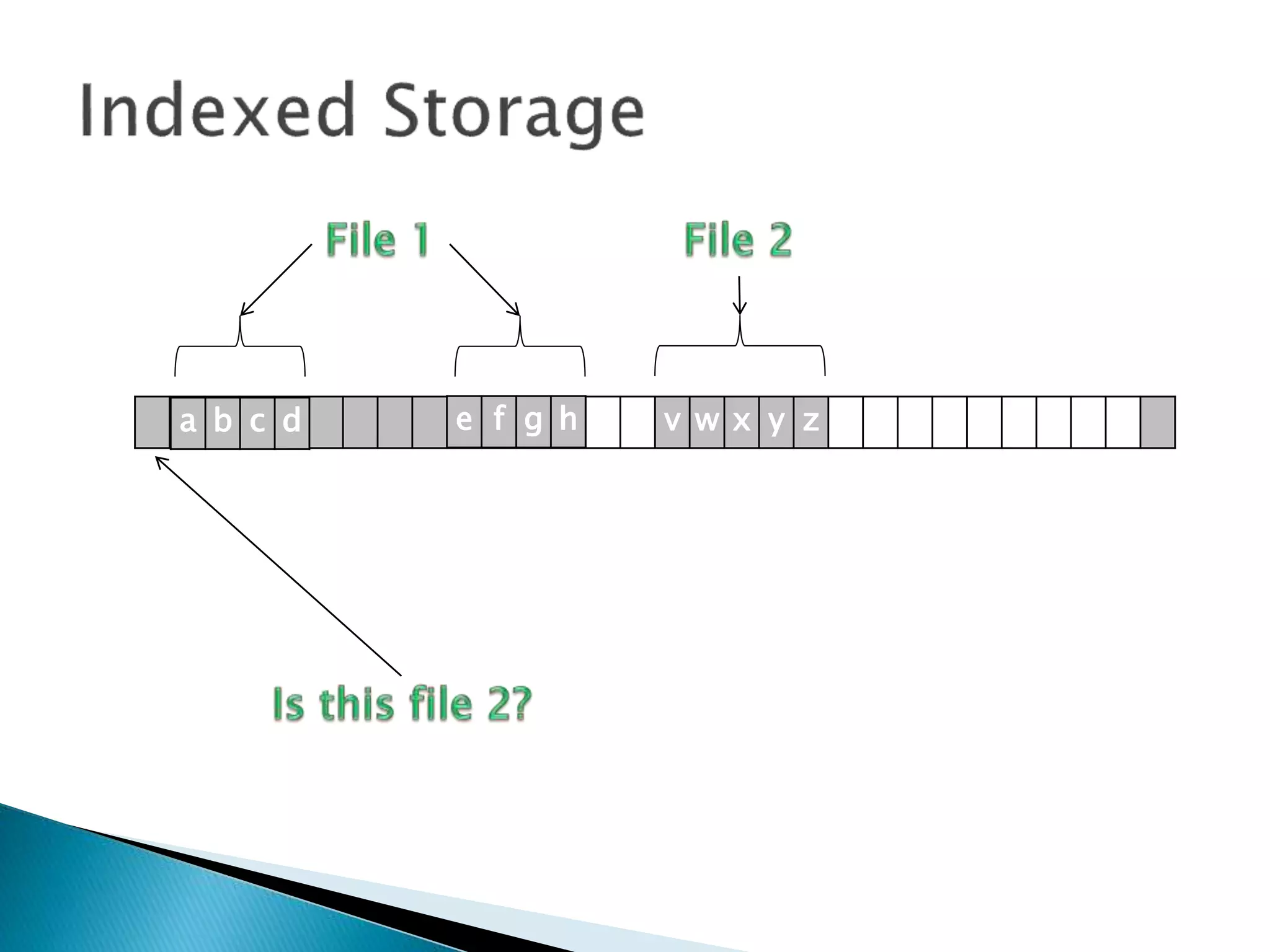
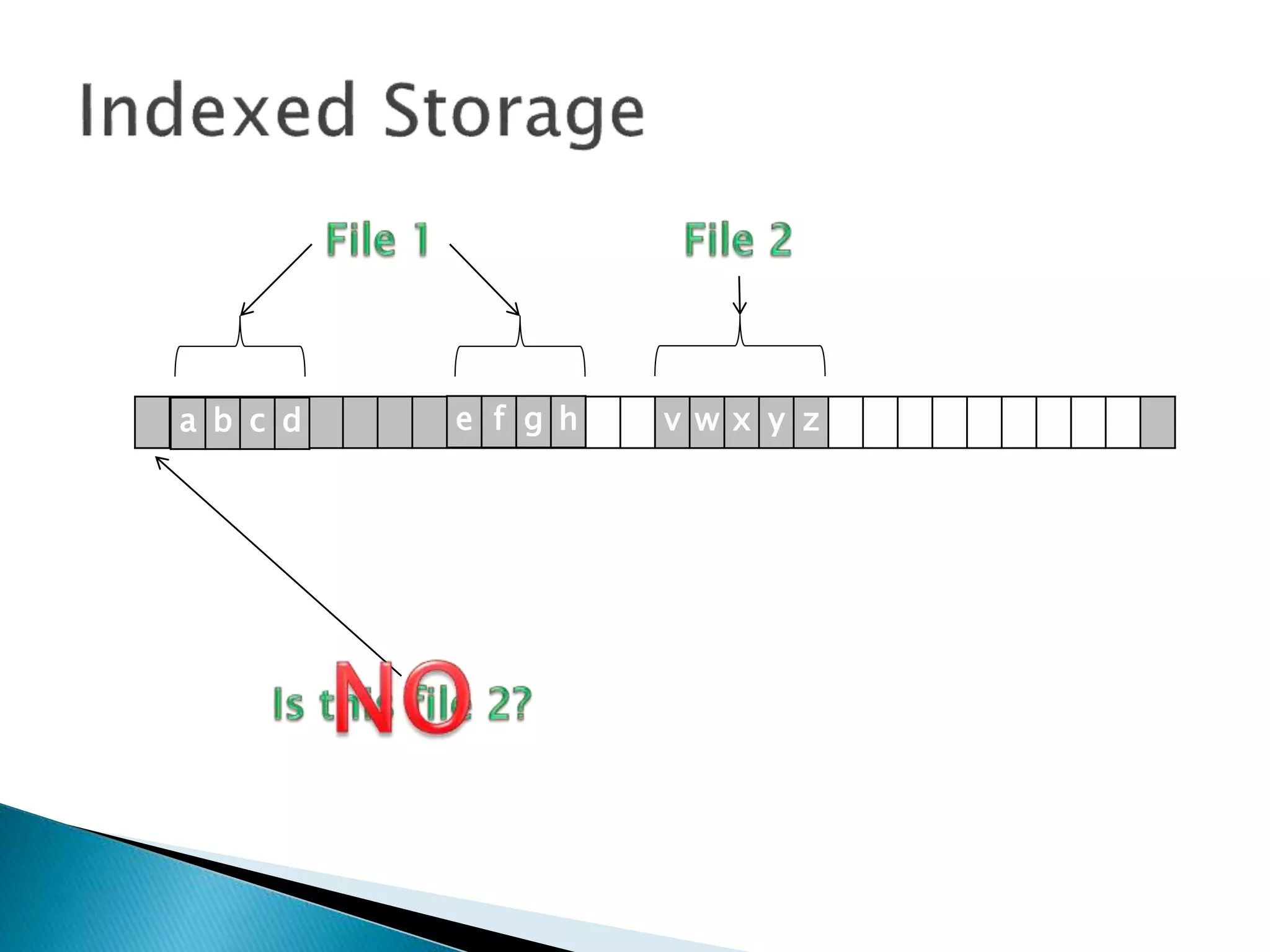
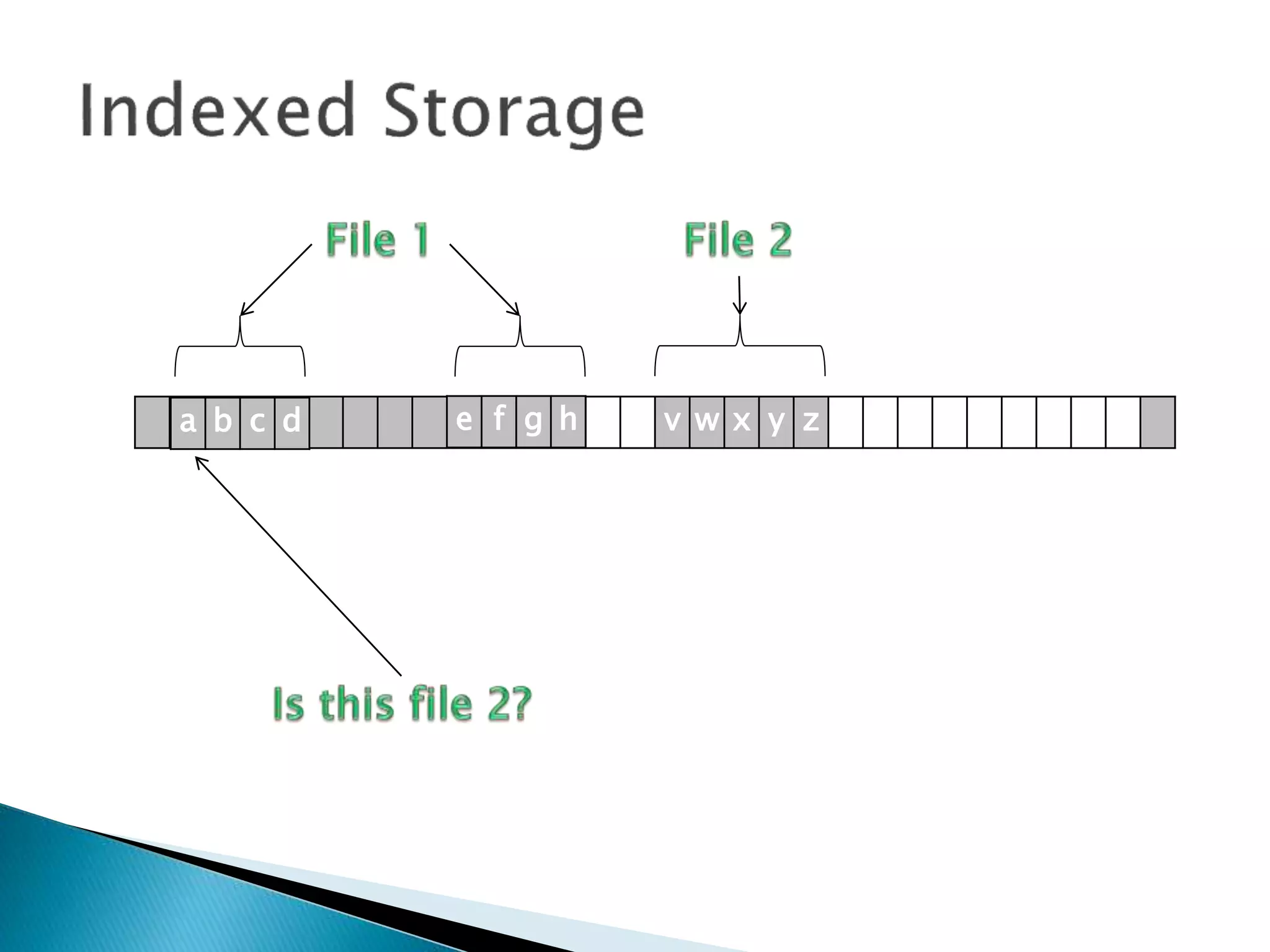
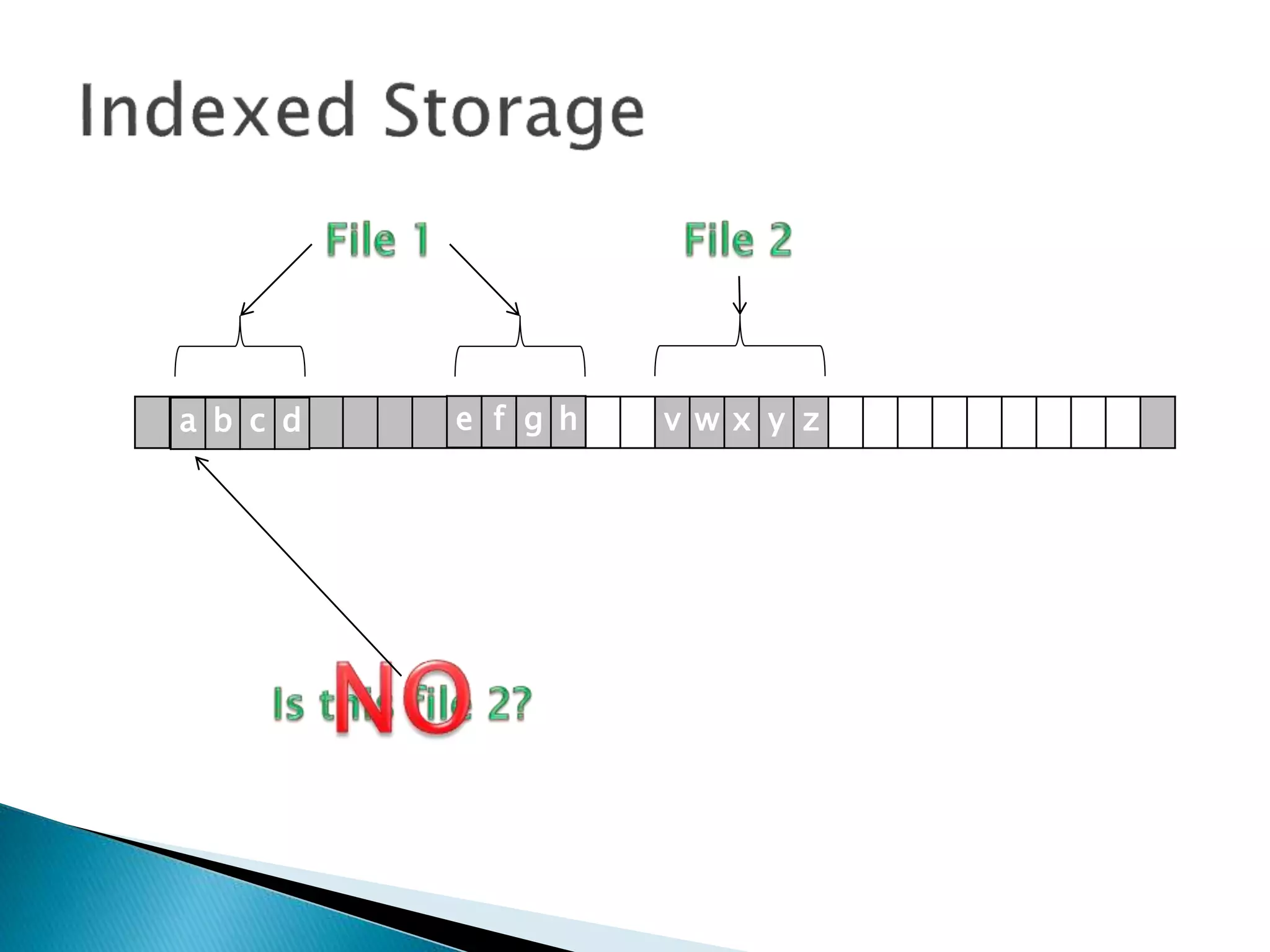
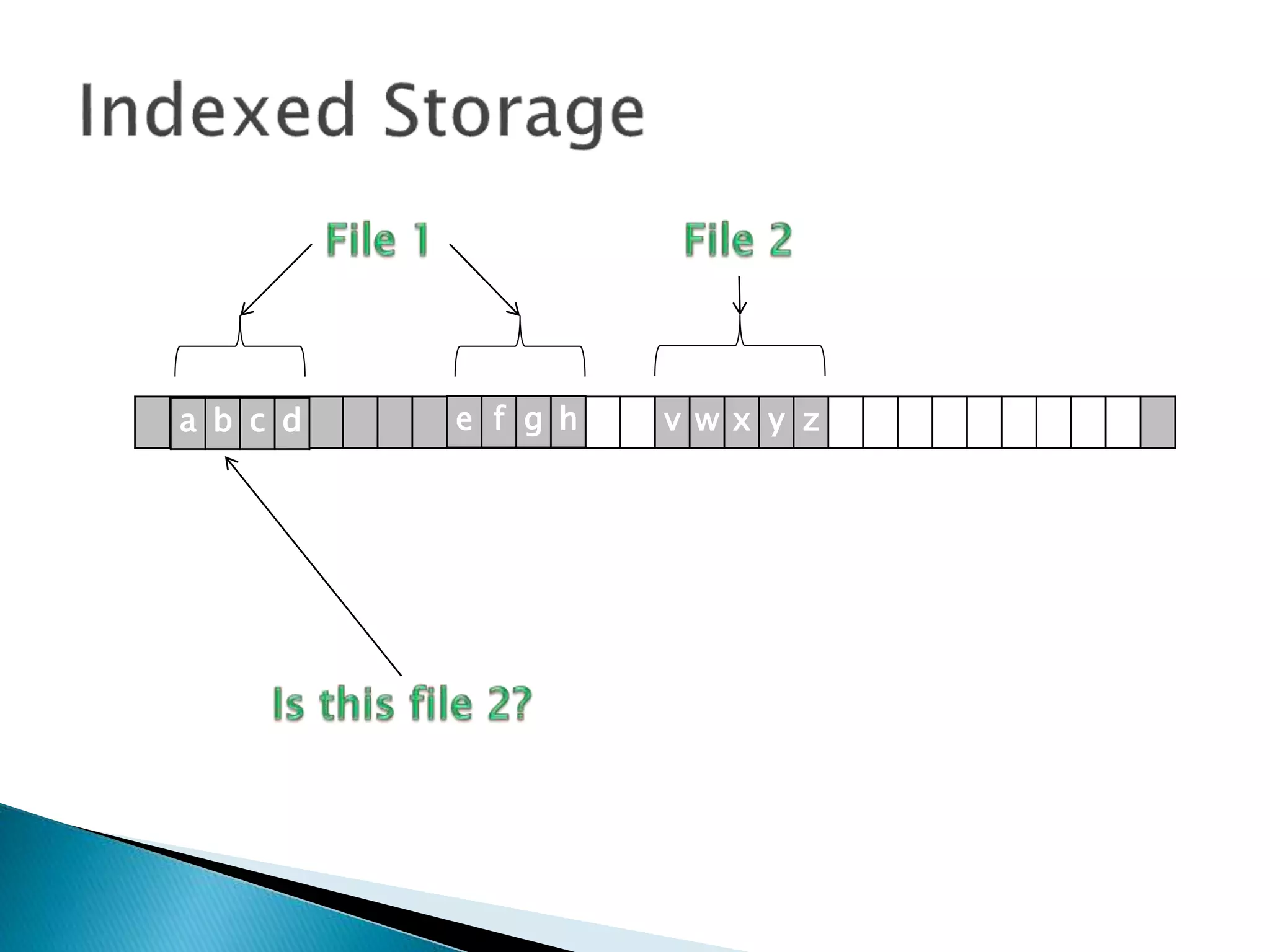
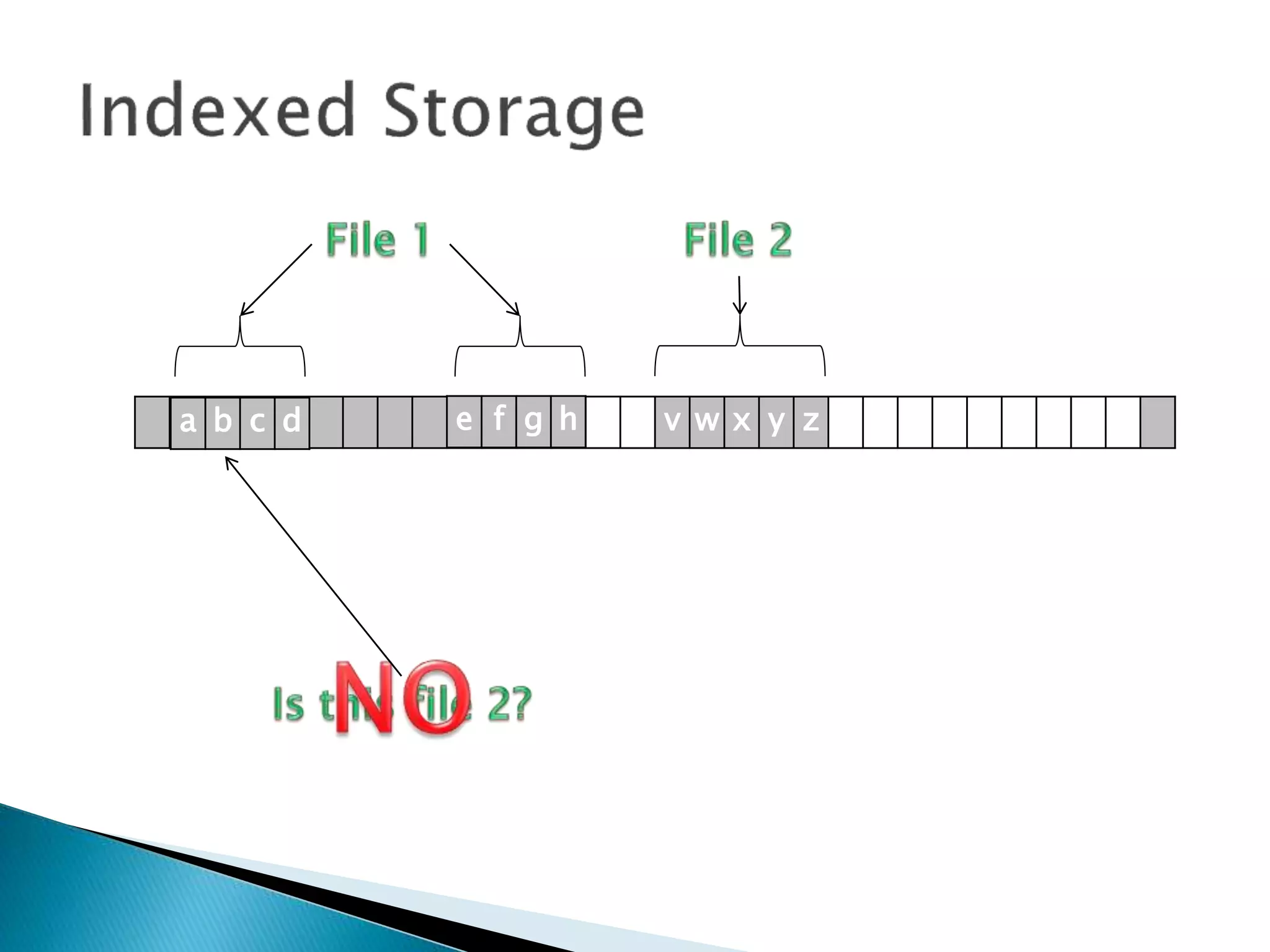
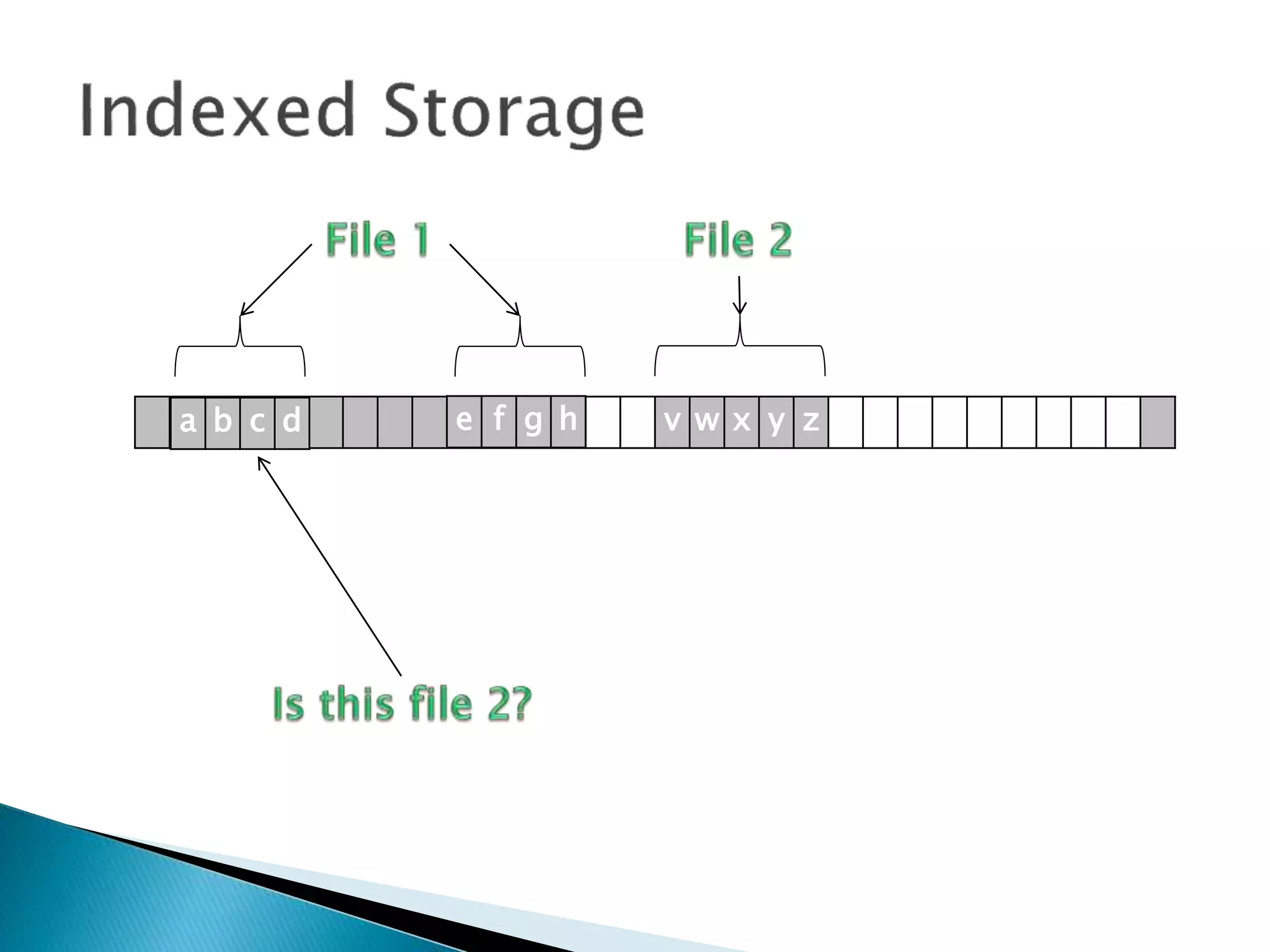
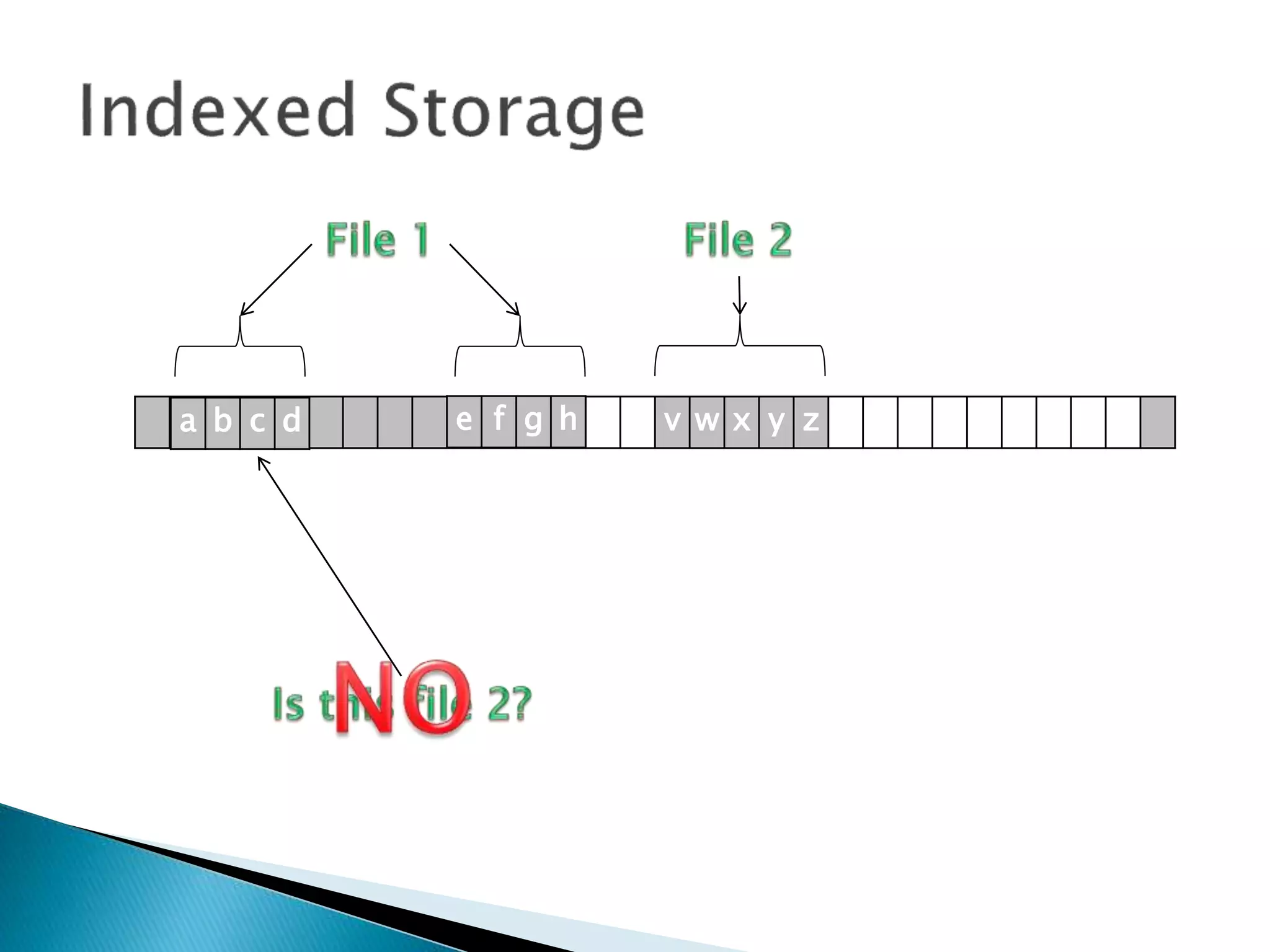
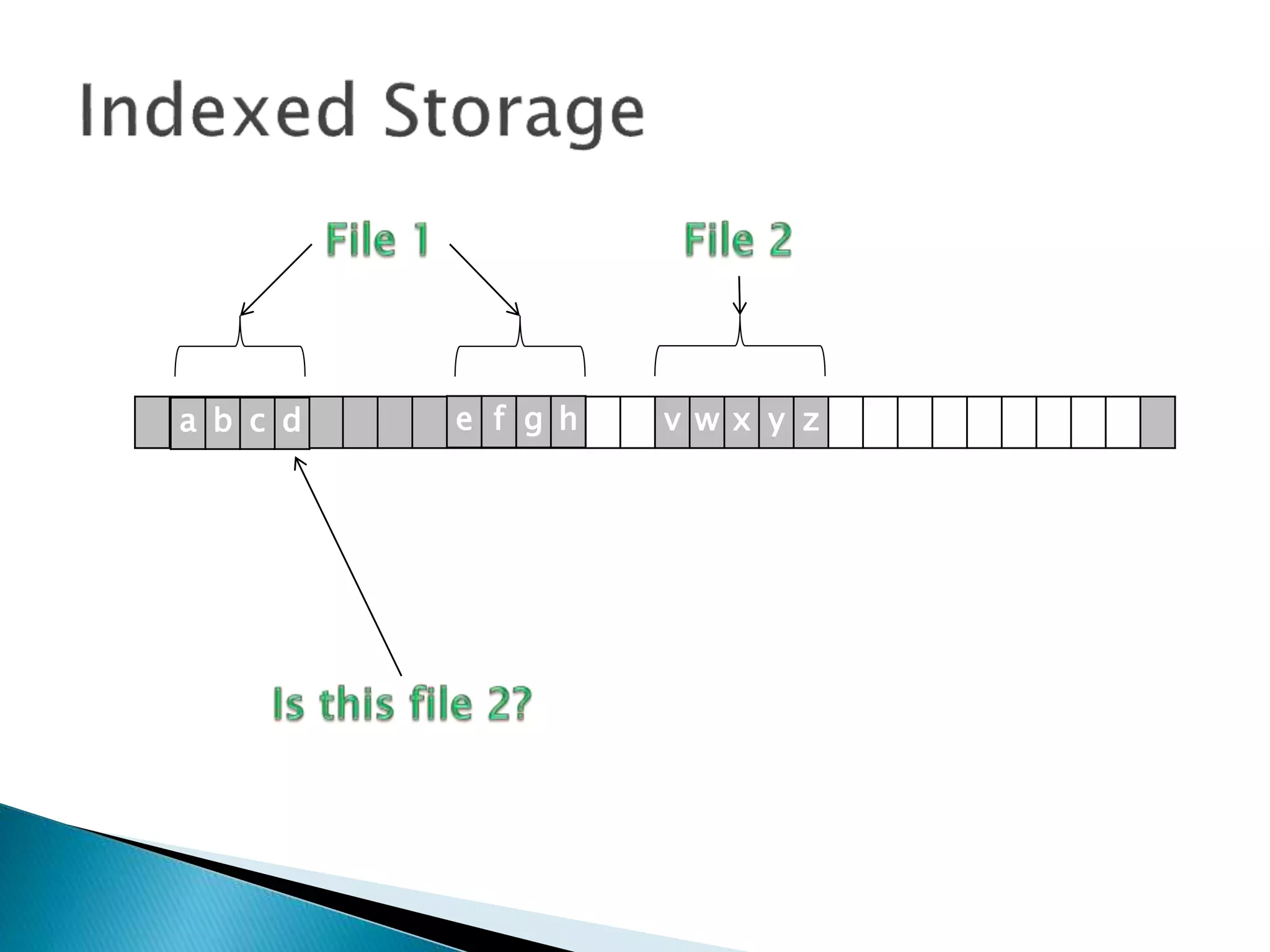
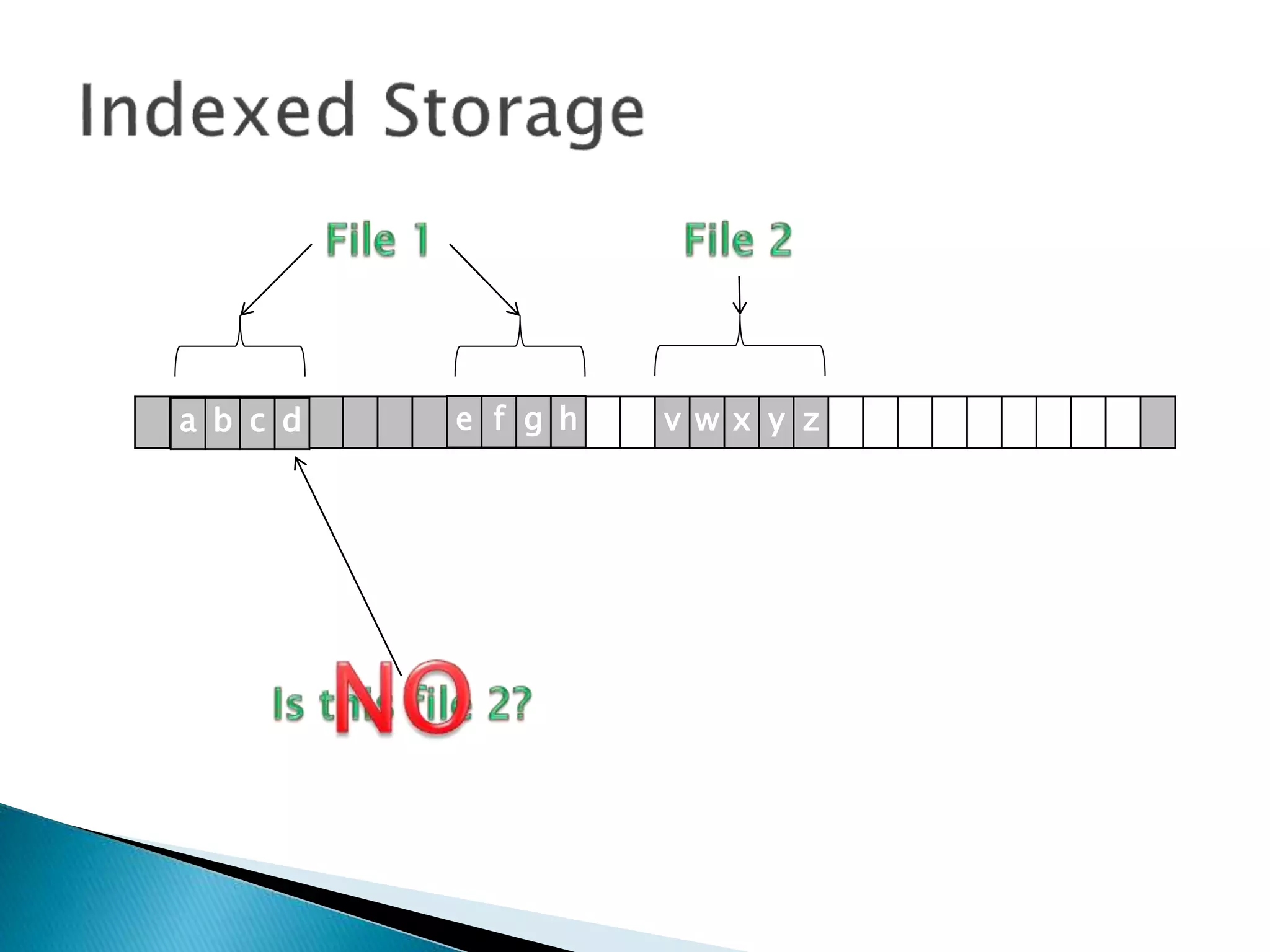
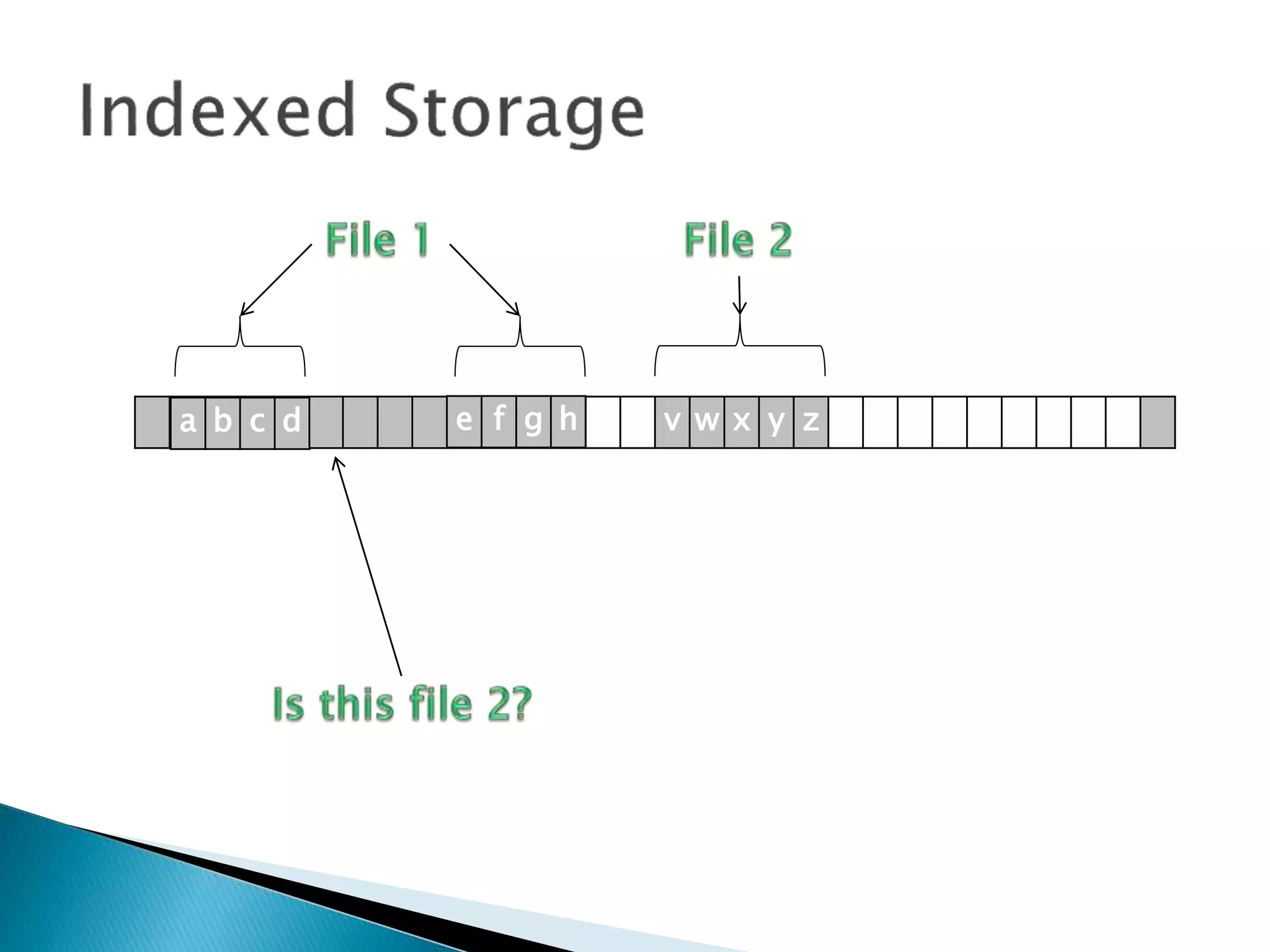
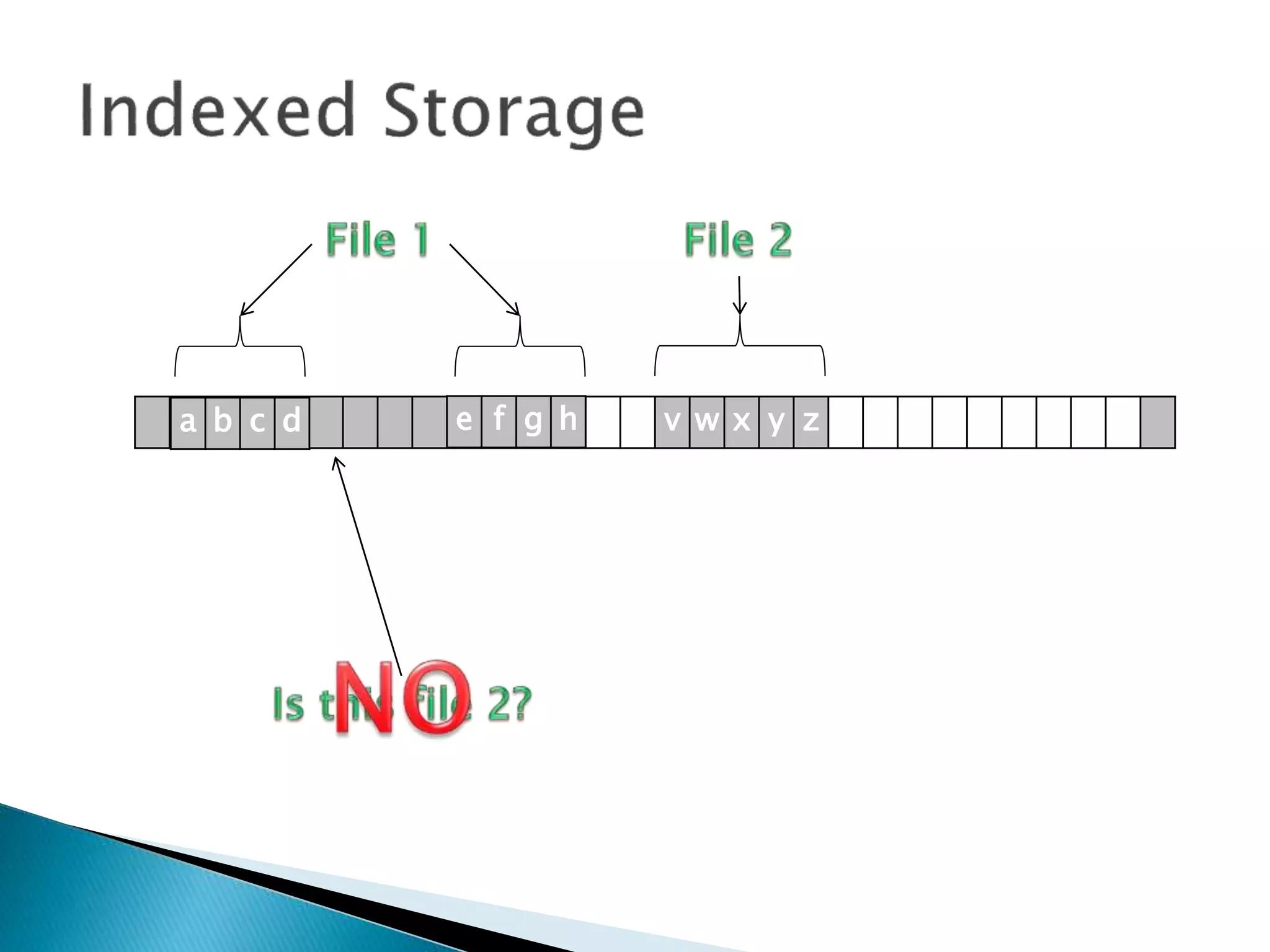
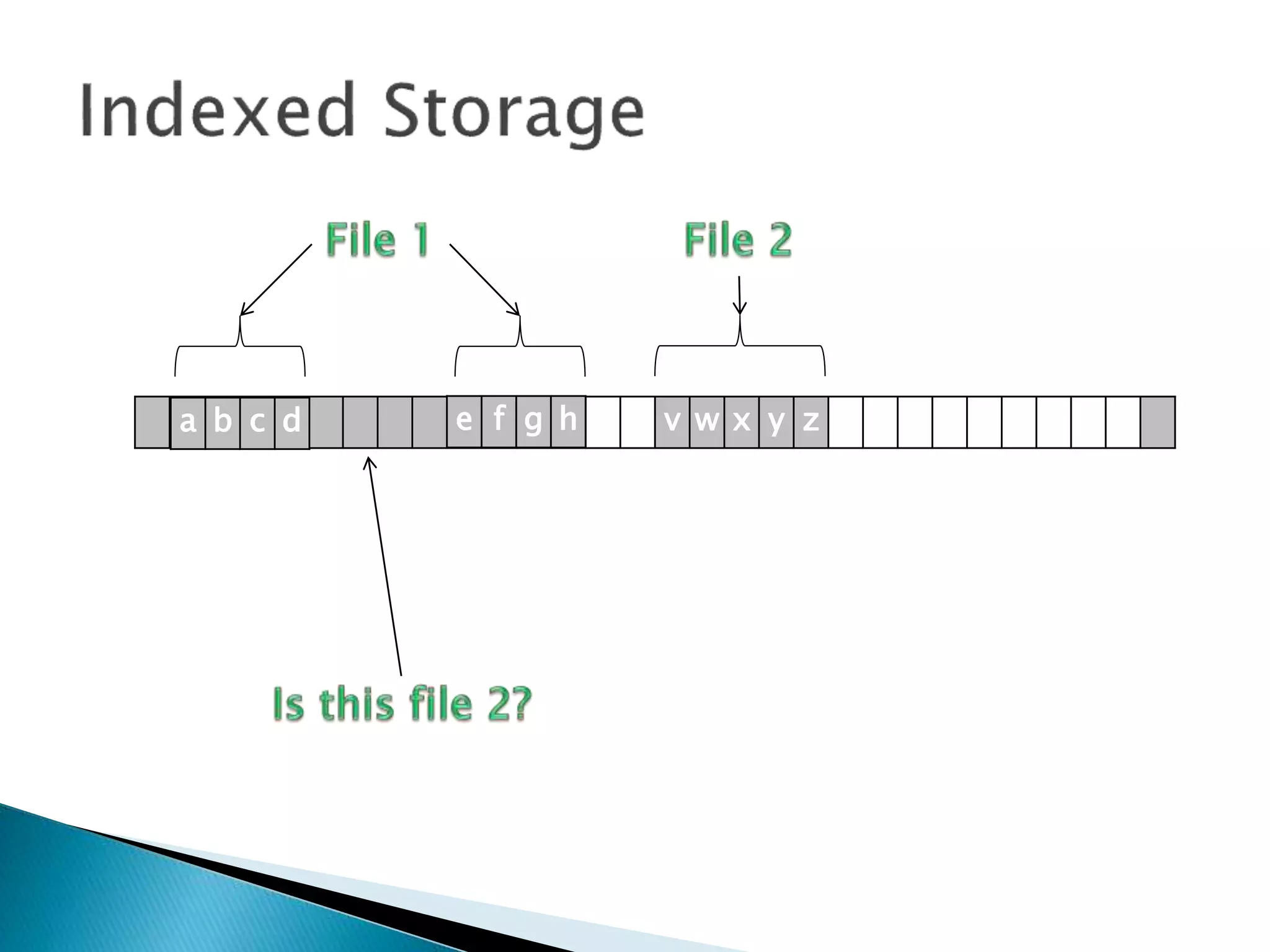
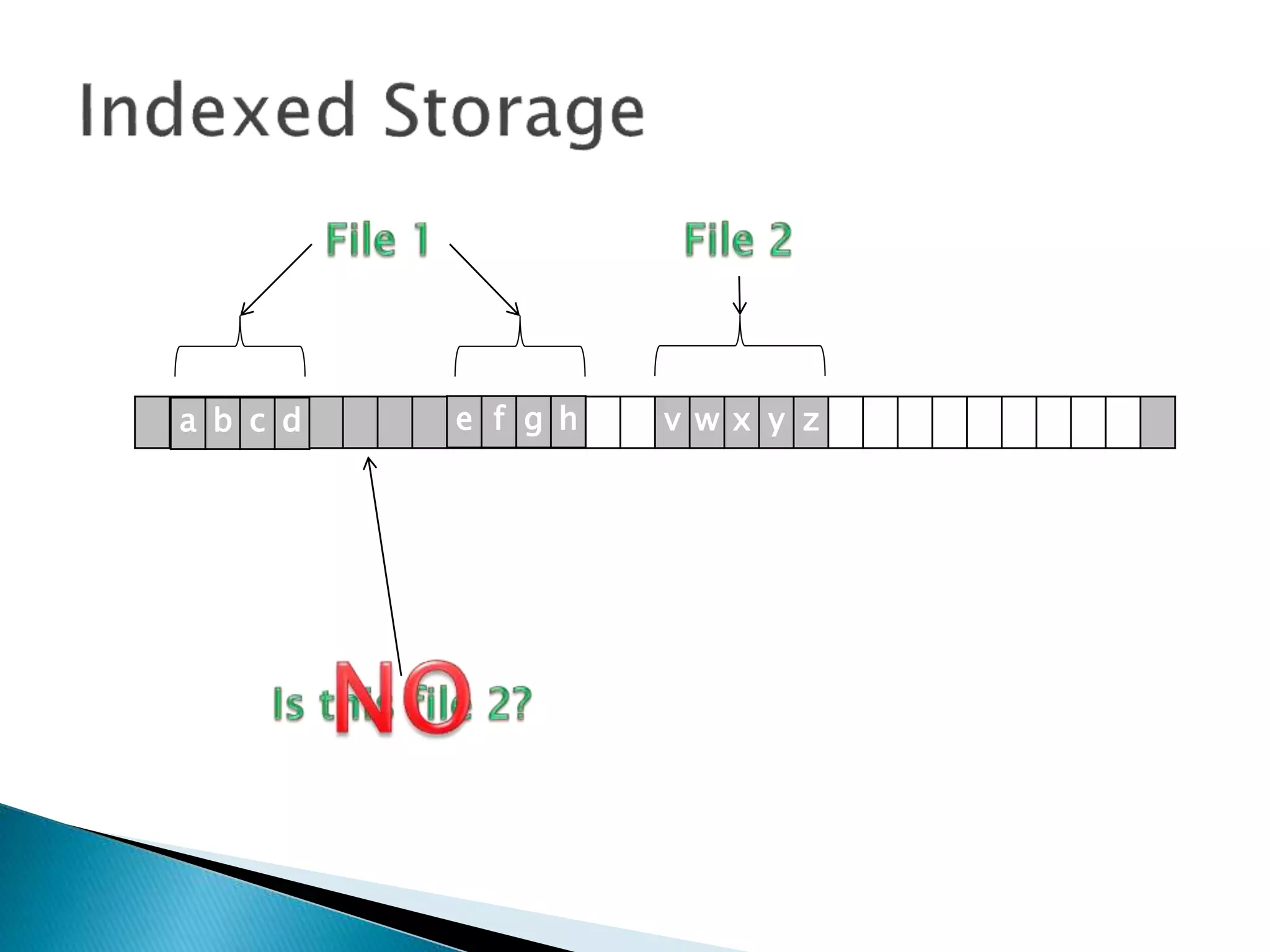
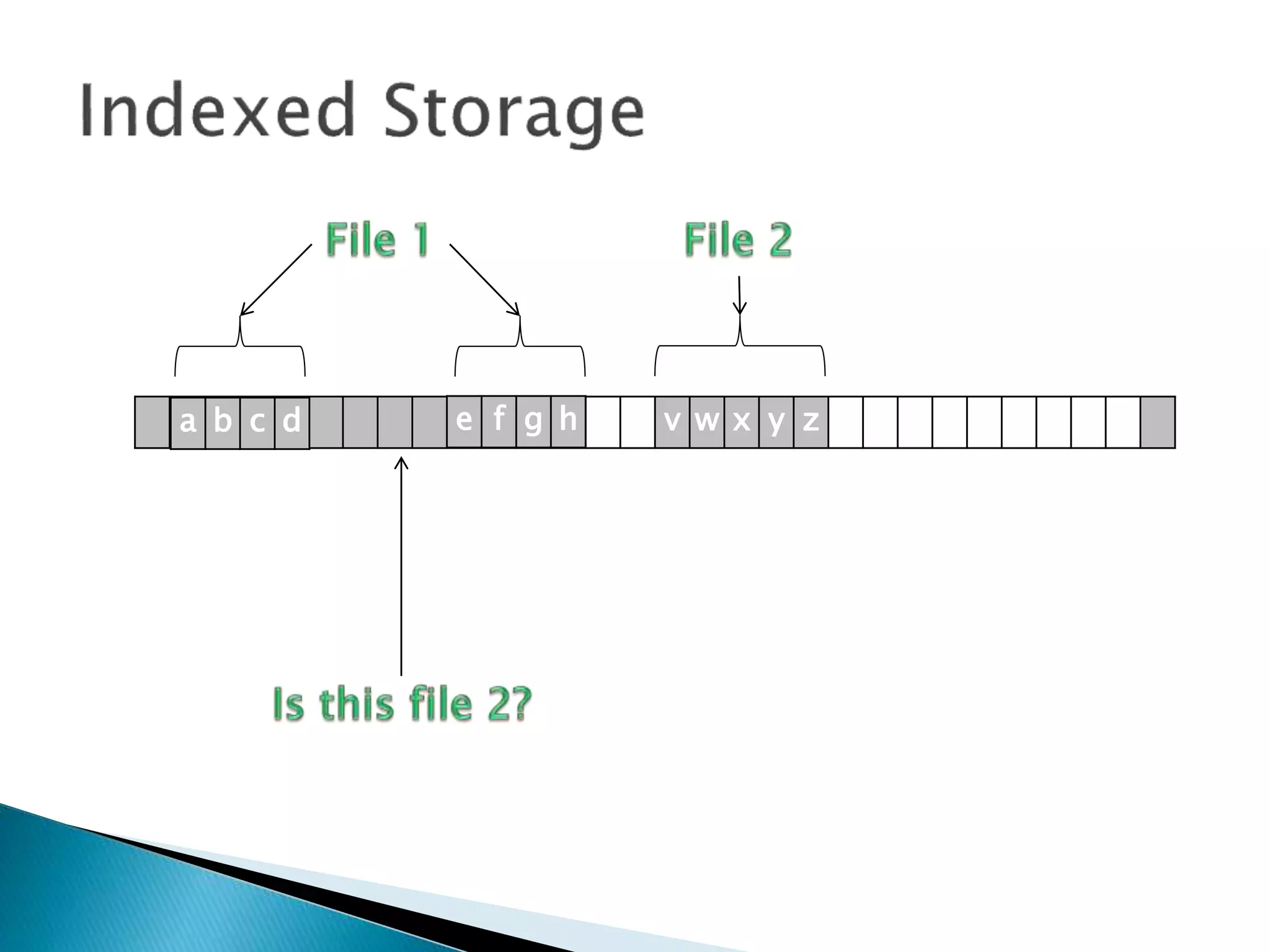
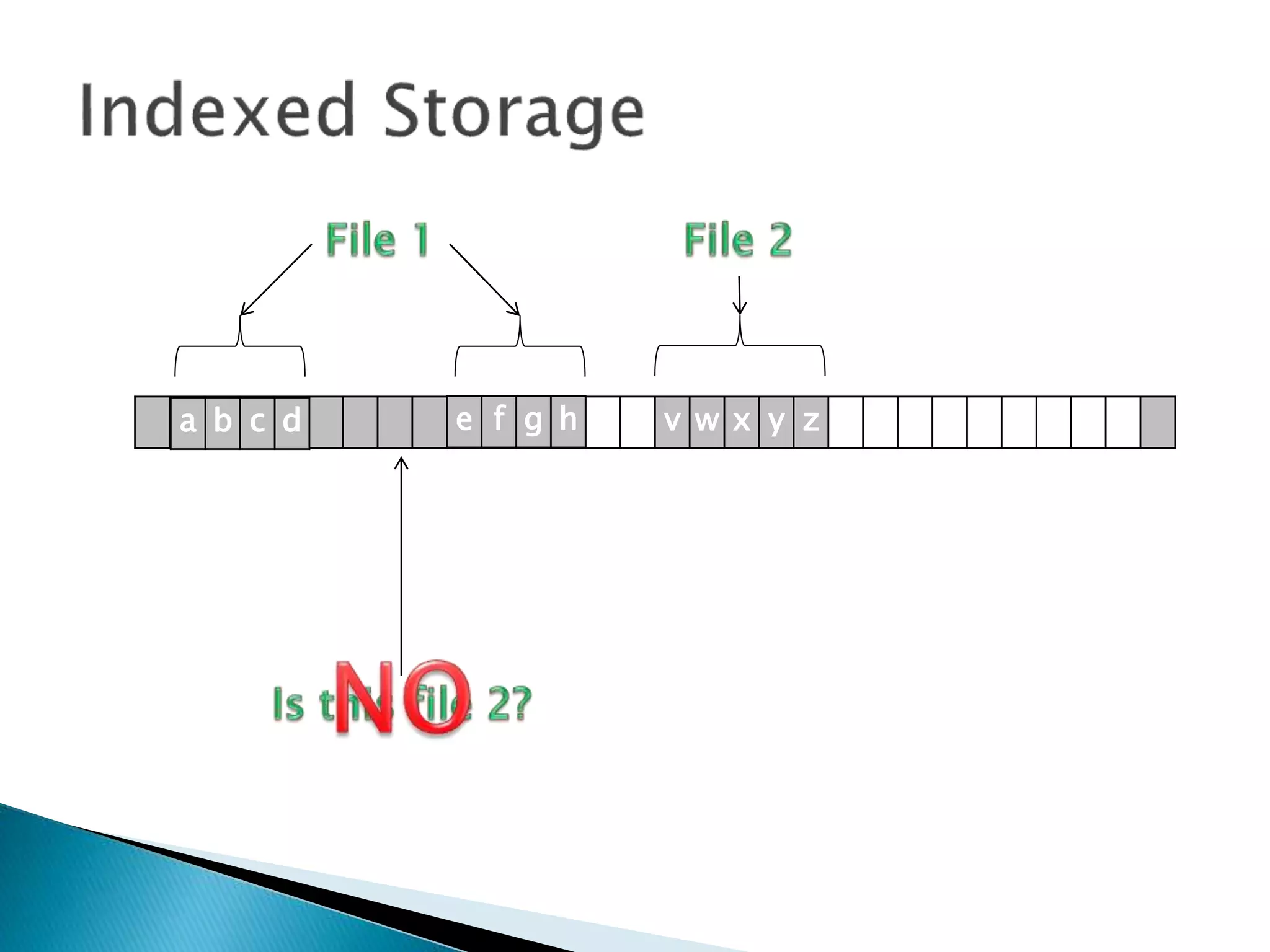
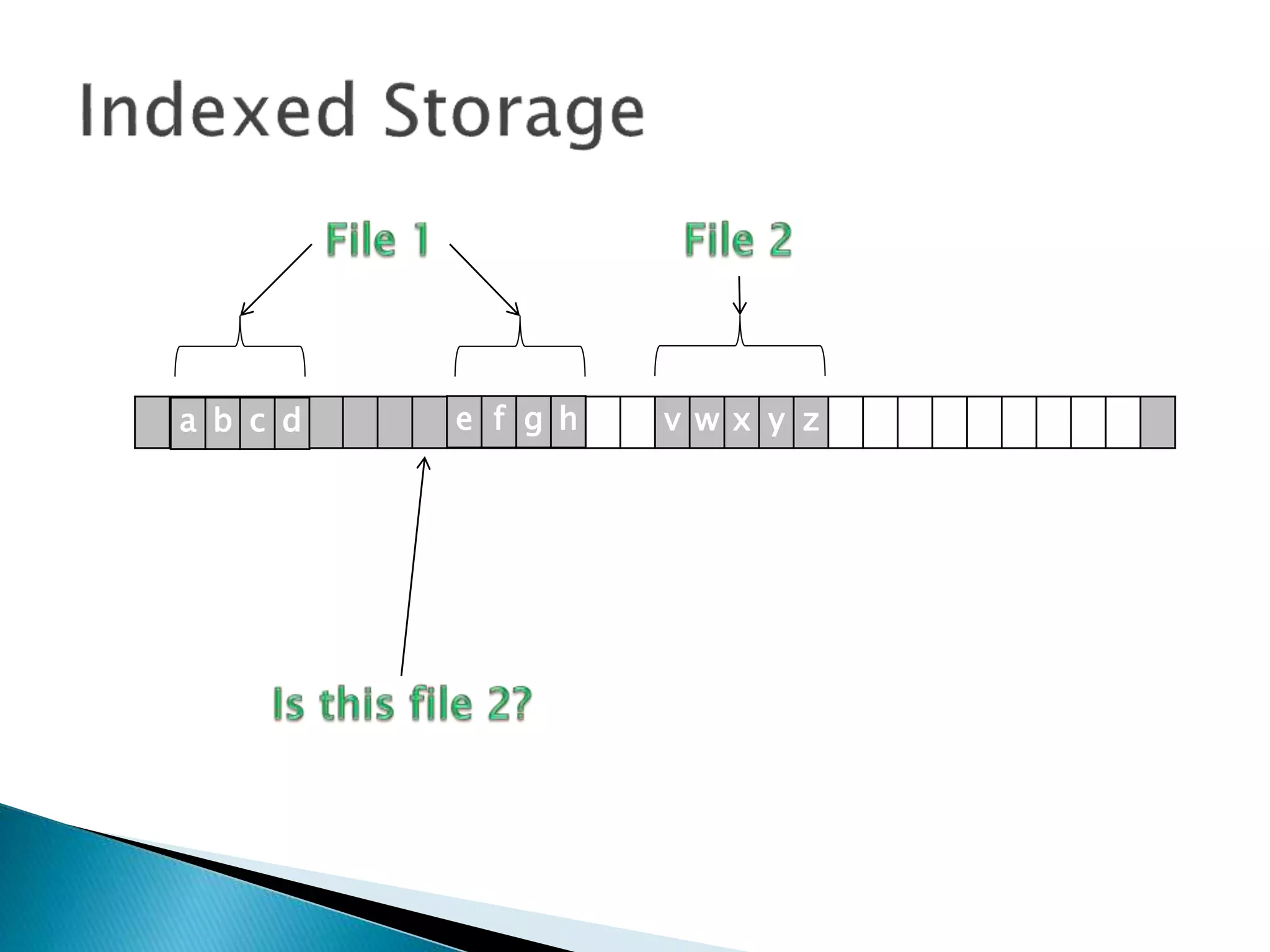
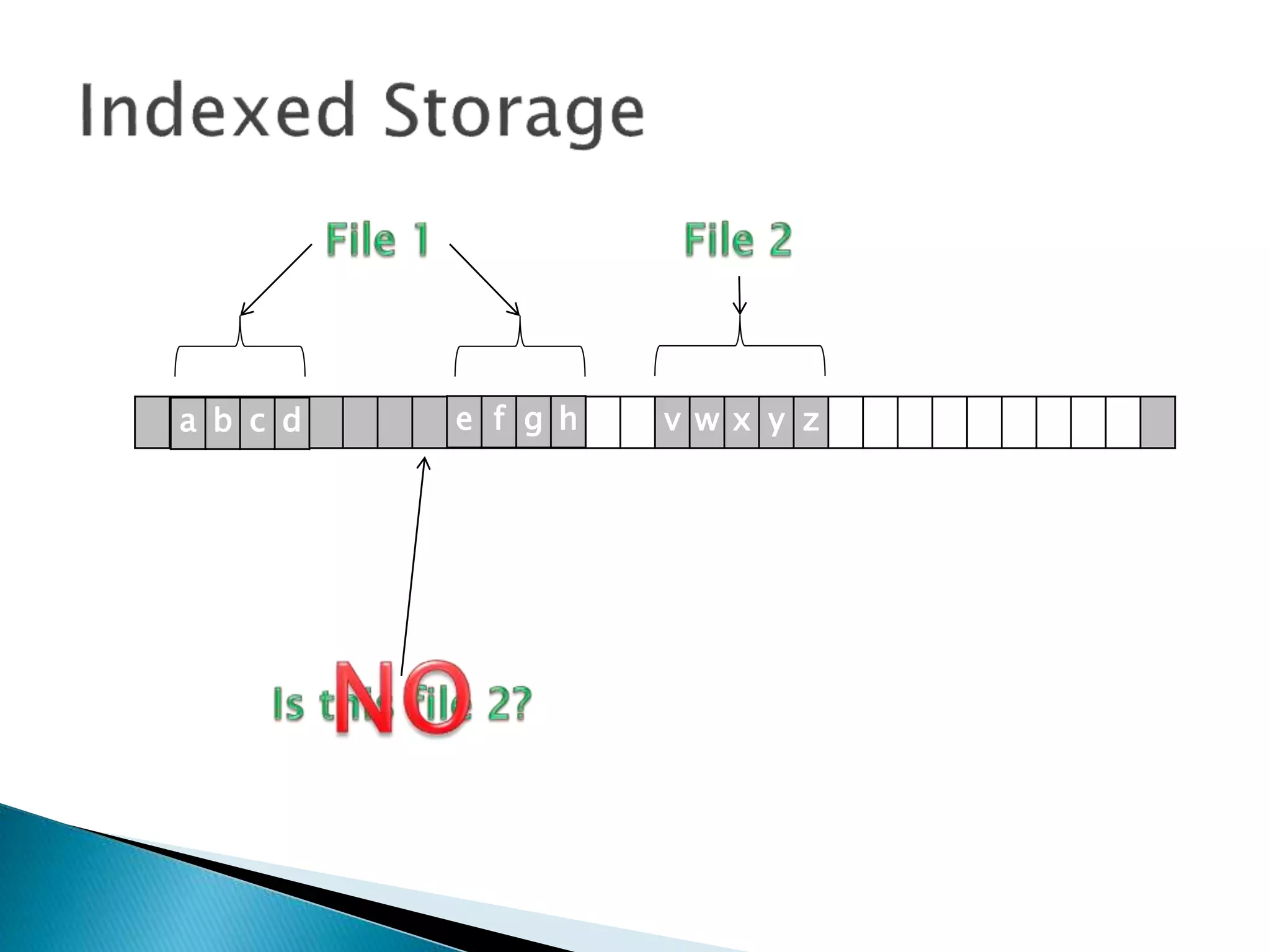
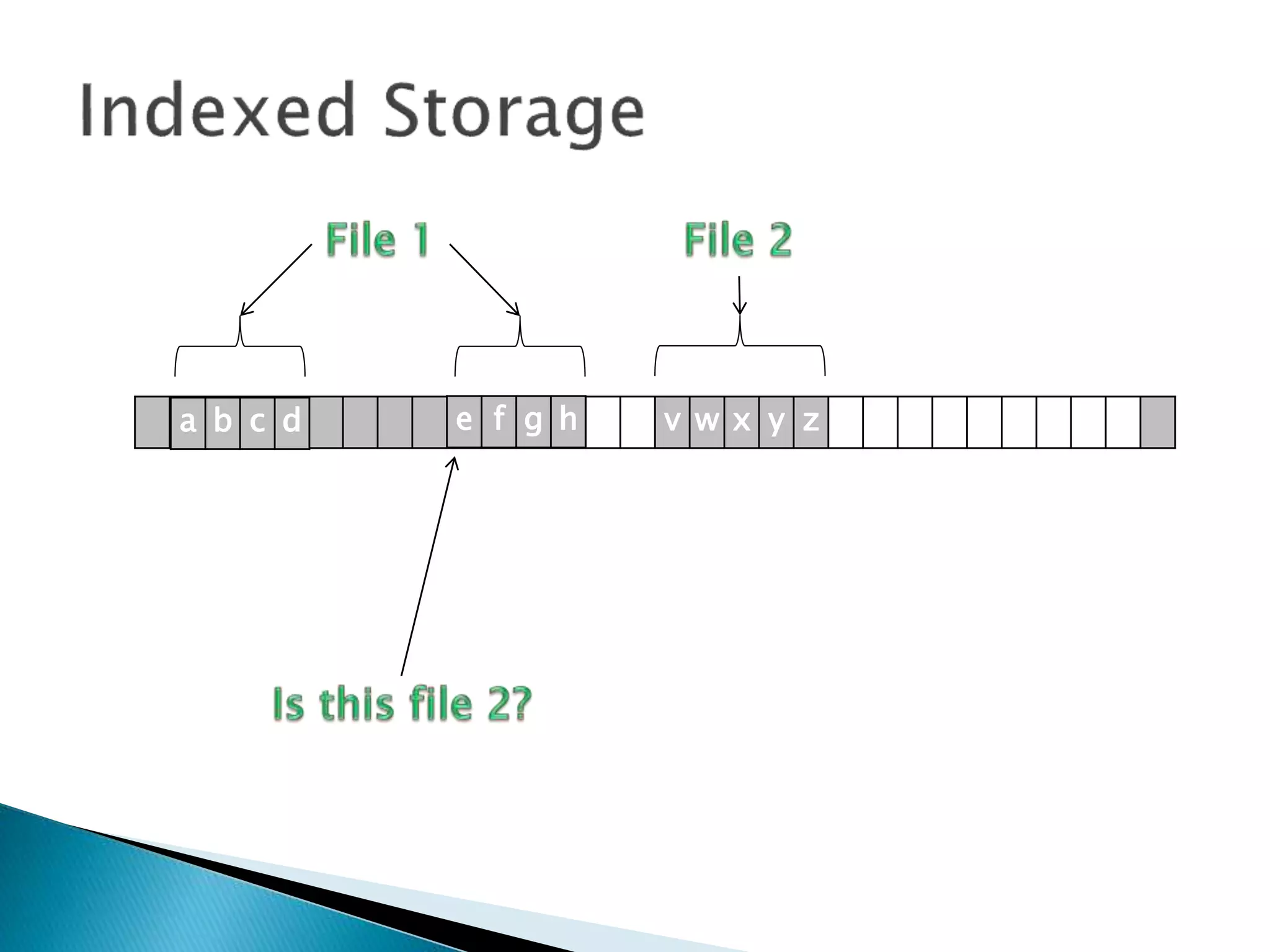
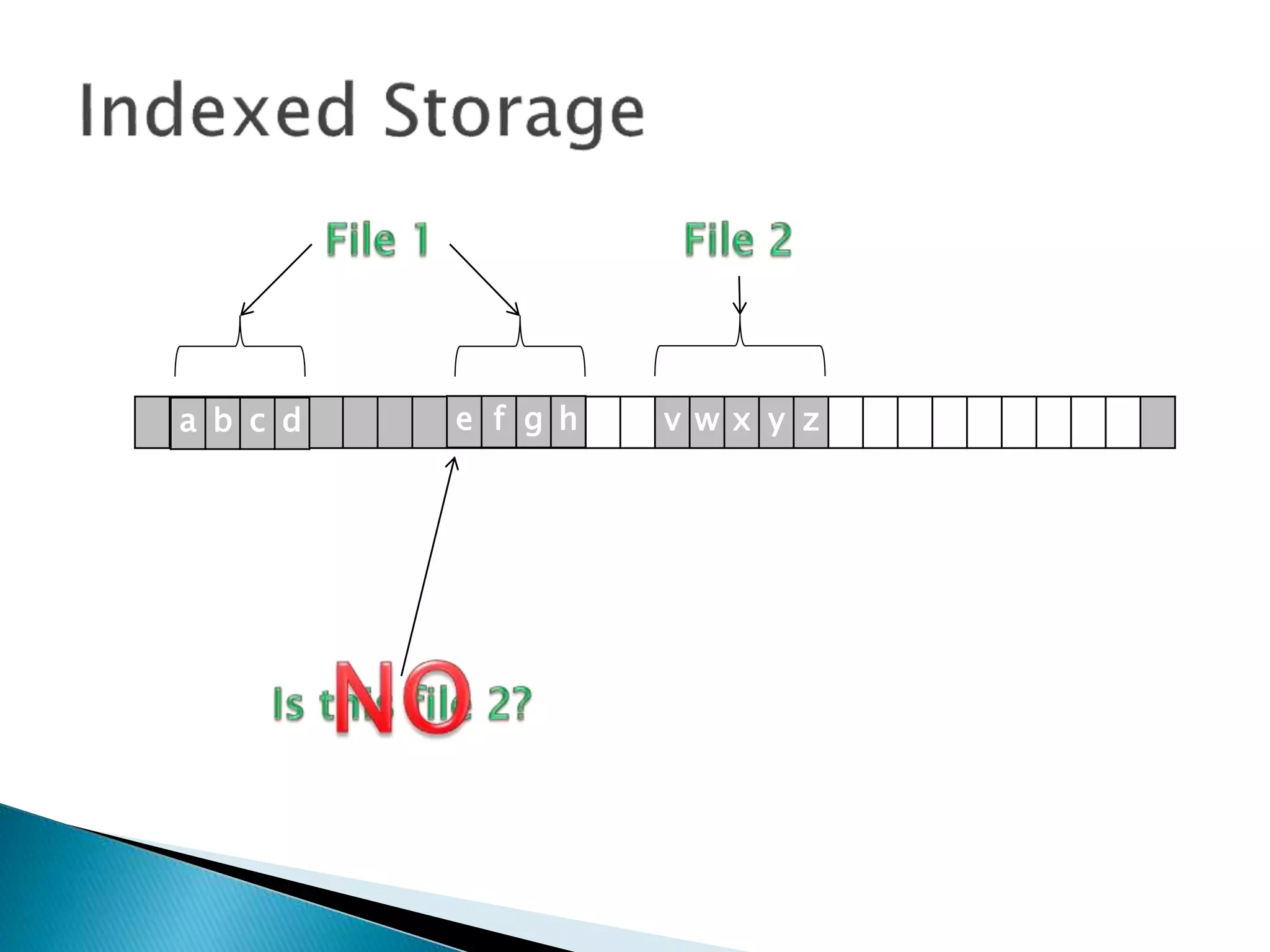
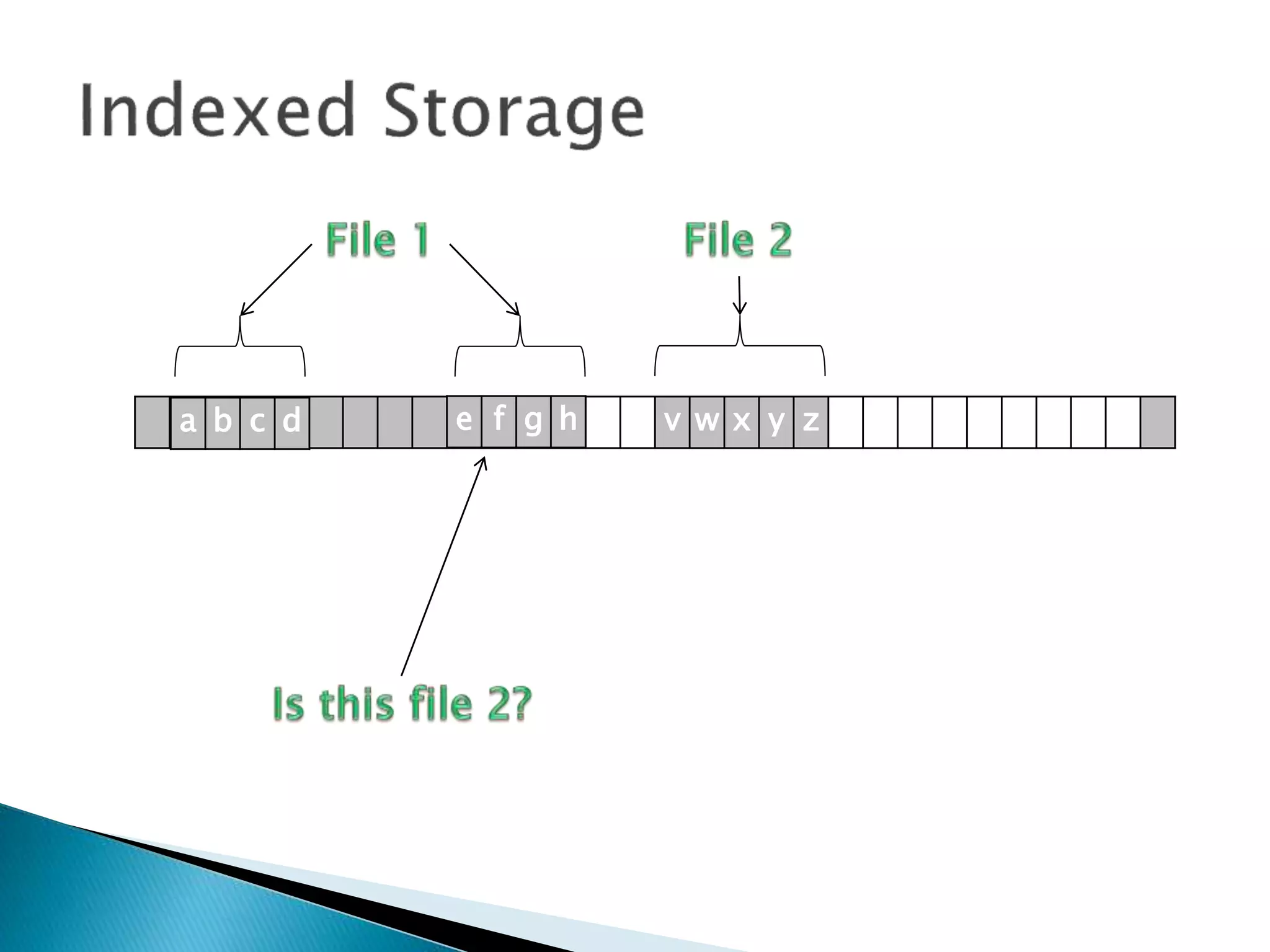
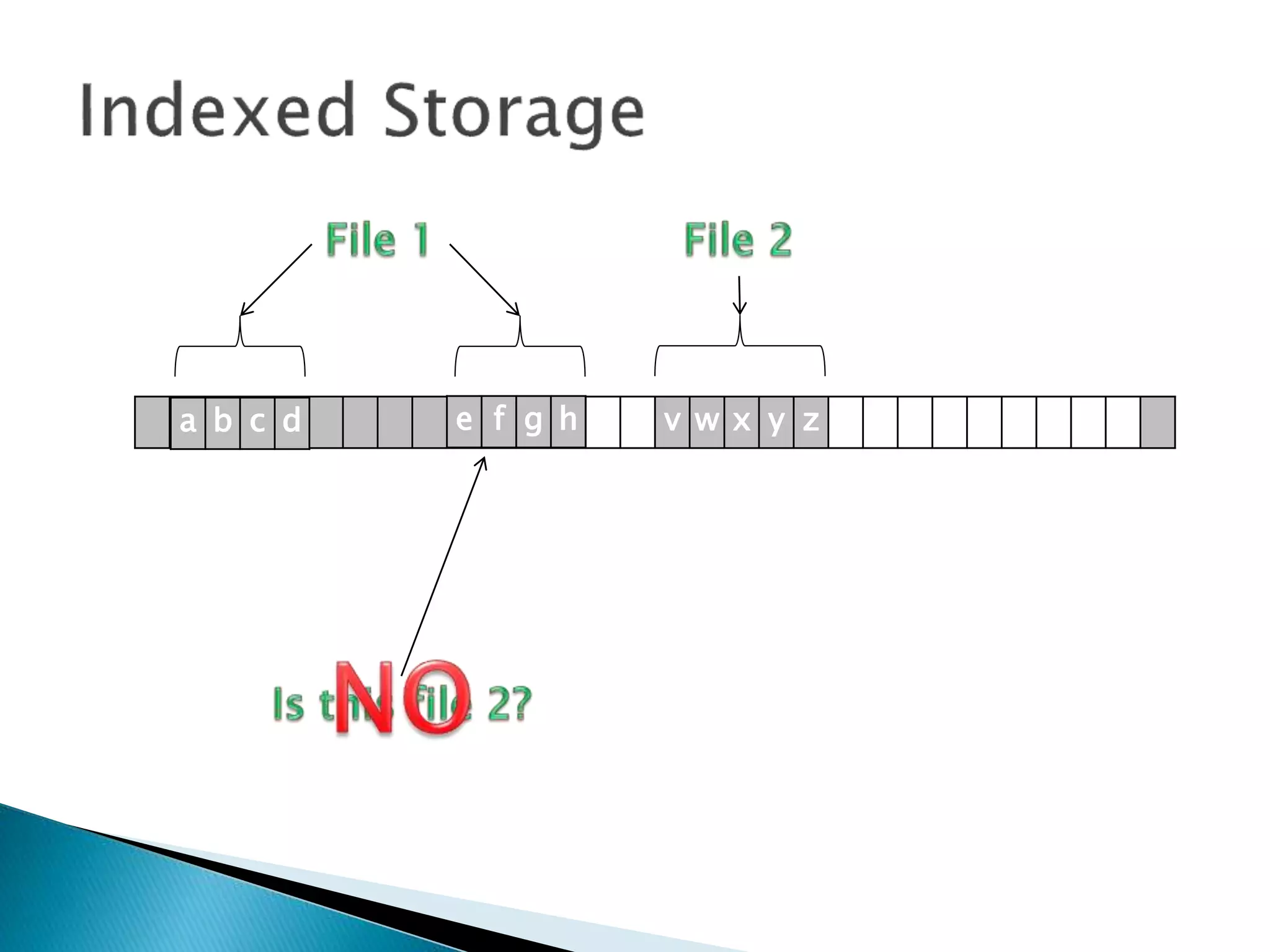
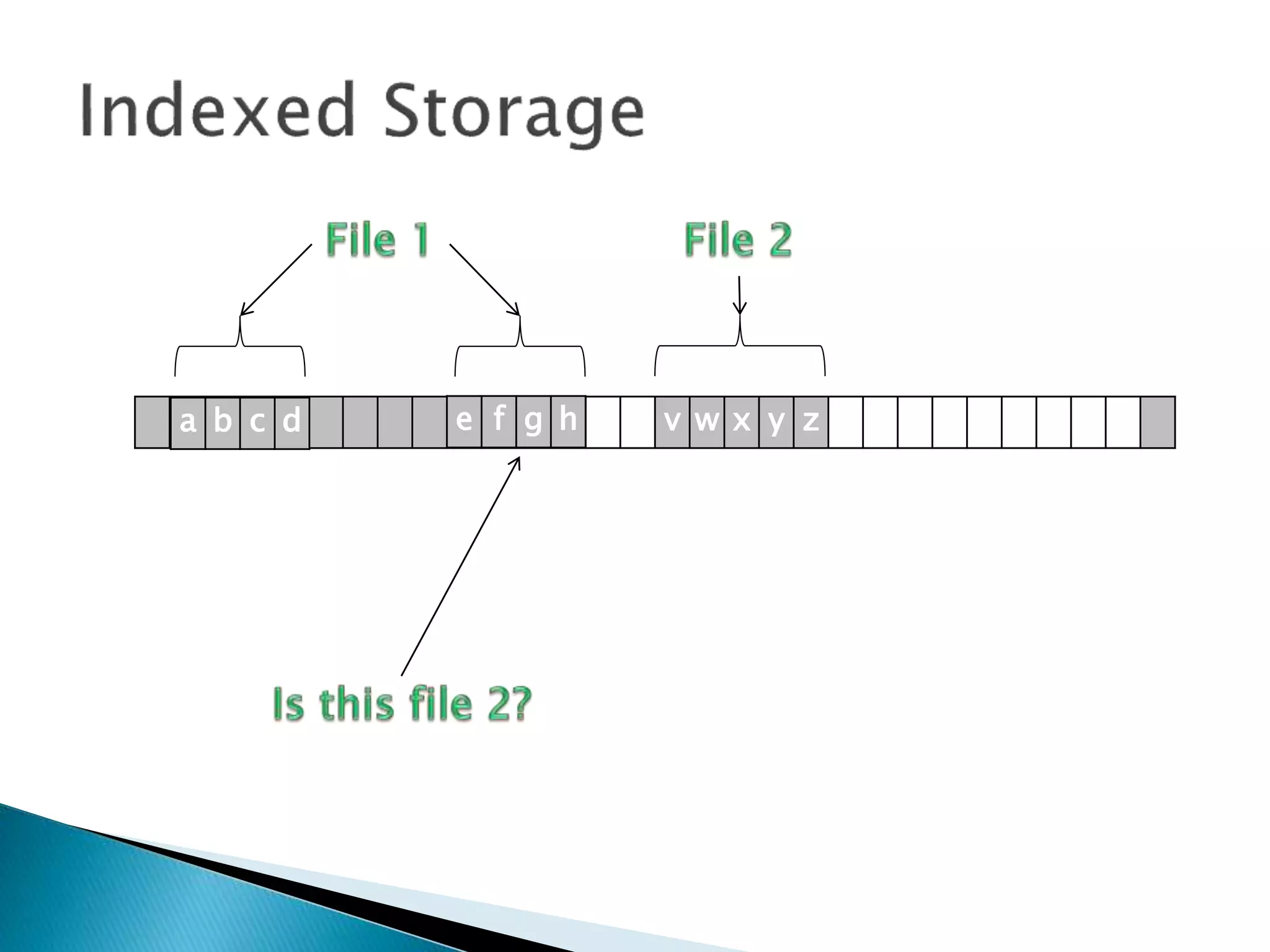
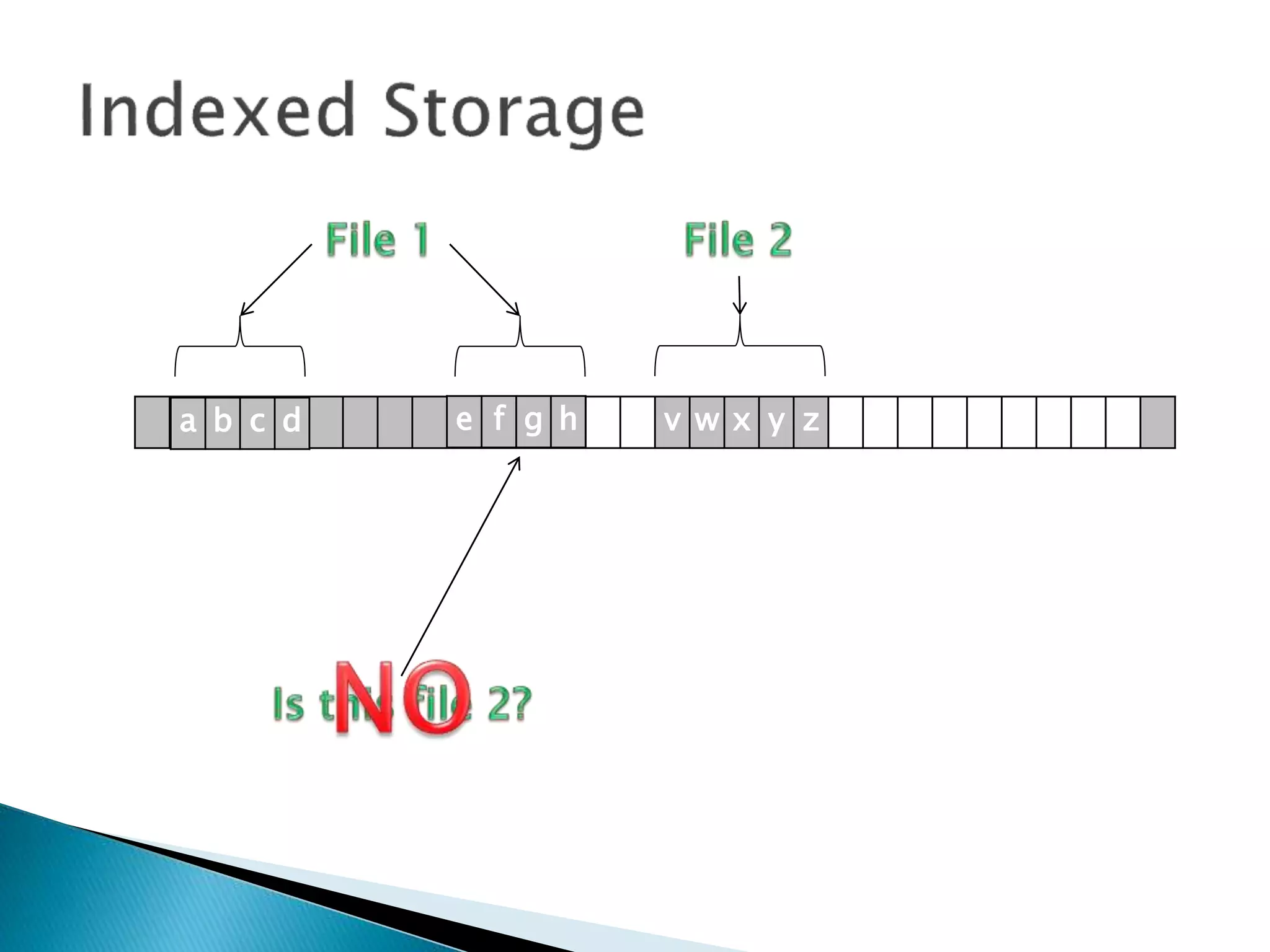
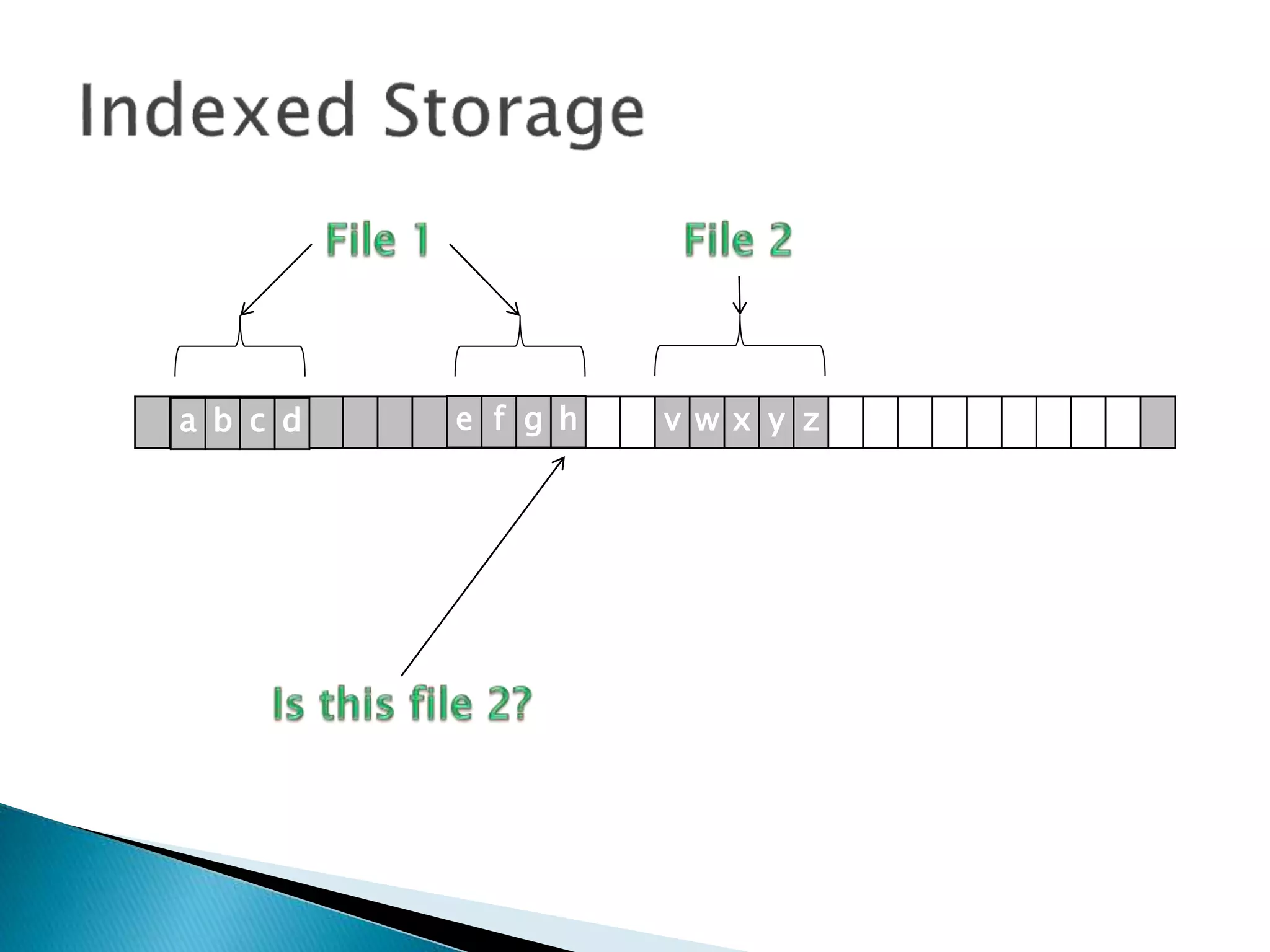
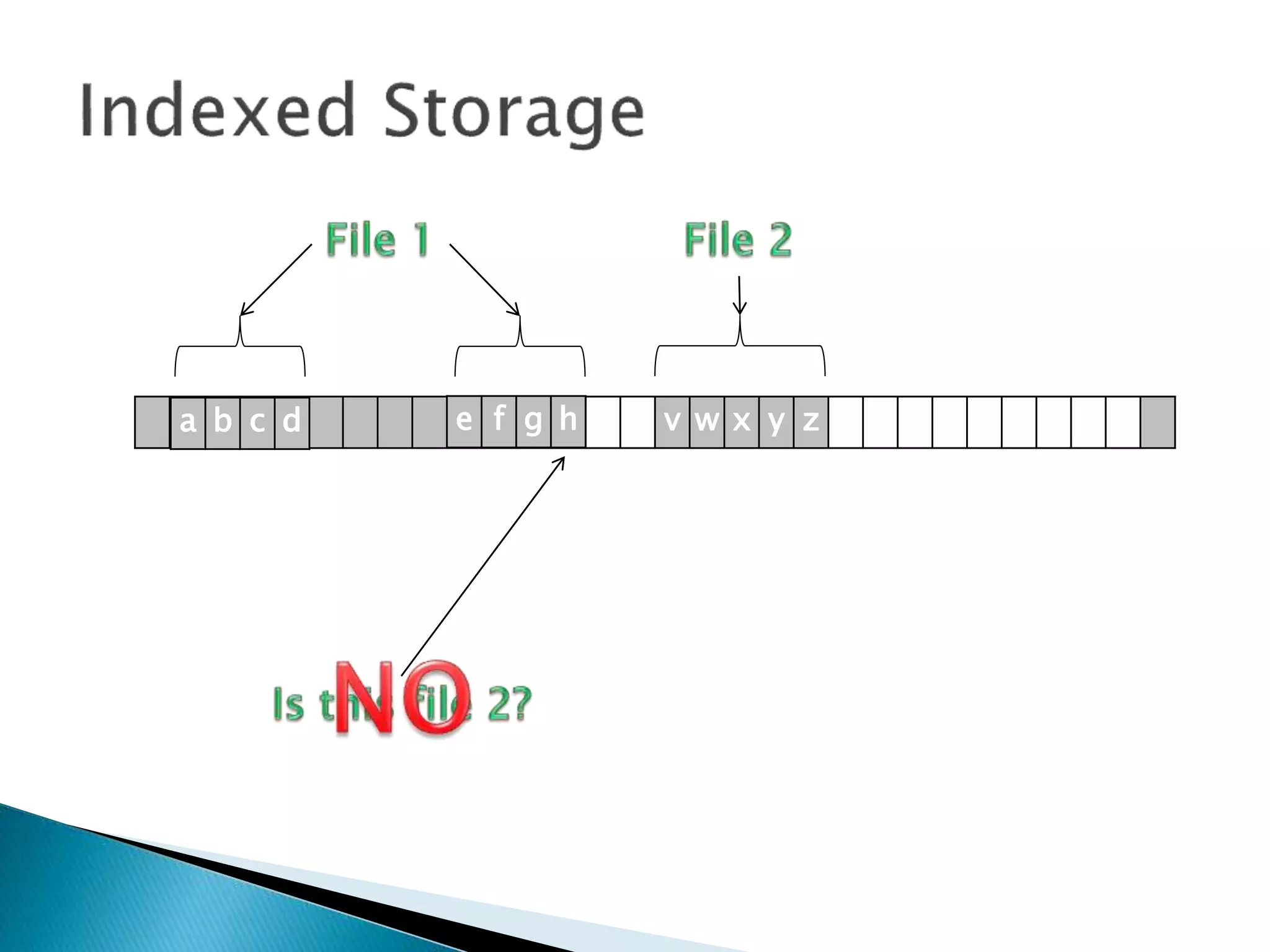
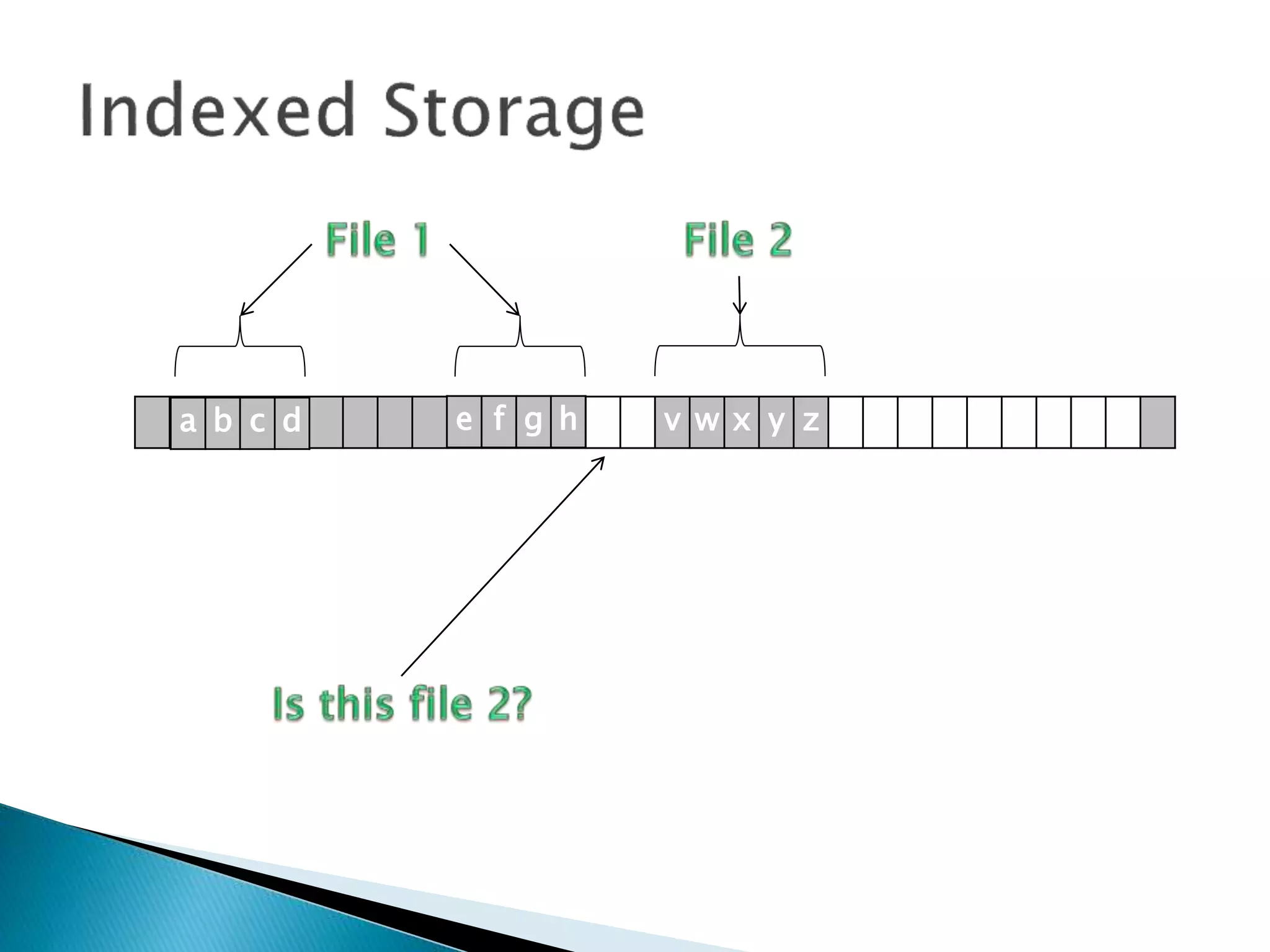
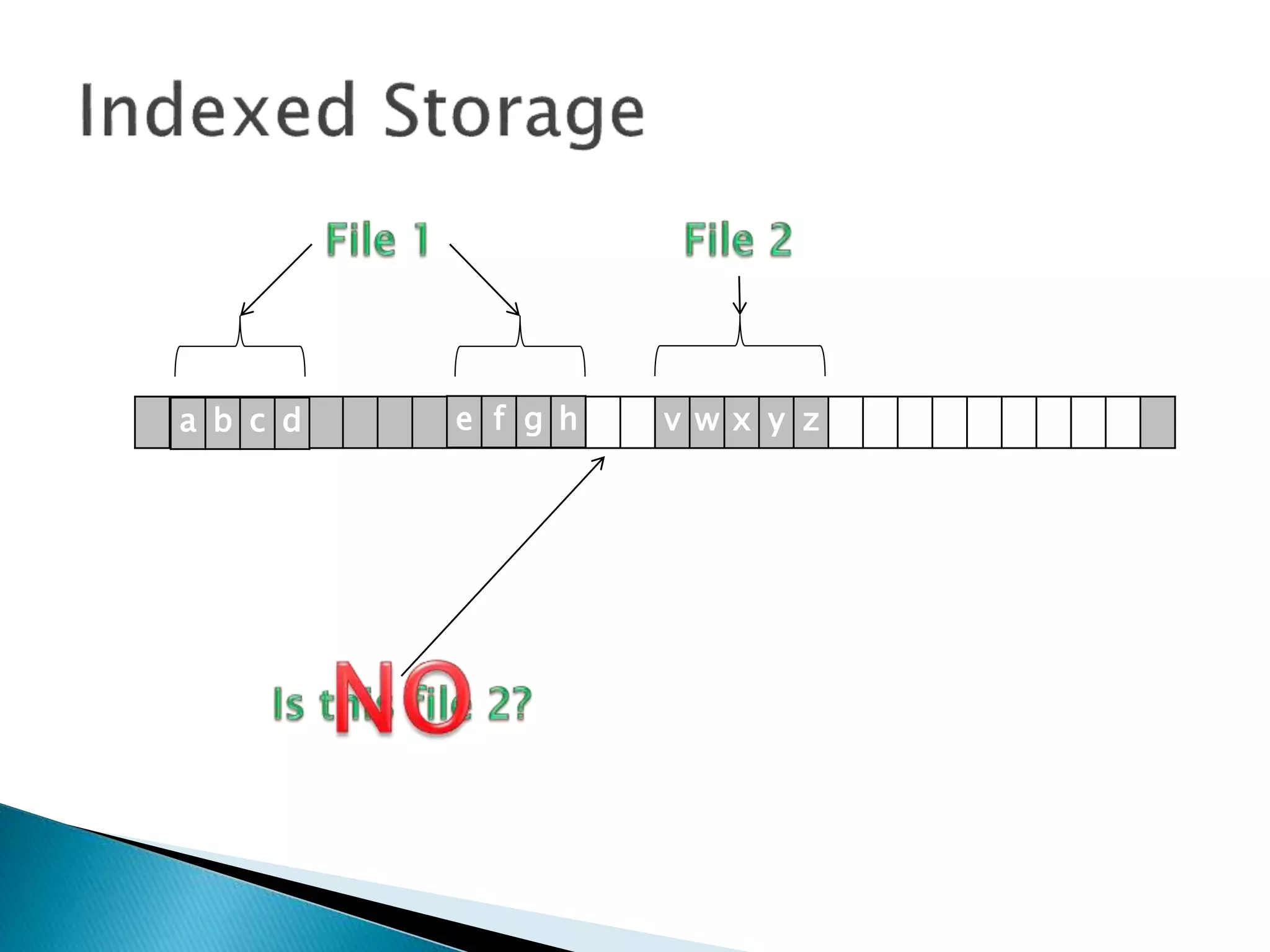
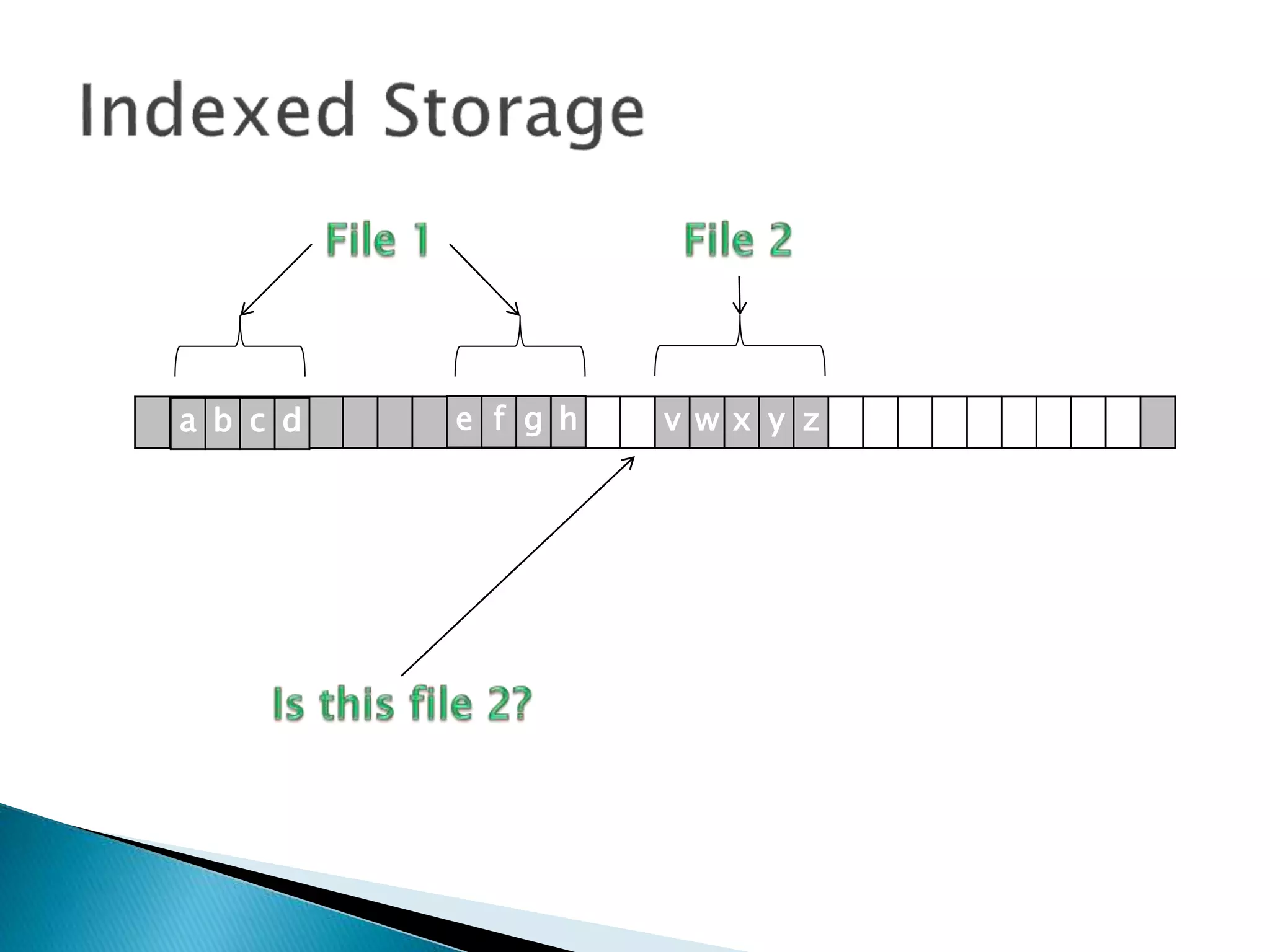
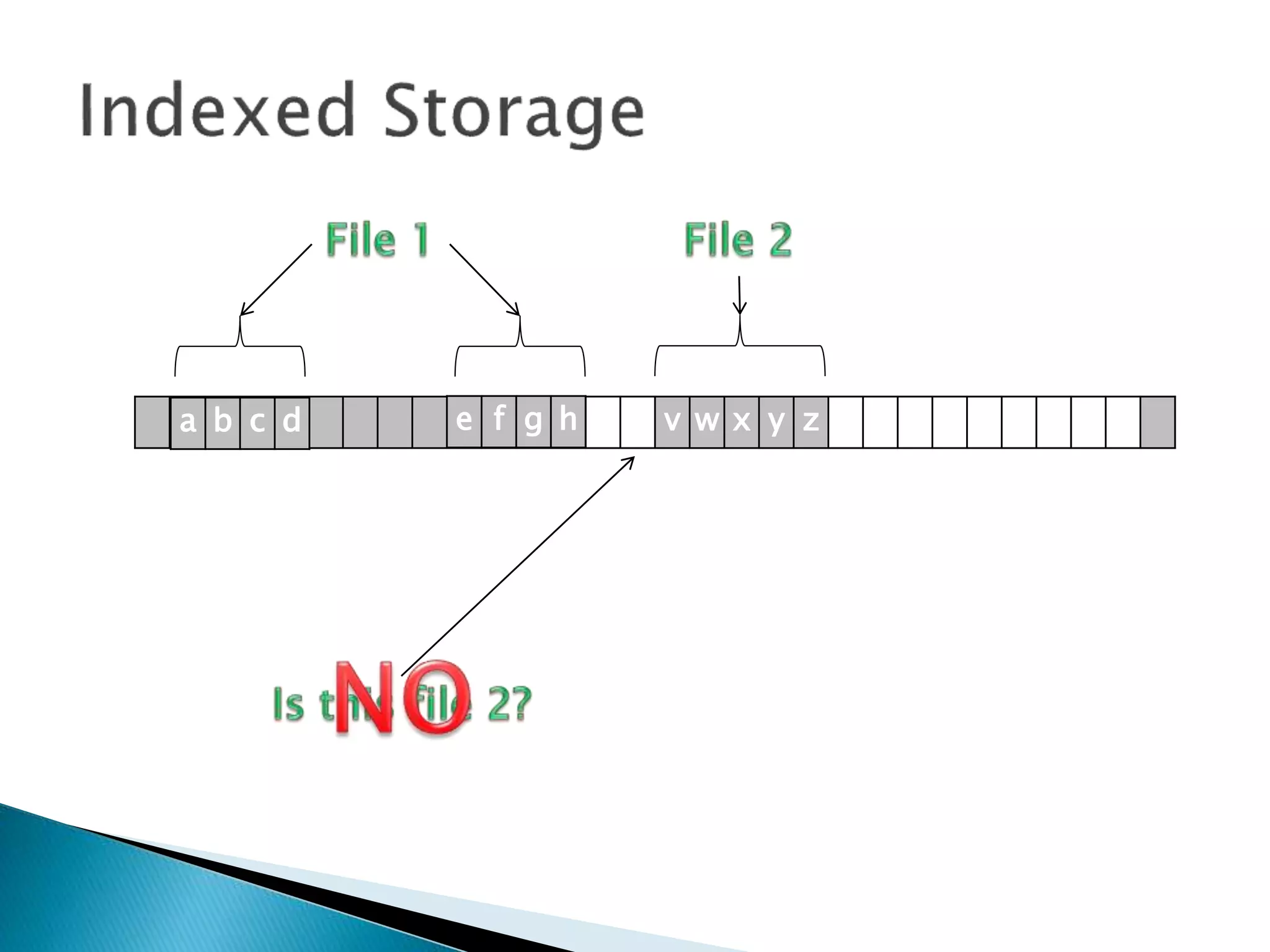
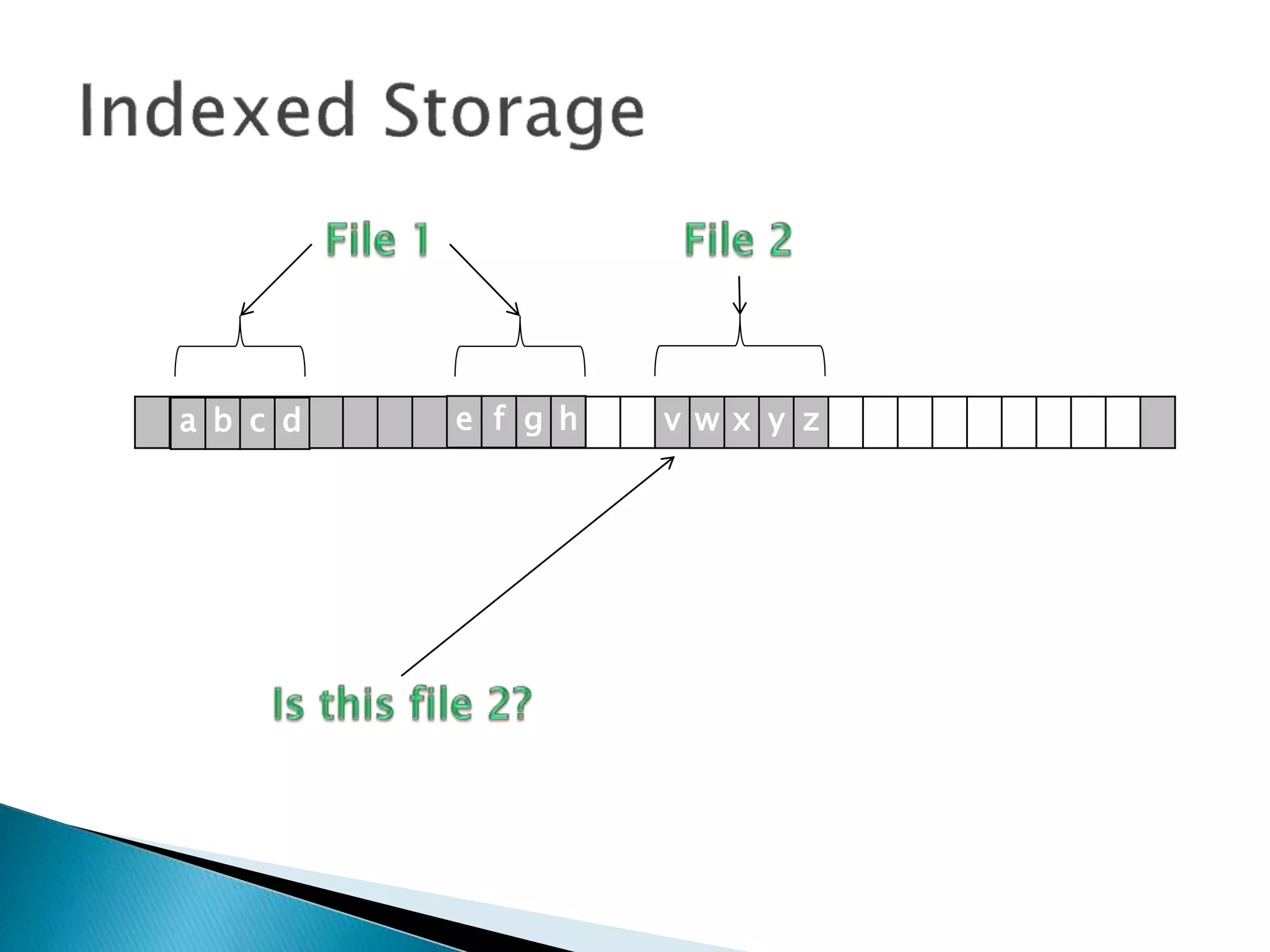
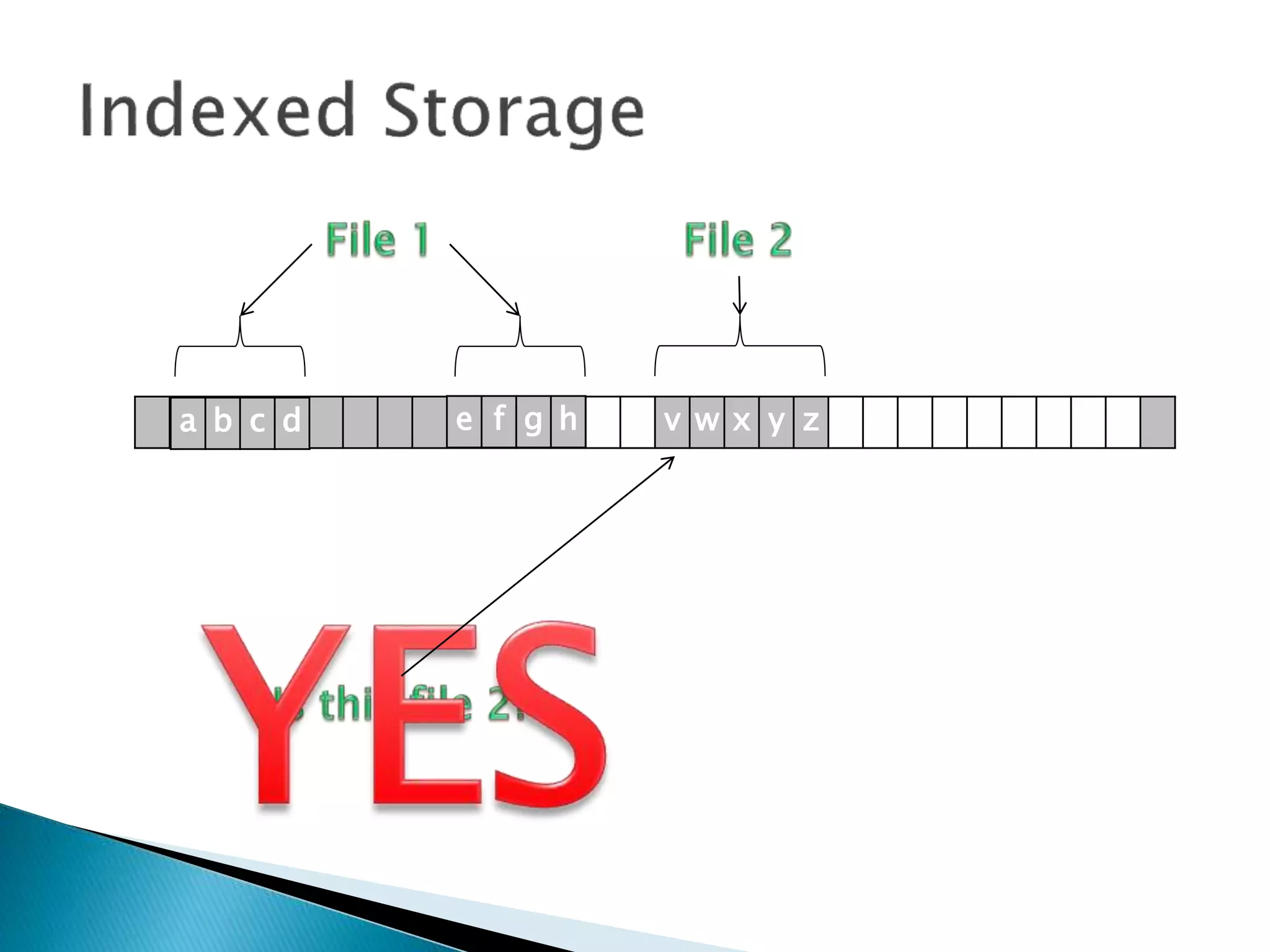
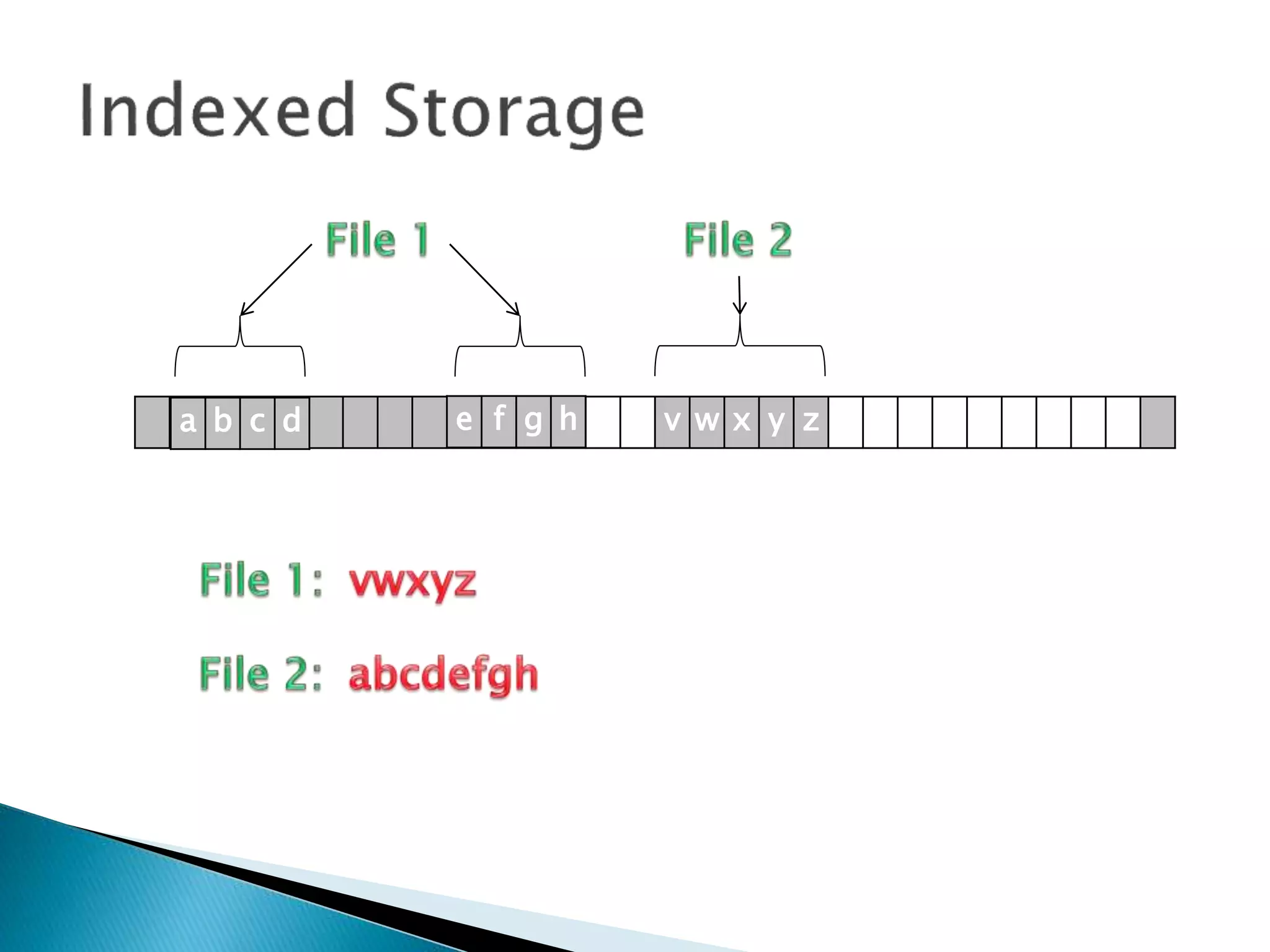
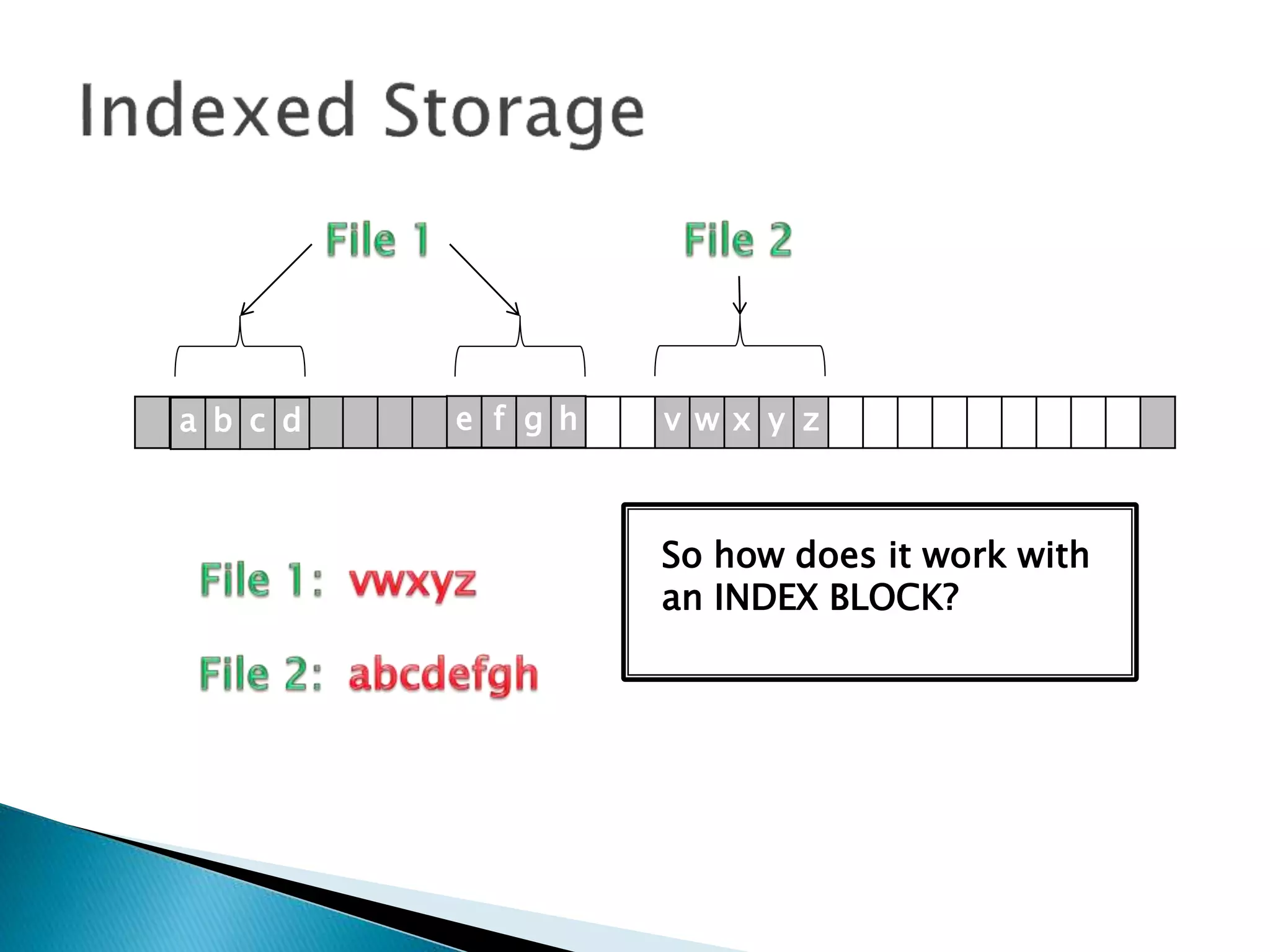
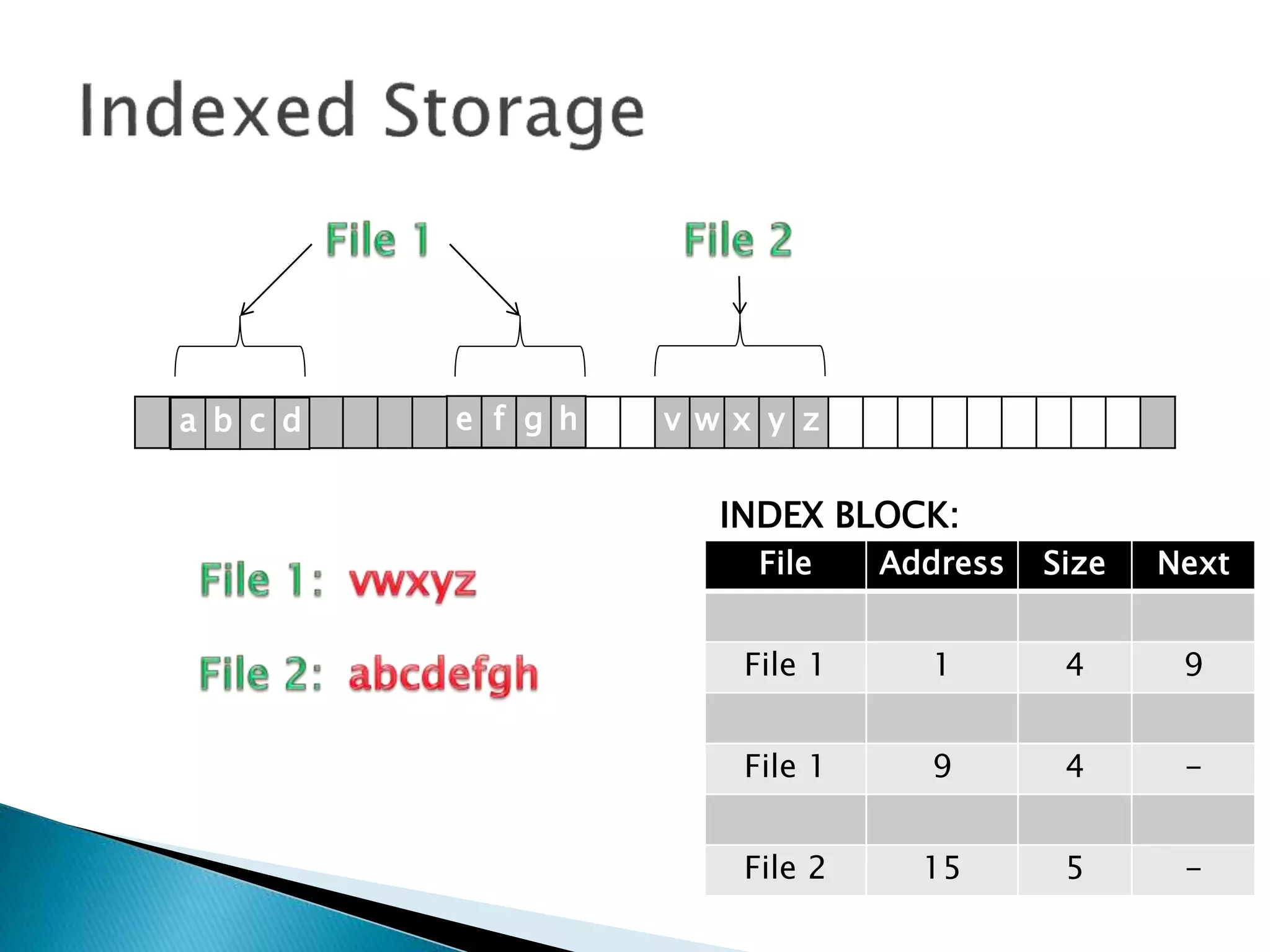
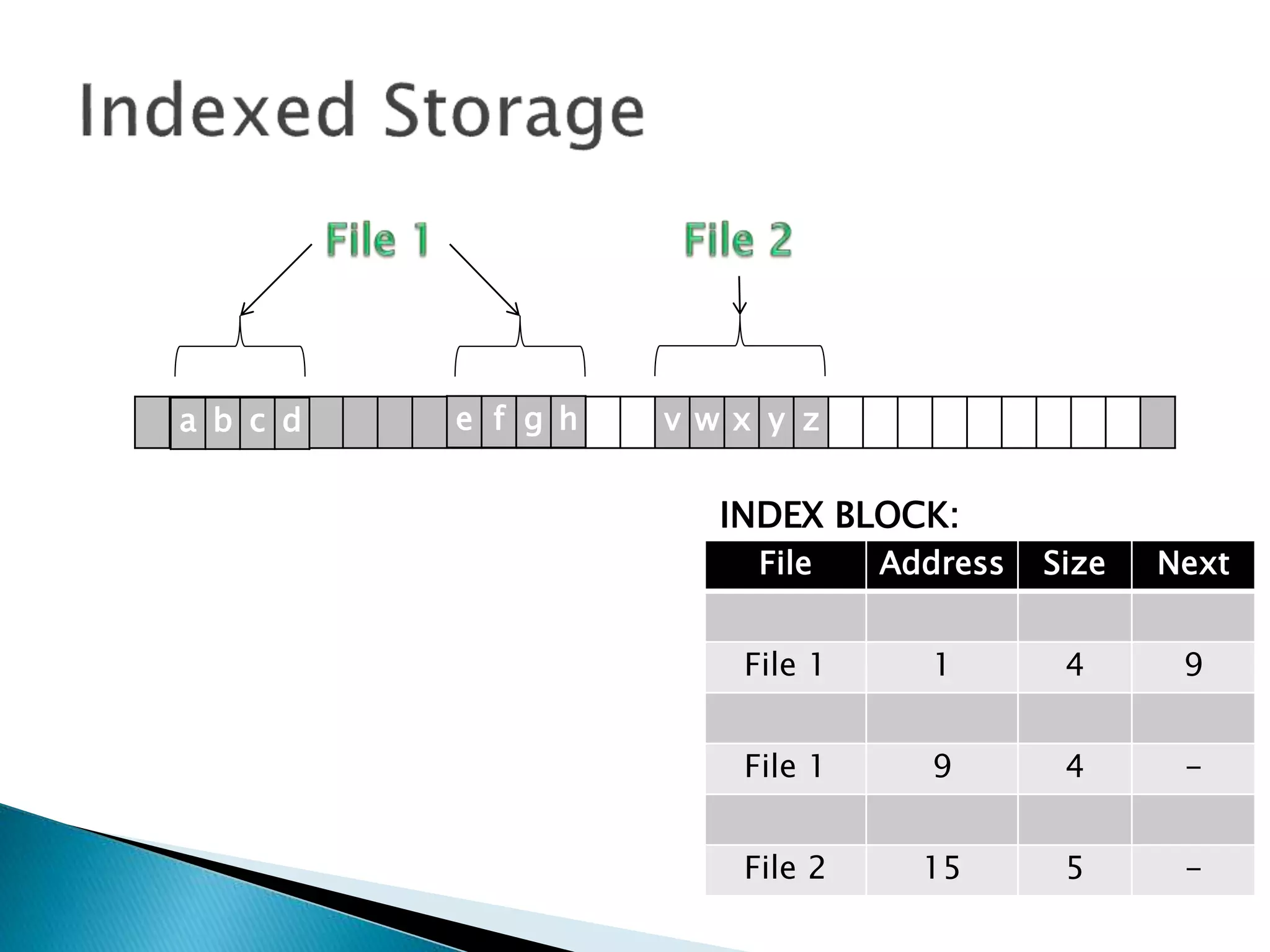
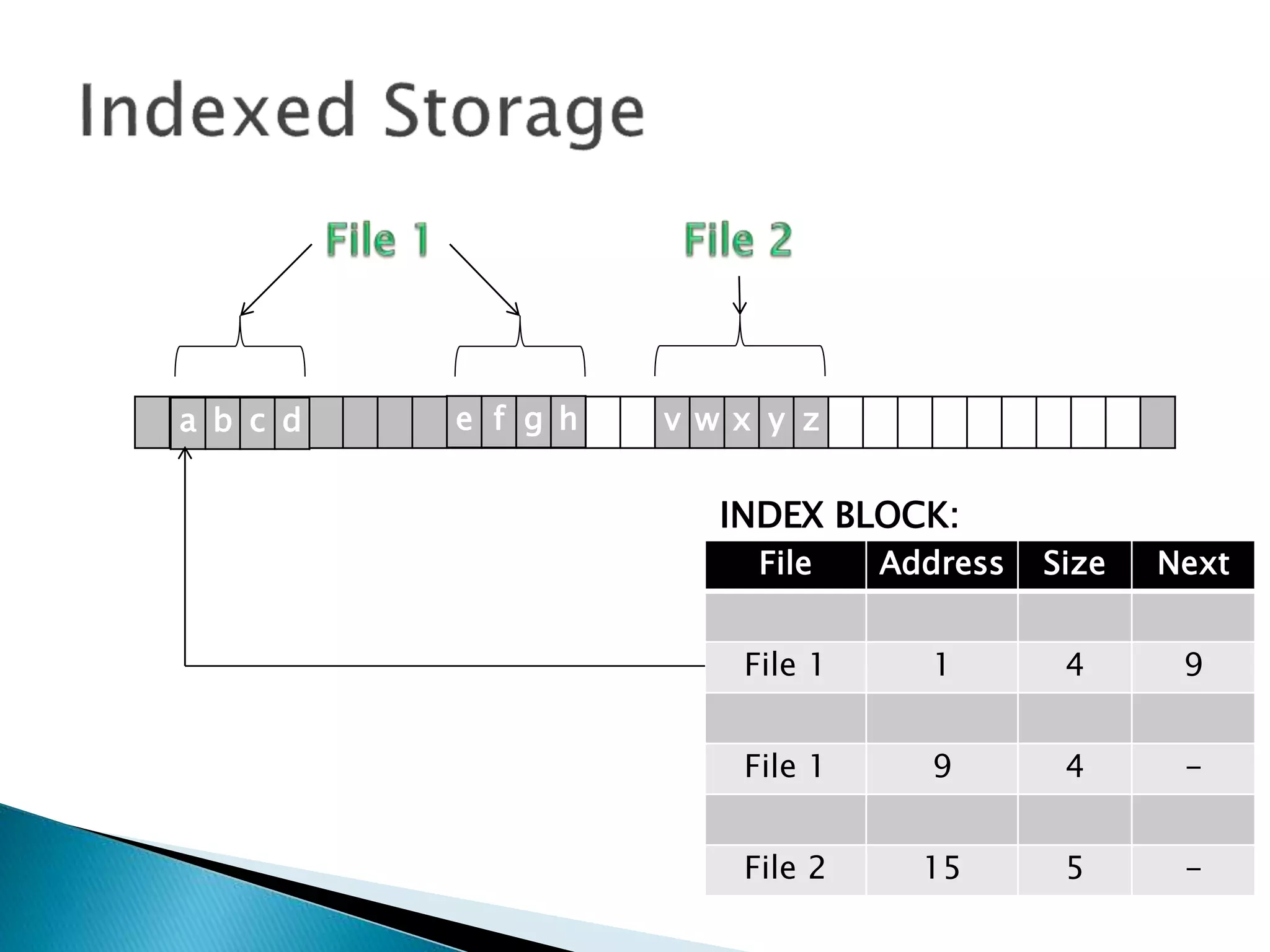
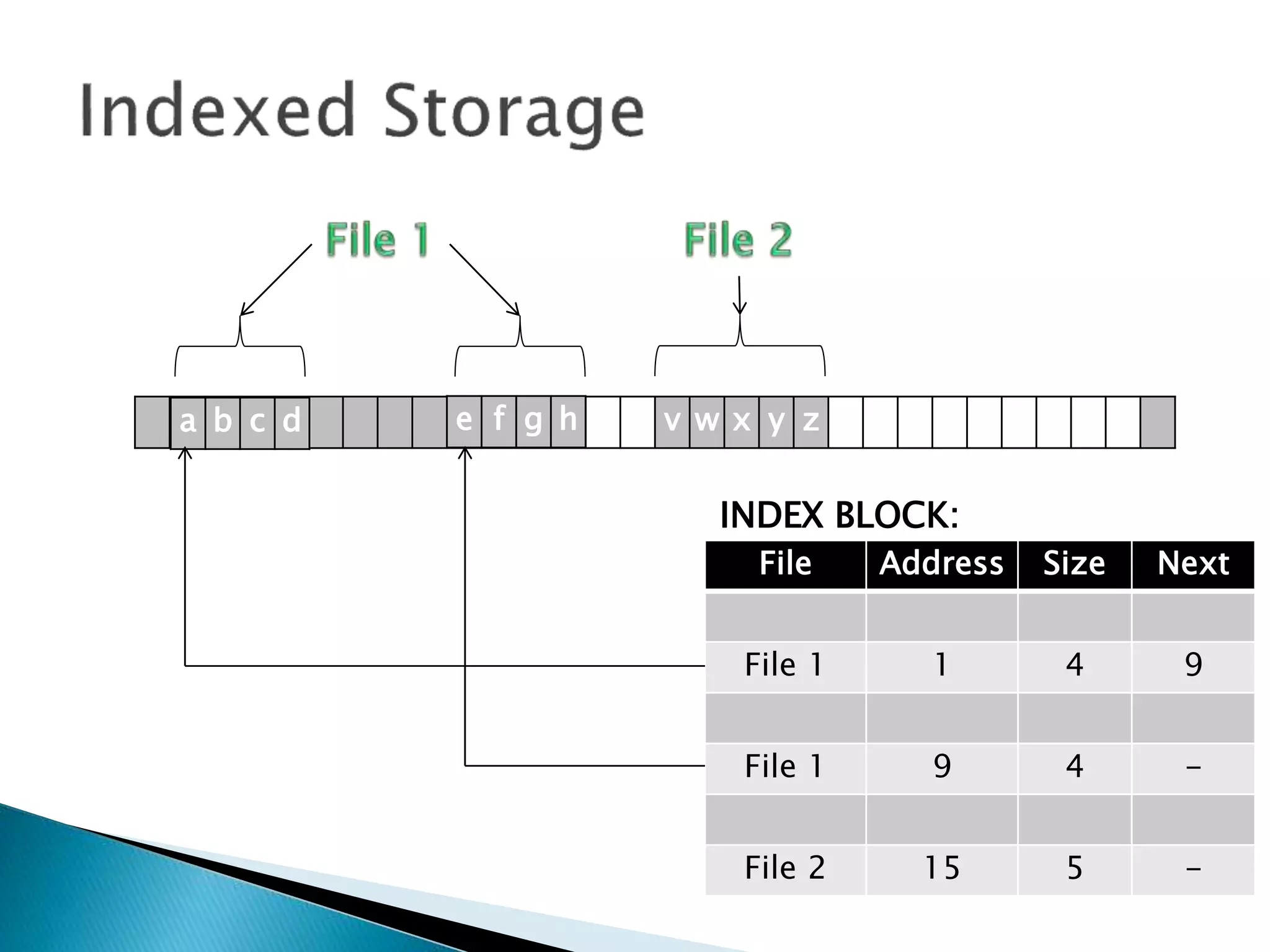
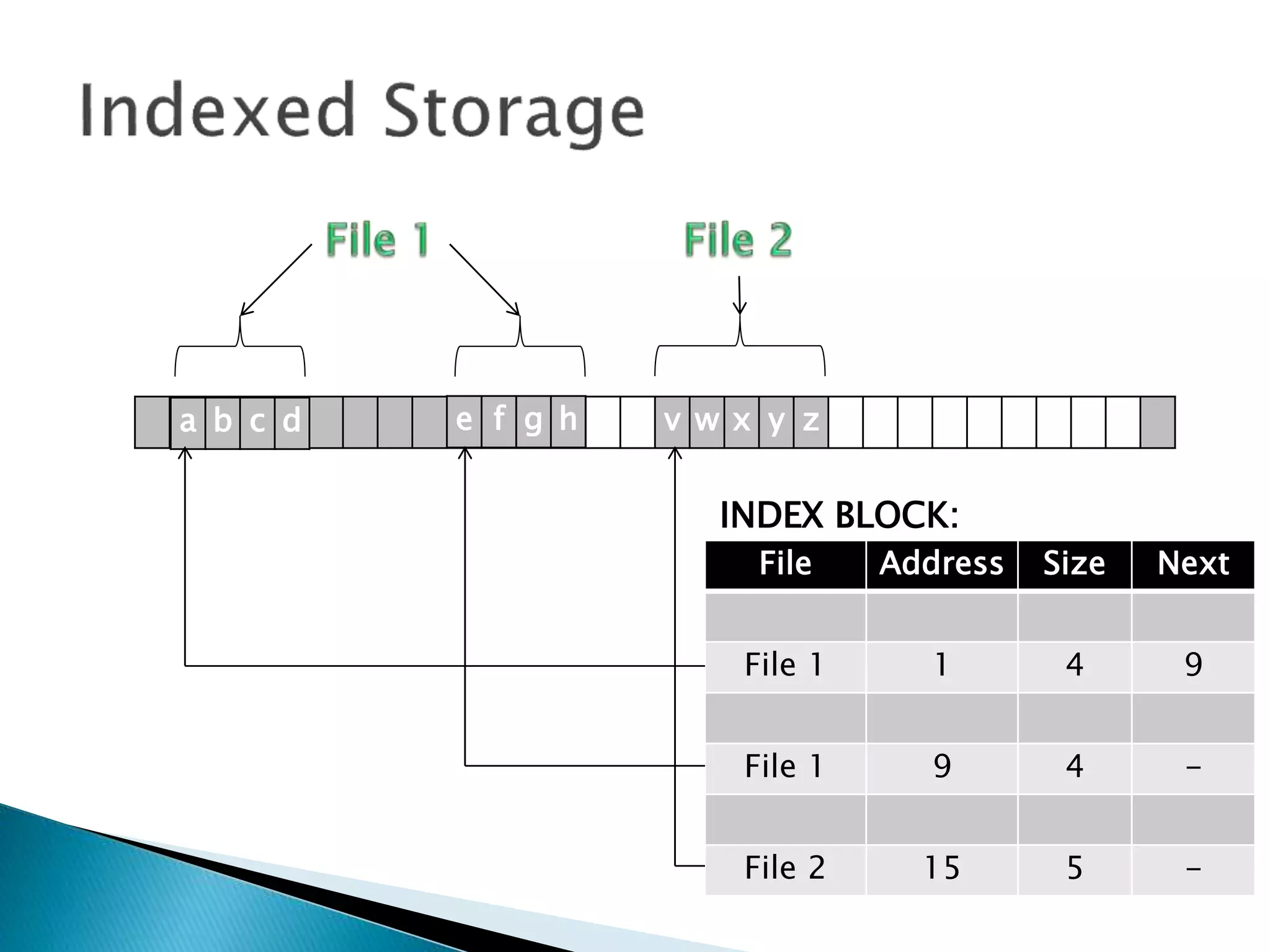
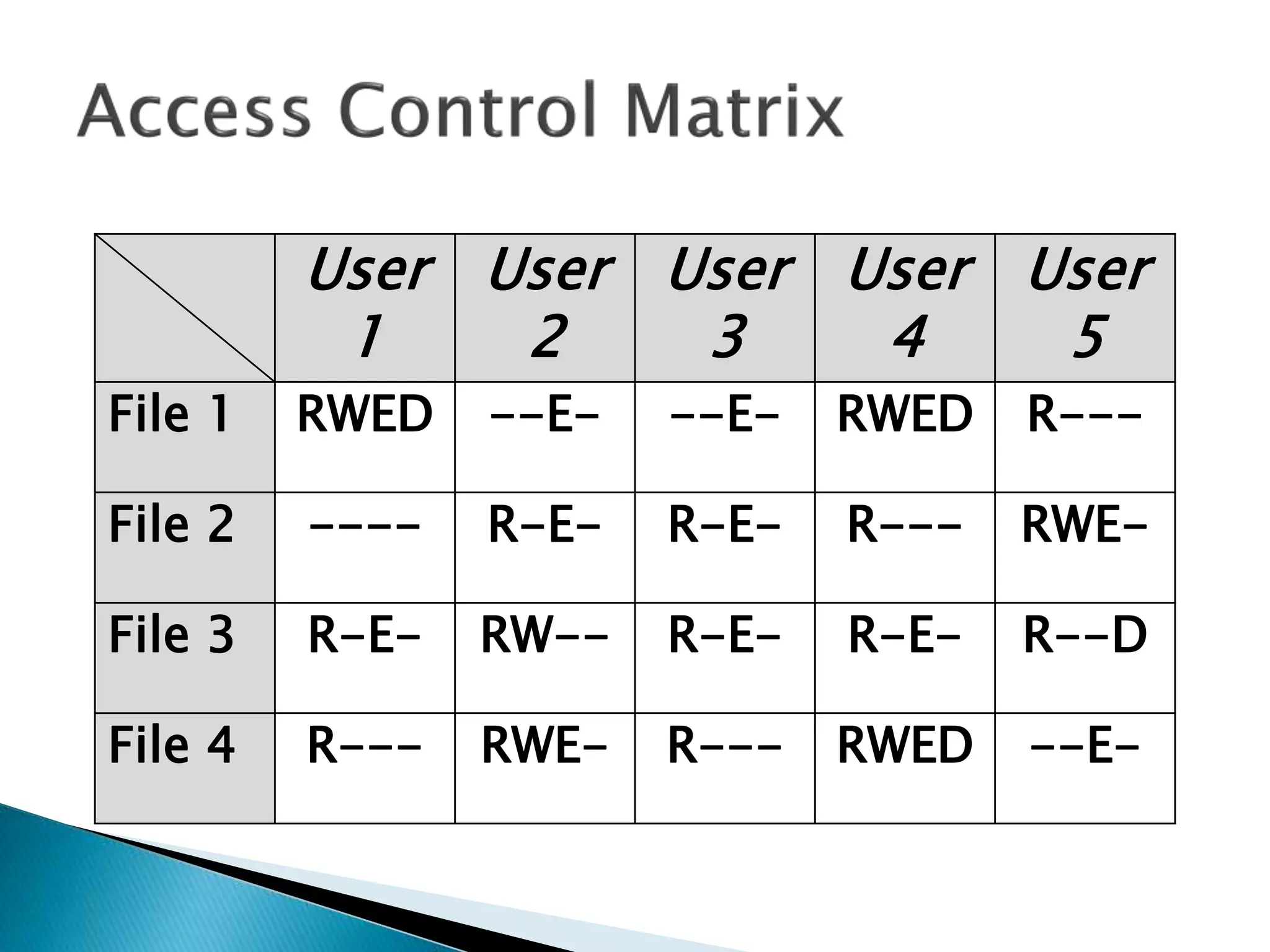
The document discusses how operating systems manage files and memory allocation. It explains that from the computer's perspective, there are no actual files, only blocks of allocated and unallocated memory. The file manager in the operating system creates the illusion of files and folders by tracking memory locations and implementing file allocation policies. Files can be stored contiguously, non-contiguously, or through indexed allocation with pointers. Access controls determine which users can access which files.













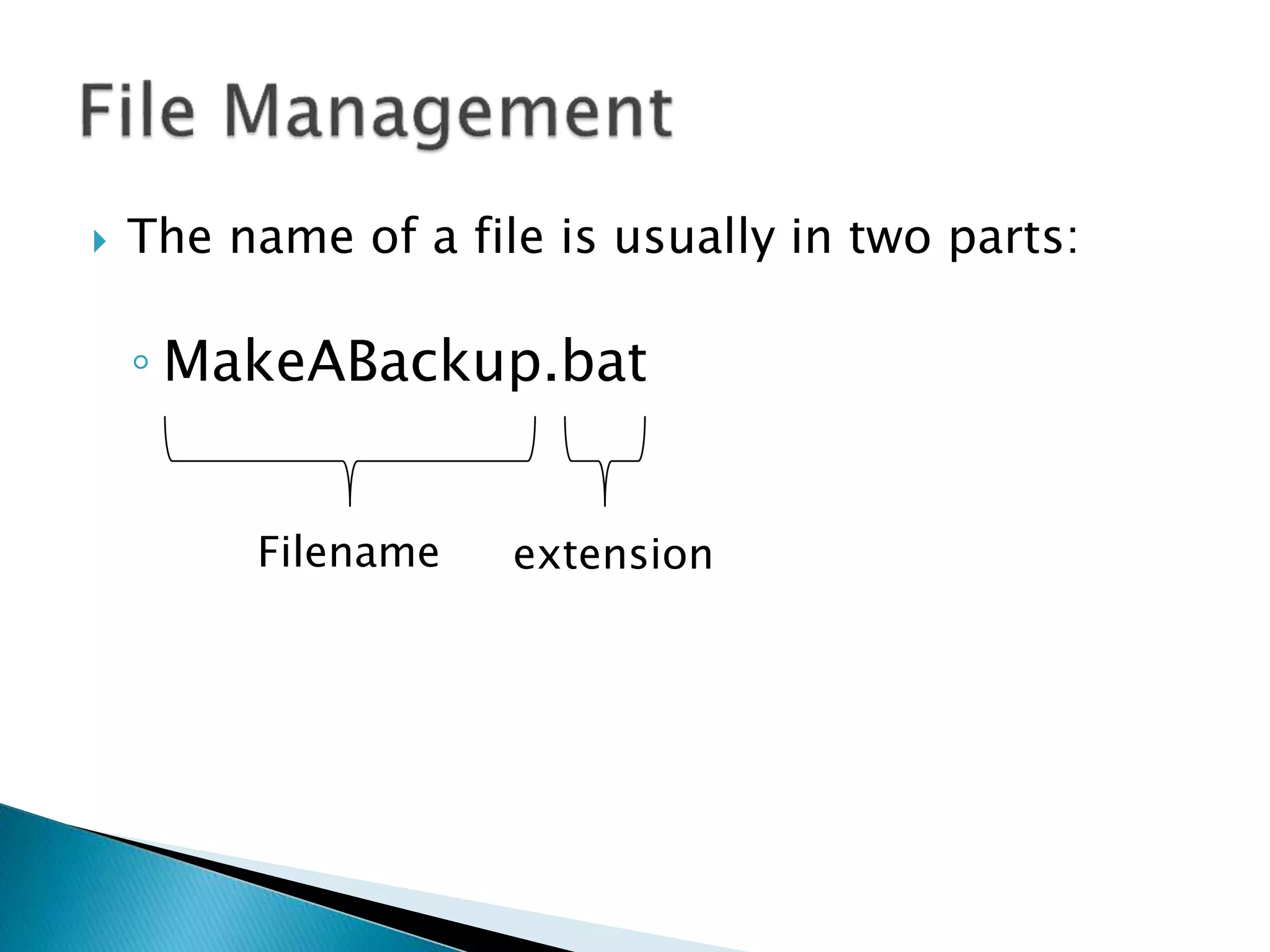
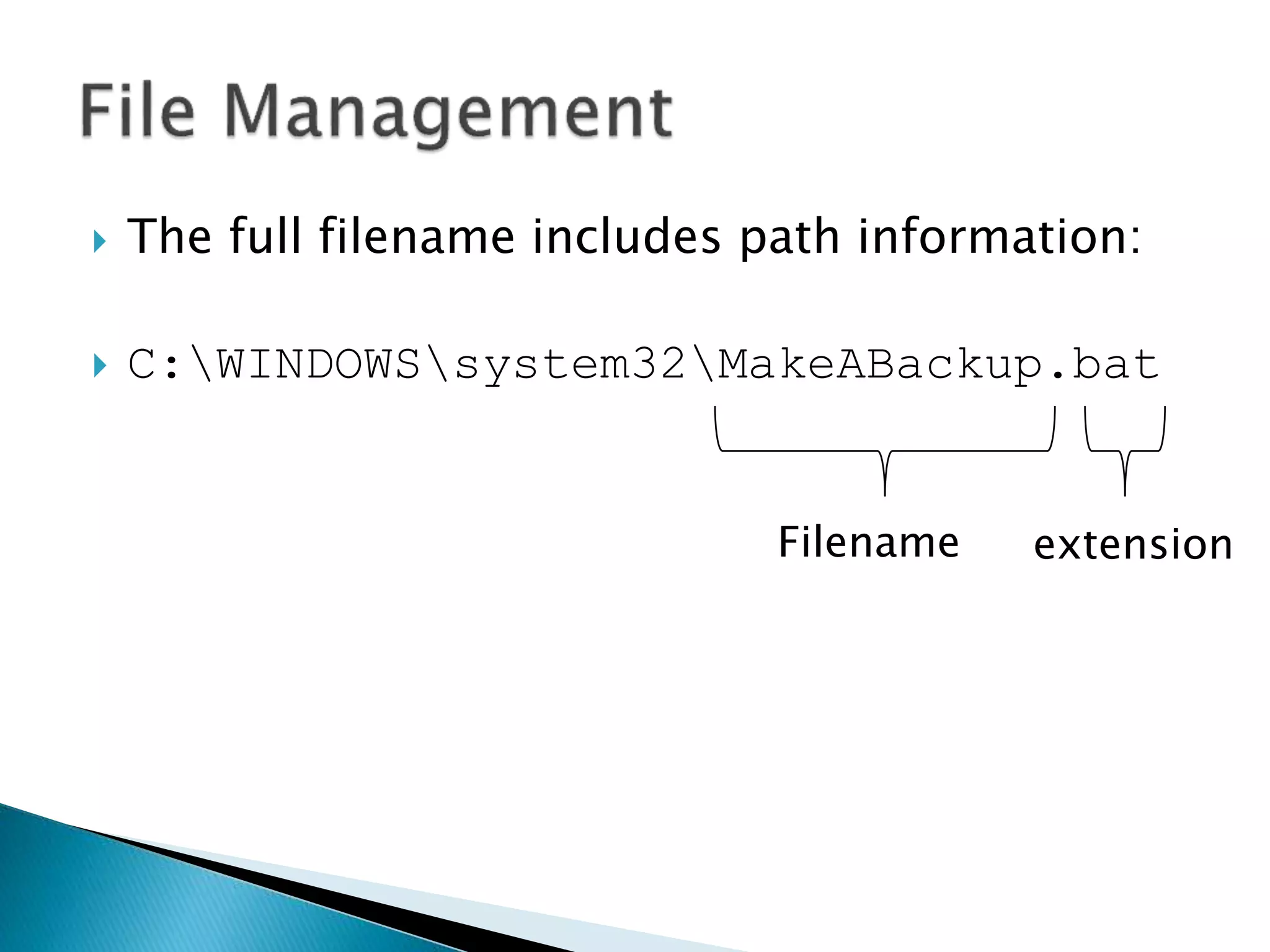




















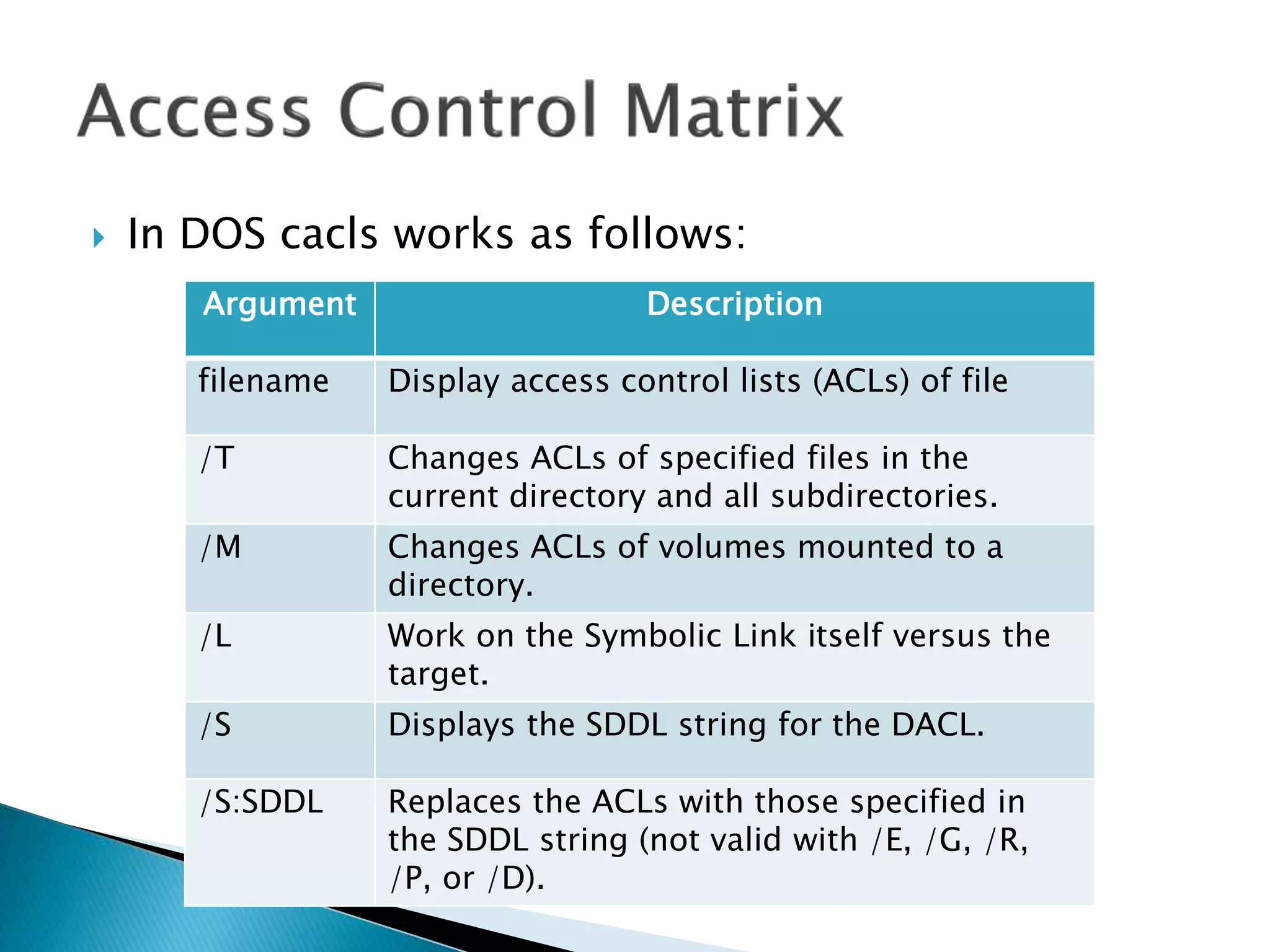
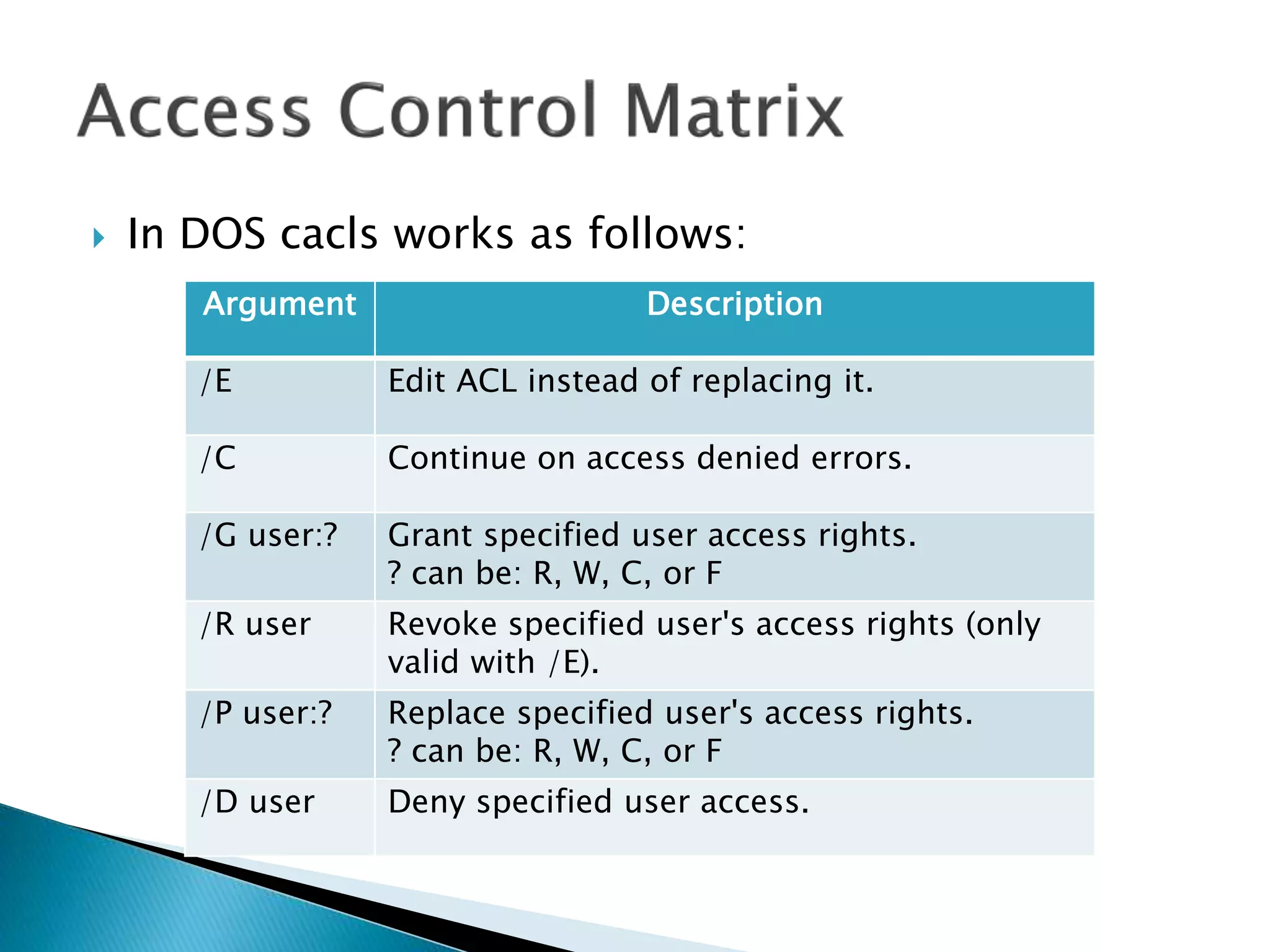
![ In DOS if we want to grant permissions to
file, e.g. MakeABackup.bat, we do:
cacls filename [/T] [/M] [/L] [/S[:SDDL]] [/E]
[/C] [/G user:?] [/R user [...]] [/P user:? [...]]
[/D user [...]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatingsystems1-week7-filemanagement-150302124420-conversion-gate02/75/Operating-Systems-File-Management-112-2048.jpg)